Class 12 : Poltical Science (English) – Lesson 7.Globalisation
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY

🌍 Detailed Explanation
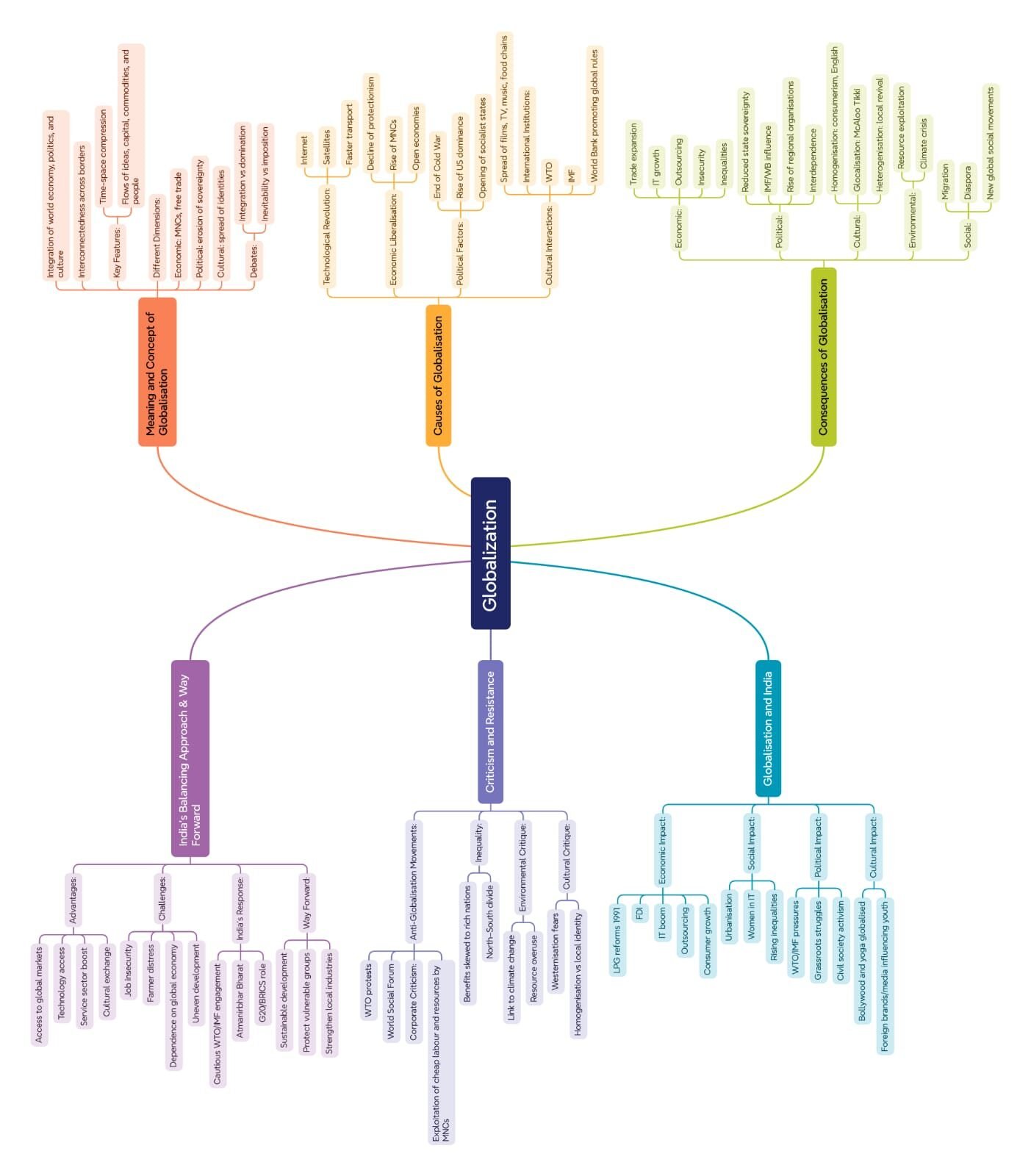
🔹 1. Meaning of Globalisation
🌏 Globalisation refers to the process of growing interconnection and interdependence among countries—economically, politically, socially, and culturally.
It implies that events in one part of the world affect others instantly.
It integrates national economies into a global economy, encouraging free flow of goods, capital, services, ideas, and people.
