Class 12 : Biology (English) – Lesson 10: Biotechnology and its Applications
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🌟 Introduction
🧬 Biotechnology has transformed modern biology and human life.
🌾 It contributes to agriculture (GM crops, biofortification),
💉 medicine (gene therapy, recombinant proteins),
🌍 environment (bioremediation, bio-plastics), and
⚖️ raises ethical issues (biosafety, biodiversity concerns).
🌾 Applications in Agriculture
Genetically Modified Crops (GM Crops)
🌽 Bt cotton: Contains Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) toxin gene → kills bollworm.

🍆 Bt brinjal: Engineered to resist fruit and shoot borer.
🌿 Herbicide-resistant soybean/maize: Allow selective weed control.
🍚 Golden Rice: Enriched with β-carotene (Vitamin A precursor).
Biofortification (Nutrient Enrichment)
Iron-rich rice, protein-enriched maize, vitamin-fortified wheat.
👩⚕️ Aim: combat malnutrition and “hidden hunger”.
Molecular Farming (Edible Vaccines)
Plants engineered to produce vaccines/proteins.
Example: Hepatitis B surface antigen in tobacco/potato.
💉 Applications in Medicine
Recombinant Proteins
💉 Insulin (Humulin) — produced by E. coli with human insulin gene.
🛡️ Interferons — used in viral/cancer therapy.
🧩 Monoclonal antibodies — trastuzumab for breast cancer, rituximab for lymphoma.
Gene Therapy
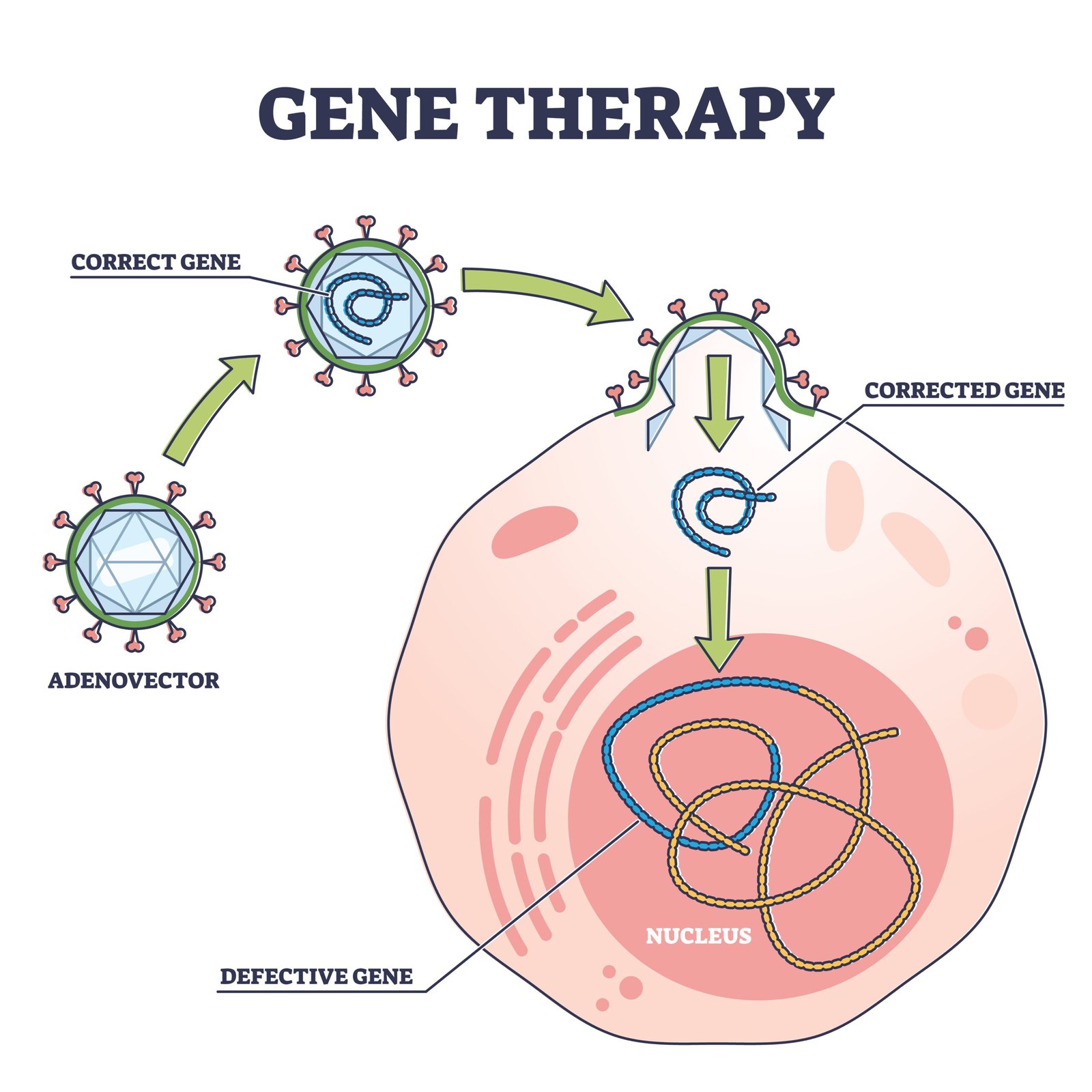
Replacement of defective genes.
Example: ADA deficiency corrected via lymphocyte gene transfer.
Molecular Diagnosis
🔍 PCR — amplifies pathogen-specific DNA (HIV, TB).
🧬 RT-PCR — detects RNA viruses (e.g., SARS-CoV-2).
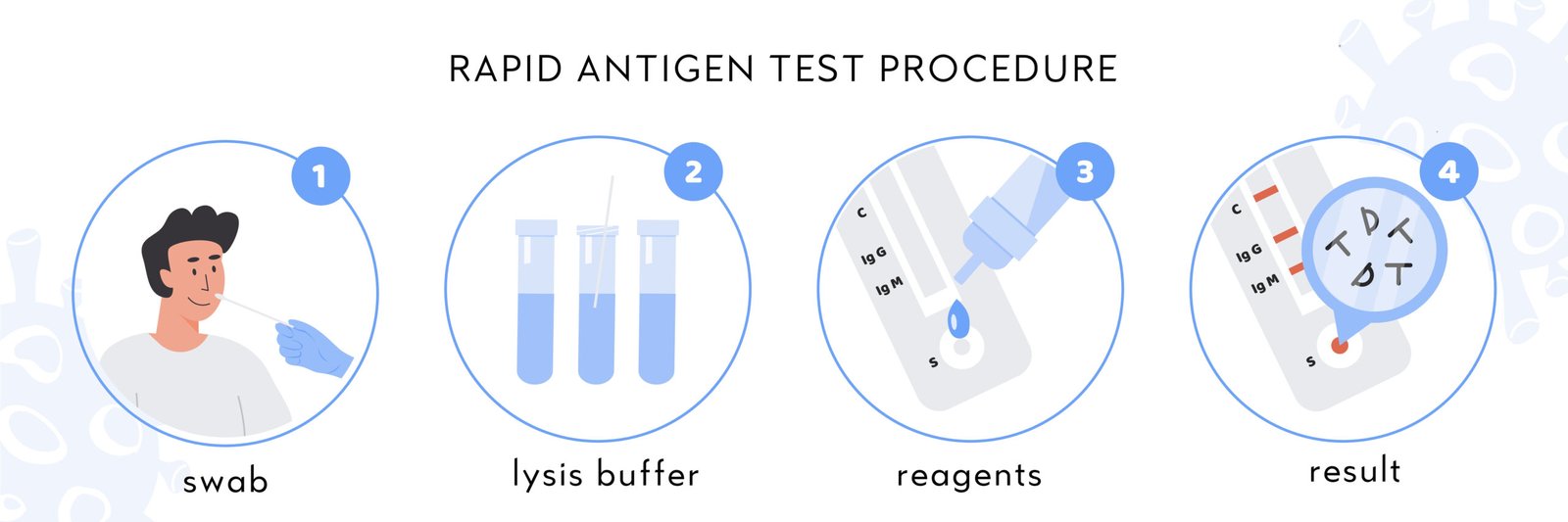
🧪 ELISA — antibody/antigen detection.
🔎 DNA probes & fingerprinting — genetic disorder detection.
Pharmacogenomics
Designing personalised drugs based on patient’s genetic profile.
🌍 Environmental Applications
🦠 Bioremediation: Microbes degrade pollutants.
✔️ Pseudomonas putida — oil spill clean-up.
🌱 Biofertilisers: Engineered Rhizobium, cyanobacteria enhance soil fertility.
🌿 Biodegradable Plastics: Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs).
💧 Sewage Treatment: Recombinant microbes accelerate waste degradation.
🛡️ Safety, Social & Ethical Issues
⚠️ Biosafety concerns:
GM crops may reduce biodiversity or produce allergens.
Genes could transfer to wild relatives.
⚖️ Ethical concerns:
Human cloning and germline modification debated.
Equity in access to biotechnology (cost, patents).
📌 Regulatory framework:
GEAC (Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee, India) monitors GMO release.
Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety governs international transport of GMOs.
📝 Summary (~300 words)
Biotechnology applications span agriculture, medicine, and environmental management. In agriculture, Bt cotton, Bt brinjal, herbicide-tolerant crops, and Golden Rice demonstrate how genetic engineering improves productivity and nutrition. Biofortification enriches crops with vitamins and minerals, while molecular farming enables edible vaccines.
In medicine, recombinant proteins (insulin, monoclonal antibodies, interferons) are mass-produced. Gene therapy offers cures for genetic disorders like ADA deficiency. Molecular diagnostics (PCR, ELISA, RT-PCR, DNA probes) allow early detection of diseases. Pharmacogenomics customises drugs for patients.
Environmental applications include bioremediation (microbes clearing pollutants), biofertilisers, and biodegradable plastics (PHB, PHAs). Sewage treatment is also improved with engineered microbes.
However, biotechnology raises biosafety and ethical concerns, such as risks to biodiversity, GMO controversies, and debates on cloning. Regulatory bodies like GEAC and international agreements like the Cartagena Protocol ensure safety and ethics.
Thus, biotechnology holds promise for sustainable development but requires responsible use.
🎯 Quick Recap
🌽 Agriculture: GM crops (Bt cotton, Bt brinjal, Golden Rice), biofortification, edible vaccines.
💉 Medicine: Recombinant insulin, monoclonal antibodies, gene therapy, diagnostics, pharmacogenomics.
🌍 Environment: Bioremediation, biodegradable plastics, sewage treatment.
⚖️ Issues: Biosafety (biodiversity risk), ethics (cloning, patents), regulation (GEAC, Cartagena Protocol).
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔹 Q1. Which part of the plant is best suited for making virus-free plants and why?
✅ Answer:
🌱 Shoot apical meristem is best suited.
Viruses spread through vascular tissues (phloem/xylem).
Meristematic cells are actively dividing and lack vascular connections → usually free of viruses.
Used in meristem culture to obtain virus-free plants (e.g., banana, sugarcane).
🔹 Q2. What is the major advantage of producing plants by micropropagation?
✅ Answer:
🌿 Major advantage = production of a large number of genetically identical plants (clones) in a short time.
All clones have desired traits.
Useful for rare/endangered plants, and for horticulture and agriculture.
🔹 Q3. Find out what the various components of the medium used for propagation of an explant in vitro are.
✅ Answer:
The commonly used medium is Murashige and Skoog (MS medium), containing:
💧 Water – solvent.
🍚 Carbon source – sucrose.
⚗️ Inorganic salts – macro and micro-nutrients (N, P, K, Mg, Fe, etc.).
🧬 Vitamins – like thiamine, nicotinic acid.
🌱 Growth regulators – auxins (for root), cytokinins (for shoot).
🧂 Gelling agent – agar.
🔹 Q4. Crystals of Bt toxin produced by some bacteria do not kill the bacteria themselves because –
✅ Answer:
The correct option is:
🟢 (C) Toxin is inactive.
In Bacillus thuringiensis, Bt toxin is stored as an inactive protoxin.
It becomes active only in the alkaline gut of insects, not in bacteria.
🔹 Q5. What are transgenic bacteria? Illustrate using any one example.
✅ Answer:
🧬 Transgenic bacteria = bacteria carrying a foreign gene introduced by recombinant DNA technology.
Example: E. coli engineered with human insulin gene.
✔️ Produces human insulin (Humulin).
✔️ Safe and free of allergic reactions compared to animal insulin.
🔹 Q6. Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of production of genetically modified crops.
✅ Answer:
Advantages:
🌽 Higher yield and resistance (e.g., Bt cotton against bollworm).
🌿 Reduced pesticide use.
🍚 Nutritional enhancement (Golden Rice rich in vitamin A).
💧 Tolerance to drought/salinity.
Disadvantages:
⚠️ Possible ecological imbalance (gene flow to wild relatives).
🦋 Impact on non-target organisms (e.g., pollinators, butterflies).
⚖️ Ethical and biosafety concerns.
❌ Resistance development in pests with long-term use.
🔹 Q7. What are Cry proteins? Name an organism that produces it. How has man exploited this protein to his benefit?
✅ Answer:
Cry proteins = insecticidal proteins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt).
Effective against insects like bollworm, beetles, mosquitoes.
Exploitation:
✔️ Gene encoding Cry protein was transferred into cotton plants → Bt cotton.
✔️ Plants now produce toxin → resistant to insect attack → reduced pesticide use.
🔹 Q8. What is gene therapy? Illustrate using the example of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
✅ Answer:
🧬 Gene therapy = treatment of genetic disorders by replacing a defective gene with a normal functional gene.
Example: ADA deficiency (a type of Severe Combined Immunodeficiency, SCID).
✔️ Caused by defective ADA enzyme → failure of immune system.
✔️ In therapy, functional ADA gene is introduced into patient’s lymphocytes using a retroviral vector.
✔️ Lymphocytes start producing ADA → temporary relief.
✔️ More permanent solutions: stem cell therapy or gene editing.
🔹 Q9. Diagrammatically represent the experimental steps in cloning and expressing a human gene (say the gene for growth hormone) into a bacterium like E. coli.
✅ Answer:
Steps (in order):
✂️ Isolation of growth hormone gene from human DNA.
🧩 Insertion of gene into plasmid vector (e.g., pBR322).
🔬 Introduction of recombinant plasmid into E. coli (transformation).
🧪 Selection of transformed cells using selectable markers.
📈 Cloning & expression — bacteria multiply and express growth hormone.
🧴 Harvest & purification of recombinant hormone for medical use.
🔹 Q10. Can you suggest a method to remove oil (hydrocarbon) from seeds based on your understanding of rDNA technology and chemistry of oil?
✅ Answer:
Oils are triglycerides (glycerol + fatty acids).
Method:
✔️ Introduce gene encoding lipase enzyme into seeds via genetic engineering.
✔️ Lipase hydrolyses oil into glycerol + fatty acids, reducing oil content.
This could help in producing oil-free seeds for industrial use.
🔹 Q11. Find out from internet what is Golden Rice.
✅ Answer:
🍚 Golden Rice = genetically modified rice enriched with β-carotene (pro-vitamin A).
Genes introduced: phytoene synthase (daffodil) + crtI gene (bacterium Erwinia).
Benefit: prevents vitamin A deficiency, which causes blindness in children.
🔹 Q12. Does our blood have proteases and nucleases?
✅ Answer:
Yes ✅
🧪 Proteases — present in blood plasma and lysosomes (e.g., thrombin, plasmin) → involved in clotting and protein digestion.
🧬 Nucleases — present in white blood cells, degrade foreign nucleic acids (defense role).
🔹 Q13. Consult internet and find out how to make orally active protein pharmaceutical. What is the major problem to be encountered?
✅ Answer:
Orally active protein drugs must survive stomach acid and digestive enzymes.
Strategies:
✔️ Encapsulation in protective coatings (liposomes, nanoparticles).
✔️ Use of enzyme inhibitors along with the drug.
Major problem ⚠️: Proteolytic enzymes and gastric acidity degrade proteins before absorption in intestine.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTION PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS CHAPTER ONLY
🟢 Section A — Very Short Answer Questions
🔹 Q1. Which part of the plant is used to produce virus-free plants?
🔵 (A) Root tip
🟢 (B) Shoot apical meristem
🟠 (C) Flower bud
🔴 (D) Leaf lamina
✅ Answer: (B) Shoot apical meristem
🔹 Q2. Name the bacterium that produces Bt toxin.
🔵 (A) Rhizobium
🟢 (B) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
🟠 (C) Bacillus thuringiensis
🔴 (D) E. coli
✅ Answer: (C) Bacillus thuringiensis
🔹 Q3. Which rice variety was genetically engineered to contain β-carotene?
🔵 (A) IR-8 rice
🟢 (B) Golden Rice
🟠 (C) Basmati Rice
🔴 (D) Hybrid Rice
✅ Answer: (B) Golden Rice
🔹 Q4. Expand ADA deficiency.
🔵 (A) Adenosine Diphosphate Anemia
🟢 (B) Adenosine Deaminase Deficiency
🟠 (C) Adenine DNA Deficiency
🔴 (D) Adenosine Dehydrogenase Anomaly
✅ Answer: (B) Adenosine Deaminase Deficiency
🔹 Q5. Give one example of a biofortified crop.
🔵 (A) Bt cotton
🟢 (B) Iron-fortified rice
🟠 (C) Golden Rice
🔴 (D) Protein-enriched potato
✅ Answer: (B) Iron-fortified rice
🔹 Q6. Which enzyme is used to cut DNA at specific sites?
🔵 (A) DNA polymerase
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) Restriction endonuclease
🔴 (D) RNA polymerase
✅ Answer: (C) Restriction endonuclease
🔹 Q7. Name one biodegradable plastic produced by microbes.
🔵 (A) Nylon
🟢 (B) Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB)
🟠 (C) Teflon
🔴 (D) Polyester
✅ Answer: (B) Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB)
🔹 Q8. Which bacterium is used as a vector for gene transfer in plants?
🔵 (A) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
🟢 (B) Clostridium
🟠 (C) Streptococcus
🔴 (D) Pseudomonas
✅ Answer: (A) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
🔹 Q9. Which technique is used to amplify DNA?
🔵 (A) ELISA
🟢 (B) PCR
🟠 (C) Electrophoresis
🔴 (D) Hybridization
✅ Answer: (B) PCR
🔹 Q10. Name one monoclonal antibody used in cancer therapy.
🔵 (A) Trastuzumab
🟢 (B) Insulin
🟠 (C) Interferon
🔴 (D) Ritonavir
✅ Answer: (A) Trastuzumab
🟡 Section B — Short Answer Questions
🔹 Q11. What is micropropagation? State one advantage.
✅ Answer:
In vitro regeneration of plants from small tissue explants.
Advantage: Produces large numbers of disease-free, genetically identical clones quickly.
🔹 Q12. Why does Bt toxin not kill the bacteria that produce it?
🔵 (A) Bacteria are resistant to toxin
🟢 (B) Toxin is immature
🟠 (C) Toxin is inactive
🔴 (D) Toxin is stored in vacuole
✅ Answer: (C) Toxin is inactive
🔹 Q13. What are transgenic bacteria? Give one example.
✅ Answer:
Bacteria modified by introducing foreign genes.
Example: E. coli engineered with human insulin gene → produces recombinant insulin (Humulin).
🔹 Q14. Mention one advantage and one disadvantage of GM crops.
✅ Answer:
Advantage: Increased resistance to pests → higher yield.
Disadvantage: Risk of ecological imbalance and gene flow.
🔹 Q15. Define Cry proteins. Name an organism that produces them.
✅ Answer:
Cry proteins = insecticidal proteins.
Produced by Bacillus thuringiensis.
🔹 Q16. What is gene therapy?
✅ Answer:
Technique of correcting defective genes.
Example: Used to treat ADA deficiency.
🔹 Q17. Expand PCR. Who developed it?
✅ Answer:
PCR = Polymerase Chain Reaction.
Developed by Kary Mullis in 1983.
🟠 Section C — Short Answer II
🔹 Q18. What are Cry proteins? Name the organism that produces them.
🔵 (A) Proteins from E. coli
🟢 (B) Insecticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis
🟠 (C) Growth proteins from yeast
🔴 (D) Antifungal proteins from Rhizobium
✅ Answer: (B) Insecticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis
🔹 Q19. What is gene therapy? Give an example.
✅ Answer:
Technique of correcting defective genes.
Example: ADA deficiency treated by inserting functional ADA gene into lymphocytes.
🔹 Q20. What is ELISA test used for?
🔵 (A) Detecting DNA mutations
🟢 (B) Detecting presence of antigen/antibody in infections
🟠 (C) Identifying plant pathogens only
🔴 (D) Detecting RNA viruses only
✅ Answer: (B) Detecting presence of antigen/antibody in infections
🔹 Q21. What is the principle of PCR?
✅ Answer:
PCR amplifies DNA exponentially using cycles of:
Denaturation
Annealing
Extension (via Taq polymerase).
🔹 Q22. Name one application each of molecular diagnostics and molecular farming.
✅ Answer:
Molecular diagnostics: PCR used to detect HIV.
Molecular farming: Edible vaccines produced in plants (e.g., Hepatitis B antigen in tobacco).
🔴 Section D — Long Answer Questions
🔹 Q23. Explain the steps involved in recombinant DNA technology.
✅ Answer:
Isolation of DNA.
Cutting of DNA using restriction endonuclease.
Insertion of DNA into vector.
Transfer of recombinant DNA into host (transformation).
Selection of recombinants.
Cloning and expression.
🔹 Q24. How has biotechnology helped in the production of insulin?
✅ Answer:
Human insulin gene introduced into E. coli.
Chains A and B produced separately and combined to form recombinant insulin (Humulin).
Advantage: free of allergic reactions.
🔹 Q25. What is bioremediation? Give one example.
✅ Answer:
Use of microbes to remove pollutants.
Example: Pseudomonas putida degrades oil spills.
🔹 Q26. Explain the process of production of Bt cotton.
✅ Answer:
Bt toxin gene (cry gene) isolated from Bacillus thuringiensis.
Introduced into cotton plant genome.
Plant produces toxin protein that kills bollworm larvae.
🔹 Q27. Write a note on biofortification.
✅ Answer:
Development of nutrient-rich crops via biotechnology.
Examples: Iron-fortified rice, protein-enriched maize, vitamin A–enriched Golden Rice.
🟣 Section E — Case Study-Based Questions
Case Study:
A group of farmers is worried about bollworm infestation in cotton. A biotechnologist suggests cultivating Bt cotton.
🔹 Q28. Why is Bt cotton resistant to bollworm?
🔵 (A) Produces alkaloids harmful to insects
🟢 (B) Produces Bt toxin proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis
🟠 (C) Has thicker leaves
🔴 (D) Absorbs pesticide from soil
✅ Answer: (B) Produces Bt toxin proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis
🔹 Q29. Which gene family encodes the Bt toxins?
🔵 (A) cry genes
🟢 (B) lac operon
🟠 (C) ori genes
🔴 (D) insulin genes
✅ Answer: (A) cry genes
🔹 Q30. Why does Bt toxin not affect humans?
🔵 (A) Humans have alkaline gut
🟢 (B) Toxin remains inactive in human gut (acidic pH)
🟠 (C) Toxin is neutralised by bile
🔴 (D) It is absorbed as vitamin A
✅ Answer: (B) Toxin remains inactive in human gut (acidic pH)
Case Study 2:
A patient with Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) due to ADA deficiency undergoes gene therapy.
🔹 Q31. Which enzyme is lacking in this disorder?
🔵 (A) Adenosine triphosphatase
🟢 (B) Adenosine deaminase
🟠 (C) DNA ligase
🔴 (D) RNA polymerase
✅ Answer: (B) Adenosine deaminase
🔹 Q32. Which type of cells are used to introduce functional ADA gene in patients?
🔵 (A) Platelets
🟢 (B) Lymphocytes
🟠 (C) Neurons
🔴 (D) Erythrocytes
✅ Answer: (B) Lymphocytes
🔹 Q33. Name one permanent treatment approach for ADA deficiency.
🔵 (A) Gene therapy with lymphocytes only
🟢 (B) Bone marrow transplantation
🟠 (C) Recombinant insulin injection
🔴 (D) Vaccination
✅ Answer: (B) Bone marrow transplantation
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔹 Q1. In genetic engineering, the significance of “Ori site” in a plasmid is:
🔵 (A) Binding of RNA polymerase
🟢 (B) Initiation of replication
🟠 (C) Antibiotic resistance
🔴 (D) Expression of foreign gene
✅ Answer: (B) Initiation of replication
Year: NEET 2023
🔹 Q2. Which of the following is not a feature of a cloning vector?
🔵 (A) Ori site
🟢 (B) Selectable marker
🟠 (C) Restriction sites
🔴 (D) Introns
✅ Answer: (D) Introns
Year: NEET 2022
🔹 Q3. Which enzyme is used to join DNA fragments in recombinant DNA technology?
🔵 (A) Restriction endonuclease
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) DNase
🔴 (D) RNA polymerase
✅ Answer: (B) DNA ligase
Year: NEET 2021
🔹 Q4. Which organism is used for gene transfer in plants?
🔵 (A) E. coli
🟢 (B) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
🟠 (C) Rhizobium
🔴 (D) Saccharomyces
✅ Answer: (B) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Year: NEET 2020
🔹 Q5. Which enzyme is used in PCR to extend primers?
🔵 (A) DNA ligase
🟢 (B) RNA polymerase
🟠 (C) Taq DNA polymerase
🔴 (D) DNase
✅ Answer: (C) Taq DNA polymerase
Year: NEET 2019
🔹 Q6. Blue colonies in blue-white screening represent:
🔵 (A) Recombinant plasmids
🟢 (B) Non-recombinant plasmids
🟠 (C) Dead cells
🔴 (D) Cells without plasmid
✅ Answer: (B) Non-recombinant plasmids
Year: NEET 2019
🔹 Q7. The technique of gene amplification in vitro is:
🔵 (A) PCR
🟢 (B) ELISA
🟠 (C) Electrophoresis
🔴 (D) Hybridization
✅ Answer: (A) PCR
Year: NEET 2018
🔹 Q8. Which enzyme is used to cut DNA at specific recognition sites?
🔵 (A) DNA ligase
🟢 (B) DNA polymerase
🟠 (C) Restriction endonuclease
🔴 (D) Topoisomerase
✅ Answer: (C) Restriction endonuclease
Year: NEET 2017
🔹 Q9. Cry proteins are obtained from:
🔵 (A) Agrobacterium
🟢 (B) E. coli
🟠 (C) Bacillus thuringiensis
🔴 (D) Rhizobium
✅ Answer: (C) Bacillus thuringiensis
Year: NEET 2017
🔹 Q10. Which plasmid is widely used as a cloning vector?
🔵 (A) pBR322
🟢 (B) F plasmid
🟠 (C) Ti plasmid
🔴 (D) Cosmid
✅ Answer: (A) pBR322
Year: NEET 2016
🔹 Q11. ADA deficiency is treated by:
🔵 (A) Bone marrow transplantation
🟢 (B) Gene therapy
🟠 (C) Both (A) and (B)
🔴 (D) Vaccination
✅ Answer: (C) Both (A) and (B)
Year: NEET 2016
🔹 Q12. Which enzyme digests bacterial cell walls during DNA isolation?
🔵 (A) Lysozyme
🟢 (B) Chitinase
🟠 (C) Pectinase
🔴 (D) Protease
✅ Answer: (A) Lysozyme
Year: AIPMT 2015
🔹 Q13. Which bacteria is used in production of insulin?
🔵 (A) Agrobacterium
🟢 (B) Rhizobium
🟠 (C) E. coli
🔴 (D) Lactobacillus
✅ Answer: (C) E. coli
Year: AIPMT 2015
🔹 Q14. Which step is not a part of PCR?
🔵 (A) Denaturation
🟢 (B) Annealing
🟠 (C) Translation
🔴 (D) Extension
✅ Answer: (C) Translation
Year: AIPMT 2014
🔹 Q15. Which enzyme unwinds DNA strands during replication?
🔵 (A) Helicase
🟢 (B) Ligase
🟠 (C) Polymerase
🔴 (D) Restriction endonuclease
✅ Answer: (A) Helicase
Year: AIPMT 2014
🔹 Q16. The function of selectable markers in a plasmid is:
🔵 (A) Gene amplification
🟢 (B) Selection of recombinants
🟠 (C) Initiation of replication
🔴 (D) Transcription termination
✅ Answer: (B) Selection of recombinants
Year: AIPMT 2013
🔹 Q17. Which enzyme removes RNA primers in DNA replication?
🔵 (A) DNA polymerase I
🟢 (B) DNA polymerase III
🟠 (C) Ligase
🔴 (D) Helicase
✅ Answer: (A) DNA polymerase I
Year: AIPMT 2013
🔹 Q18. Which is the first step in rDNA technology?
🔵 (A) DNA isolation
🟢 (B) DNA ligation
🟠 (C) Transformation
🔴 (D) Cloning
✅ Answer: (A) DNA isolation
Year: AIPMT 2012
🔹 Q19. Which of the following enzymes is required for downstream processing?
🔵 (A) Proteases
🟢 (B) Restriction endonucleases
🟠 (C) DNases
🔴 (D) RNases
✅ Answer: (A) Proteases
Year: AIPMT 2012
🔹 Q20. Which technique is used to diagnose HIV?
🔵 (A) ELISA
🟢 (B) PCR
🟠 (C) Both (A) and (B)
🔴 (D) Western blot only
✅ Answer: (C) Both (A) and (B)
Year: AIPMT 2011
🔹 Q21. Which enzyme is used to digest fungal cell walls?
🔵 (A) Lysozyme
🟢 (B) Chitinase
🟠 (C) Cellulase
🔴 (D) Pectinase
✅ Answer: (B) Chitinase
Year: AIPMT 2011
🔹 Q22. Which of the following is not used in recombinant DNA technology?
🔵 (A) Restriction enzymes
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) Taq polymerase
🔴 (D) DNase
✅ Answer: (D) DNase
Year: AIPMT 2010
🔹 Q23. Which step follows ligation in rDNA technology?
🔵 (A) Transformation
🟢 (B) Downstream processing
🟠 (C) Transcription
🔴 (D) Translation
✅ Answer: (A) Transformation
Year: AIPMT 2010
🔹 Q24. What is the use of a bioreactor?
🔵 (A) DNA cutting
🟢 (B) Large-scale production of biomolecules
🟠 (C) Gene transfer
🔴 (D) DNA fingerprinting
✅ Answer: (B) Large-scale production of biomolecules
Year: AIPMT 2009
🔹 Q25. In blue-white colony selection, white colonies indicate:
🔵 (A) Recombinant plasmids
🟢 (B) Non-recombinant plasmids
🟠 (C) Dead cells
🔴 (D) No plasmid
✅ Answer: (A) Recombinant plasmids
Year: AIPMT 2009
🔹 Q26. In rDNA technology, which enzyme is used to cut DNA at palindromic sites?
🔵 (A) DNA ligase
🟢 (B) Restriction endonuclease
🟠 (C) Taq polymerase
🔴 (D) DNase
✅ Answer: (B) Restriction endonuclease
Year: AIPMT 2008
🔹 Q27. The first transgenic crop commercially released in India was:
🔵 (A) Golden Rice
🟢 (B) Bt cotton
🟠 (C) Soybean
🔴 (D) Mustard
✅ Answer: (B) Bt cotton
Year: AIPMT 2008
🔹 Q28. Which enzyme is used to cut open a plasmid for gene insertion?
🔵 (A) RNA polymerase
🟢 (B) Restriction endonuclease
🟠 (C) DNA polymerase
🔴 (D) Helicase
✅ Answer: (B) Restriction endonuclease
Year: AIPMT 2007
🔹 Q29. Which technique is used to separate DNA fragments?
🔵 (A) Gel electrophoresis
🟢 (B) PCR
🟠 (C) ELISA
🔴 (D) Western blot
✅ Answer: (A) Gel electrophoresis
Year: AIPMT 2007
🔹 Q30. In blue-white colony selection, white colonies represent:
🔵 (A) Non-recombinants
🟢 (B) Recombinants
🟠 (C) Dead cells
🔴 (D) Plasmid-free cells
✅ Answer: (B) Recombinants
Year: AIPMT 2006
🔹 Q31. A good cloning vector should have:
🔵 (A) Ori site
🟢 (B) Selectable markers
🟠 (C) Restriction sites
🔴 (D) All of the above
✅ Answer: (D) All of the above
Year: AIPMT 2006
🔹 Q32. In gene therapy for ADA deficiency, the functional gene is introduced into:
🔵 (A) Platelets
🟢 (B) Lymphocytes
🟠 (C) Neurons
🔴 (D) Erythrocytes
✅ Answer: (B) Lymphocytes
Year: AIPMT 2005
🔹 Q33. Which enzyme is used in isolation of fungal DNA?
🔵 (A) Pectinase
🟢 (B) Lysozyme
🟠 (C) Chitinase
🔴 (D) Protease
✅ Answer: (C) Chitinase
Year: AIPMT 2005
🔹 Q34. Which of the following is not a step in recombinant DNA technology?
🔵 (A) Isolation of DNA
🟢 (B) Ligation
🟠 (C) Amplification of RNA
🔴 (D) Transformation
✅ Answer: (C) Amplification of RNA
Year: AIPMT 2004
🔹 Q35. What is the function of Taq polymerase in PCR?
🔵 (A) Cut DNA at specific sites
🟢 (B) Synthesize DNA at high temperature
🟠 (C) Join DNA fragments
🔴 (D) Degrade RNA
✅ Answer: (B) Synthesize DNA at high temperature
Year: AIPMT 2004
🔹 Q36. In ELISA test, enzyme is linked to:
🔵 (A) Antigen or antibody
🟢 (B) DNA
🟠 (C) RNA
🔴 (D) Protein coat
✅ Answer: (A) Antigen or antibody
Year: AIPMT 2003
🔹 Q37. Which enzyme digests plant cell walls during DNA isolation?
🔵 (A) Chitinase
🟢 (B) Pectinase
🟠 (C) Lysozyme
🔴 (D) Protease
✅ Answer: (B) Pectinase
Year: AIPMT 2003
🔹 Q38. Which of the following is an example of gene therapy?
🔵 (A) Production of insulin in bacteria
🟢 (B) Treatment of ADA deficiency
🟠 (C) Bt cotton cultivation
🔴 (D) Golden Rice
✅ Answer: (B) Treatment of ADA deficiency
Year: AIPMT 2002
🔹 Q39. Recombinant insulin was first marketed as:
🔵 (A) Genulin
🟢 (B) Humulin
🟠 (C) Novolin
🔴 (D) Biosulin
✅ Answer: (B) Humulin
Year: AIPMT 2002
🔹 Q40. Which enzyme is used in DNA fingerprinting?
🔵 (A) Restriction endonuclease
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) Taq polymerase
🔴 (D) RNase
✅ Answer: (A) Restriction endonuclease
Year: AIPMT 2001
🔹 Q41. Which of the following is not required in PCR?
🔵 (A) Primers
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) Taq polymerase
🔴 (D) Template DNA
✅ Answer: (B) DNA ligase
Year: AIPMT 2001
🔹 Q42. Who developed PCR technique?
🔵 (A) Watson
🟢 (B) Kary Mullis
🟠 (C) Paul Berg
🔴 (D) Cohen
✅ Answer: (B) Kary Mullis
Year: PMT 2000
🔹 Q43. Which of the following is not an application of PCR?
🔵 (A) DNA amplification
🟢 (B) Disease detection
🟠 (C) Gene cloning
🔴 (D) Protein sequencing
✅ Answer: (D) Protein sequencing
Year: PMT 1999
🔹 Q44. Which type of DNA ends are produced by EcoRI?
🔵 (A) Blunt ends
🟢 (B) Sticky ends
🟠 (C) Circular ends
🔴 (D) Both blunt and sticky ends
✅ Answer: (B) Sticky ends
Year: PMT 1999
🔹 Q45. Which is not a characteristic of good cloning vector?
🔵 (A) Ori site
🟢 (B) High copy number
🟠 (C) Absence of selectable marker
🔴 (D) Presence of restriction sites
✅ Answer: (C) Absence of selectable marker
Year: PMT 1998
🔹 Q46. What is the use of selectable marker genes?
🔵 (A) To help clone multiply
🟢 (B) To identify recombinants from non-recombinants
🟠 (C) To initiate replication
🔴 (D) To stop transcription
✅ Answer: (B) To identify recombinants from non-recombinants
Year: PMT 1998
🔹 Q47. Which of the following is not a product of recombinant DNA technology?
🔵 (A) Insulin
🟢 (B) Interferon
🟠 (C) Bt cotton
🔴 (D) Testosterone
✅ Answer: (D) Testosterone
Year: PMT 1997
🔹 Q48. Which of the following techniques can detect HIV infection?
🔵 (A) ELISA
🟢 (B) PCR
🟠 (C) Both (A) and (B)
🔴 (D) None
✅ Answer: (C) Both (A) and (B)
Year: PMT 1997
🔹 Q49. Which of the following enzymes is used in genetic engineering for making complementary DNA (cDNA)?
🔵 (A) Restriction endonuclease
🟢 (B) Reverse transcriptase
🟠 (C) DNA ligase
🔴 (D) RNA polymerase
✅ Answer: (B) Reverse transcriptase
Year: PMT 1996
🔹 Q50. Who is regarded as the father of genetic engineering?
🔵 (A) Watson
🟢 (B) Paul Berg
🟠 (C) Kary Mullis
🔴 (D) Hargobind Khorana
✅ Answer: (B) Paul Berg
Year: PMT 1995
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🟢 Q1–Q20 (NEET Level, Moderate)
🔹 Q1. Which enzyme cuts DNA at specific recognition sequences?
🔵 (A) DNA ligase
🟢 (B) Restriction endonuclease
🟠 (C) DNA polymerase
🔴 (D) Primase
✅ Answer: (B) Restriction endonuclease
🔹 Q2. Which bacterium is commonly used to transfer genes into dicot plants?
🔵 (A) Rhizobium
🟢 (B) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
🟠 (C) E. coli
🔴 (D) Clostridium
✅ Answer: (B) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
🔹 Q3. The selectable marker gene in plasmid vectors is usually associated with:
🔵 (A) Antibiotic resistance
🟢 (B) DNA replication
🟠 (C) Enzyme activity
🔴 (D) Ori region
✅ Answer: (A) Antibiotic resistance
🔹 Q4. Which feature is essential in a plasmid vector for cloning?
🔵 (A) Ori site
🟢 (B) Selectable markers
🟠 (C) Restriction sites
🔴 (D) All of the above
✅ Answer: (D) All of the above
🔹 Q5. Which of the following is used in PCR?
🔵 (A) DNA ligase
🟢 (B) Reverse transcriptase
🟠 (C) Taq polymerase
🔴 (D) Lysozyme
✅ Answer: (C) Taq polymerase
🔹 Q6. Which enzyme digests bacterial cell walls during DNA isolation?
🔵 (A) Lysozyme
🟢 (B) Chitinase
🟠 (C) Pectinase
🔴 (D) Protease
✅ Answer: (A) Lysozyme
🔹 Q7. ADA deficiency is an example of a disorder treated by:
🔵 (A) Chemotherapy
🟢 (B) Gene therapy
🟠 (C) Vaccination
🔴 (D) Monoclonal antibodies
✅ Answer: (B) Gene therapy
🔹 Q8. Which of the following is used for gene transfer in monocot plants?
🔵 (A) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
🟢 (B) Biolistics (gene gun)
🟠 (C) Microinjection
🔴 (D) Transformation via plasmids
✅ Answer: (B) Biolistics (gene gun)
🔹 Q9. In blue-white colony selection, white colonies indicate:
🔵 (A) Recombinants
🟢 (B) Non-recombinants
🟠 (C) Dead cells
🔴 (D) No plasmid
✅ Answer: (A) Recombinants
🔹 Q10. Which of the following is not used in recombinant DNA technology?
🔵 (A) Restriction enzymes
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) Taq polymerase
🔴 (D) DNase
✅ Answer: (D) DNase
🔹 Q11. The first step in recombinant DNA technology is:
🔵 (A) Ligation
🟢 (B) DNA isolation
🟠 (C) Transformation
🔴 (D) Screening
✅ Answer: (B) DNA isolation
🔹 Q12. Which bioreactor is most widely used for large-scale production?
🔵 (A) Shake flask
🟢 (B) Air-lift bioreactor
🟠 (C) Stirred-tank bioreactor
🔴 (D) Bubble column
✅ Answer: (C) Stirred-tank bioreactor
🔹 Q13. The principle of PCR is based on:
🔵 (A) DNA replication in vivo
🟢 (B) DNA amplification in vitro
🟠 (C) RNA transcription
🔴 (D) Protein translation
✅ Answer: (B) DNA amplification in vitro
🔹 Q14. Which enzyme is used to seal nicks in DNA backbone?
🔵 (A) Restriction endonuclease
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) DNA polymerase
🔴 (D) Helicase
✅ Answer: (B) DNA ligase
🔹 Q15. Golden Rice is genetically modified to improve:
🔵 (A) Protein content
🟢 (B) Vitamin A content
🟠 (C) Iron content
🔴 (D) Amino acids
✅ Answer: (B) Vitamin A content
🔹 Q16. Which enzyme digests fungal cell walls in DNA isolation?
🔵 (A) Lysozyme
🟢 (B) Chitinase
🟠 (C) Pectinase
🔴 (D) Cellulase
✅ Answer: (B) Chitinase
🔹 Q17. In ELISA test, enzyme is linked to:
🔵 (A) DNA
🟢 (B) Antigen/Antibody
🟠 (C) RNA
🔴 (D) Protein coat
✅ Answer: (B) Antigen/Antibody
🔹 Q18. Cry proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis are effective against:
🔵 (A) Bollworms
🟢 (B) Nematodes
🟠 (C) Weeds
🔴 (D) Viruses
✅ Answer: (A) Bollworms
🔹 Q19. Recombinant insulin is marketed as:
🔵 (A) Biosulin
🟢 (B) Humulin
🟠 (C) Novolin
🔴 (D) Genulin
✅ Answer: (B) Humulin
🔹 Q20. Who is known as the father of genetic engineering?
🔵 (A) Watson
🟢 (B) Paul Berg
🟠 (C) Kary Mullis
🔴 (D) Cohen
✅ Answer: (B) Paul Berg
🟡 Q21–Q25 (Transition into higher NEET-level difficulty)
🔹 Q21. Which enzyme is required to remove RNA primers during DNA replication?
🔵 (A) DNA polymerase III
🟢 (B) DNA polymerase I
🟠 (C) Helicase
🔴 (D) Ligase
✅ Answer: (B) DNA polymerase I
🔹 Q22. Which of the following does not belong to downstream processing?
🔵 (A) Separation
🟢 (B) Purification
🟠 (C) Packaging
🔴 (D) Transformation
✅ Answer: (D) Transformation
🔹 Q23. In recombinant insulin production, why were A and B chains produced separately in E. coli?
🔵 (A) To simplify purification
🟢 (B) To avoid misfolding of proinsulin
🟠 (C) To reduce cost
🔴 (D) To increase yield
✅ Answer: (B) To avoid misfolding of proinsulin
🔹 Q24. Which of the following is not a feature of PCR?
🔵 (A) Denaturation
🟢 (B) Annealing
🟠 (C) Extension
🔴 (D) Transcription
✅ Answer: (D) Transcription
🔹 Q25. Which enzyme is used to prepare complementary DNA (cDNA)?
🔵 (A) Reverse transcriptase
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) DNA polymerase
🔴 (D) RNase
✅ Answer: (A) Reverse transcriptase
🟡 Q26–Q40 (NEET Level, Higher Difficulty)
🔹 Q26. Which of the following is not a feature of a good cloning vector?
🔵 (A) Ori site
🟢 (B) Selectable markers
🟠 (C) Large size
🔴 (D) Restriction sites
✅ Answer: (C) Large size
🔹 Q27. Which enzyme is used to prepare cDNA from mRNA?
🔵 (A) RNA polymerase
🟢 (B) Reverse transcriptase
🟠 (C) DNA ligase
🔴 (D) DNase
✅ Answer: (B) Reverse transcriptase
🔹 Q28. The Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium is modified and used because:
🔵 (A) It causes crown gall disease
🟢 (B) It acts as a cloning vector after disarming
🟠 (C) It has no Ori site
🔴 (D) It is antibiotic-resistant only
✅ Answer: (B) It acts as a cloning vector after disarming
🔹 Q29. Which is the correct order in PCR?
🔵 (A) Extension → Annealing → Denaturation
🟢 (B) Denaturation → Annealing → Extension
🟠 (C) Annealing → Denaturation → Extension
🔴 (D) Denaturation → Extension → Annealing
✅ Answer: (B) Denaturation → Annealing → Extension
🔹 Q30. In gene therapy for ADA deficiency, functional ADA gene is introduced into:
🔵 (A) Lymphocytes
🟢 (B) Neurons
🟠 (C) Hepatocytes
🔴 (D) Platelets
✅ Answer: (A) Lymphocytes
🔹 Q31. Which one of the following is not an application of PCR?
🔵 (A) Amplification of DNA
🟢 (B) Detection of pathogens
🟠 (C) DNA fingerprinting
🔴 (D) Protein sequencing
✅ Answer: (D) Protein sequencing
🔹 Q32. Which of the following enzymes helps in joining DNA fragments?
🔵 (A) DNA polymerase
🟢 (B) DNA ligase
🟠 (C) Restriction endonuclease
🔴 (D) RNase
✅ Answer: (B) DNA ligase
🔹 Q33. Which technique is used to separate DNA fragments according to size?
🔵 (A) ELISA
🟢 (B) PCR
🟠 (C) Gel electrophoresis
🔴 (D) Hybridization
✅ Answer: (C) Gel electrophoresis
🔹 Q34. The inactive protoxin of Bt becomes active in insect gut because:
🔵 (A) Acidic pH
🟢 (B) Alkaline pH
🟠 (C) Neutral pH
🔴 (D) Enzyme action only
✅ Answer: (B) Alkaline pH
🔹 Q35. Which is not a step of recombinant DNA technology?
🔵 (A) Isolation of DNA
🟢 (B) Amplification
🟠 (C) Transcription
🔴 (D) Transformation
✅ Answer: (C) Transcription
🔹 Q36. Monoclonal antibodies are used in treatment of:
🔵 (A) Bacterial infections
🟢 (B) Cancer
🟠 (C) Nutritional deficiencies
🔴 (D) Genetic disorders
✅ Answer: (B) Cancer
🔹 Q37. Which type of ends are generated by EcoRI?
🔵 (A) Sticky ends
🟢 (B) Blunt ends
🟠 (C) Circular ends
🔴 (D) Both sticky and blunt
✅ Answer: (A) Sticky ends
🔹 Q38. Which of the following is not used in downstream processing?
🔵 (A) Separation
🟢 (B) Purification
🟠 (C) Expression in host
🔴 (D) Packaging
✅ Answer: (C) Expression in host
🔹 Q39. Which organism is used in the production of recombinant insulin?
🔵 (A) Agrobacterium
🟢 (B) E. coli
🟠 (C) Rhizobium
🔴 (D) Saccharomyces
✅ Answer: (B) E. coli
🔹 Q40. Recombinant insulin is free from complications because:
🔵 (A) It is cheaper
🟢 (B) It is identical to human insulin
🟠 (C) It is produced in animals
🔴 (D) It is taken orally
✅ Answer: (B) It is identical to human insulin
🔴 Q41–Q50 (NEET Level, Challenging)
🔹 Q41. Which technique is commonly used to detect HIV infection?
🔵 (A) PCR
🟢 (B) ELISA
🟠 (C) Both PCR and ELISA
🔴 (D) Electrophoresis
✅ Answer: (C) Both PCR and ELISA
🔹 Q42. Which enzyme is used to digest plant cell walls during DNA isolation?
🔵 (A) Lysozyme
🟢 (B) Pectinase
🟠 (C) Protease
🔴 (D) Chitinase
✅ Answer: (B) Pectinase
🔹 Q43. Which of the following is not a product of recombinant DNA technology?
🔵 (A) Insulin
🟢 (B) Interferon
🟠 (C) Bt cotton
🔴 (D) Testosterone
✅ Answer: (D) Testosterone
🔹 Q44. Which enzyme unwinds DNA strands during replication?
🔵 (A) DNA polymerase
🟢 (B) Helicase
🟠 (C) Ligase
🔴 (D) Topoisomerase
✅ Answer: (B) Helicase
🔹 Q45. In gene cloning, which is not required in PCR?
🔵 (A) Primers
🟢 (B) Template DNA
🟠 (C) Taq polymerase
🔴 (D) DNA ligase
✅ Answer: (D) DNA ligase
🔹 Q46. Which step comes immediately after ligation in rDNA technology?
🔵 (A) Transformation
🟢 (B) Screening
🟠 (C) Electrophoresis
🔴 (D) Downstream processing
✅ Answer: (A) Transformation
🔹 Q47. Which is not a medical application of biotechnology?
🔵 (A) Monoclonal antibodies
🟢 (B) Insulin production
🟠 (C) Bt crops
🔴 (D) Gene therapy
✅ Answer: (C) Bt crops
🔹 Q48. Which of the following is not essential for PCR?
🔵 (A) Taq polymerase
🟢 (B) Template DNA
🟠 (C) DNA ligase
🔴 (D) Primers
✅ Answer: (C) DNA ligase
🔹 Q49. Which of the following protocols regulates GMO handling internationally?
🔵 (A) Montreal Protocol
🟢 (B) Cartagena Protocol
🟠 (C) Kyoto Protocol
🔴 (D) Basel Protocol
✅ Answer: (B) Cartagena Protocol
🔹 Q50. Which Indian regulatory body approves release of GMOs?
🔵 (A) CSIR
🟢 (B) GEAC
🟠 (C) ICMR
🔴 (D) ICAR
✅ Answer: (B) GEAC
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
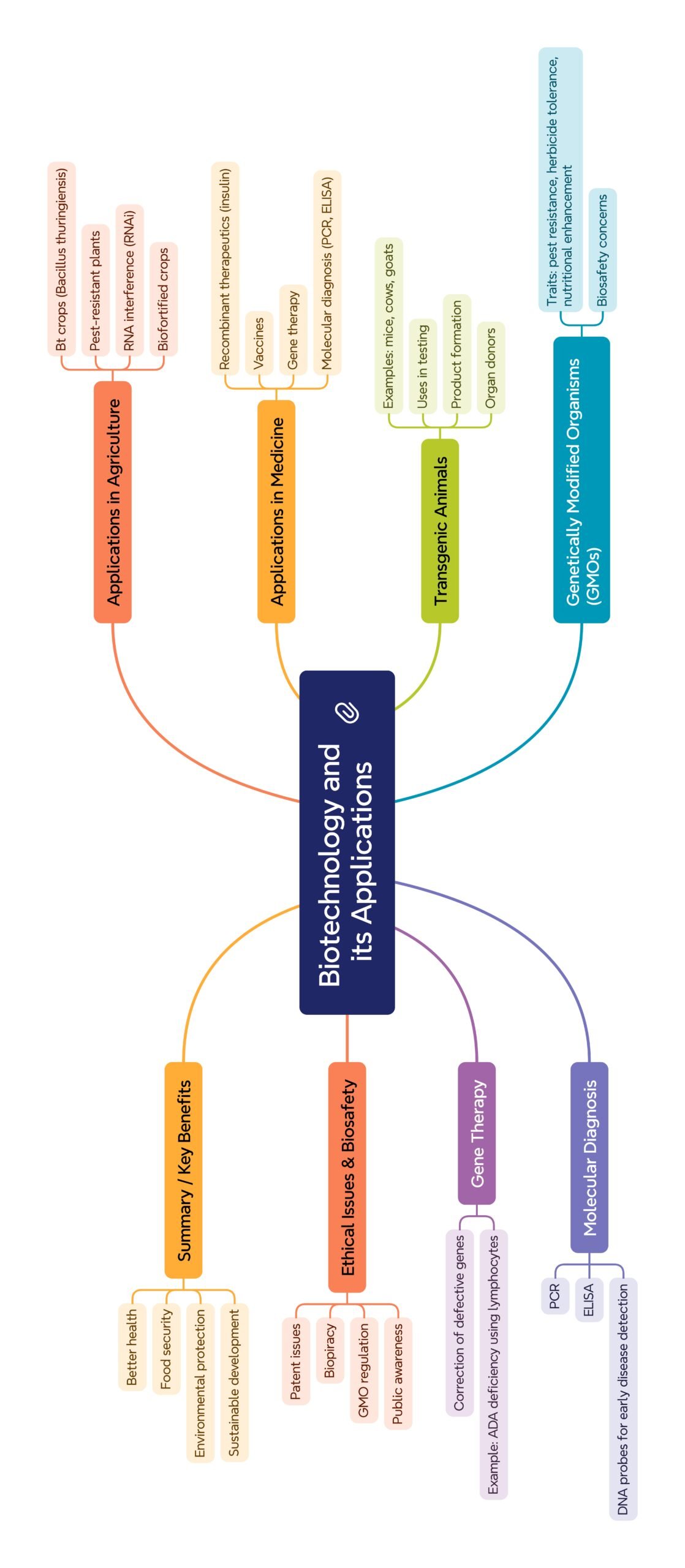
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