💡 Key Idea: The world has become a global village due to technology, trade liberalisation, and multinational corporations (MNCs).
🔹 2. Historical Background
📜 Globalisation is not new.
In the nineteenth century, colonial powers established trade routes, global markets, and spread industries.
After World War II, globalisation took a new form with:
Bretton Woods institutions (IMF & World Bank),
Expansion of international trade,
Technological advancements.
In the 1990s, post-Cold War era, countries began liberalising their economies, leading to modern economic globalisation.
🔹 3. Features of Globalisation
🌐 a. Free Trade: Reduction of tariffs and trade barriers.
💸 b. Capital Flow: Movement of investment across borders.
💼 c. Technological Exchange: Spread of innovations globally.
👥 d. Migration: Movement of people for work and study.
📺 e. Cultural Exchange: Popularity of global media, films, and fashion.
🏦 f. International Institutions: Role of WTO, IMF, World Bank, etc.
🔹 4. Economic Dimensions
💱 Economic globalisation involves:
Liberalisation of trade and investment,
Privatisation of public sectors,
Opening domestic markets to foreign competition.
🌍 Example: India’s 1991 New Economic Policy introduced LPG — Liberalisation, Privatisation, and Globalisation.
✔️ Impact:
Increased foreign investment,
Boost to services (IT, telecom),
Exposure to global competition.
But also: ⚠️ Growing inequality, ⚠️ Job insecurity in unorganised sectors.
🔹 5. Political Dimensions
⚖️ Globalisation influences governance and sovereignty:
Governments adopt policies suitable for global markets.
Rise of intergovernmental organisations (IGOs) like UN, WTO, EU.
Non-state actors (MNCs, NGOs) gain influence.
📌 Yet, nation-states remain important in policymaking and regulation.
🔹 6. Cultural Dimensions
🎬 Culture travels across borders — via movies, media, food, and fashion.
🌎 Spread of Western lifestyle (McDonald’s, Hollywood, jeans).
📱 Digital communication spreads common trends.
🧭 Cultural Homogenisation: Cultures become similar globally.
🪷 Cultural Heterogenisation: Local cultures adapt and mix with global ones (e.g., Bollywood remixing Western music).
🔹 7. Technology and Globalisation
💻 Internet, satellites, and communication revolutionised interaction. ✈️ Cheaper transportation increased mobility. 📦 E-commerce and online platforms created borderless markets.
🔹 8. Role of International Organisations
🏢 World Trade Organisation (WTO) promotes free trade but is criticised for favouring developed countries.
💰 IMF & World Bank provide financial support but impose conditions.
🌍 These institutions shape global economic policies.
🔹 9. Impact on India
📈 Positive Effects:
Growth in IT, outsourcing, and service sectors.
Access to international products and markets.
Employment in global industries.
⚠️ Negative Effects:
Threat to local industries.
Agricultural distress due to global competition.
Cultural erosion.
💡 India balances globalisation with self-reliance (Atmanirbhar Bharat).
🔹 10. Globalisation and Sovereignty
🧭 Critics argue globalisation weakens sovereignty:
Decisions influenced by IMF/WTO.
MNCs shape national policies.
✔️ Others see sovereignty adapting:
Governments collaborate globally.
New opportunities for diplomacy and economic growth.
🔹 11. Resistance to Globalisation
✊ Movements worldwide challenge globalisation’s inequalities:
Demand for fair trade, environmental protection, workers’ rights.
Example: Seattle Protest (1999) against WTO.
🌿 Civil society groups call for ethical globalisation with justice and sustainability.
🔹 12. Globalisation and Democracy
⚖️ It strengthens democracy by:
Promoting transparency and accountability.
Encouraging information exchange.
But also challenges:
Decisions by unelected bodies (IMF, WTO).
Pressure to follow global standards ignoring local needs.
🔹 13. Environmental Concerns
🌱 Globalisation increases industrialisation and consumption.
Leads to pollution, climate change, and resource depletion.
Global summits (Rio 1992, Paris 2015) stress sustainable practices.
🔹 14. Inequalities of Globalisation
📊 Developed countries dominate world trade and technology. 💡 Developing nations face unequal terms. 🧭 Within nations, urban rich benefit more than rural poor.
🔹 15. Globalisation and International Relations
🌍 Countries interdependent in economy, environment, and security. 💬 Diplomacy includes economic negotiations and trade blocs (EU, ASEAN, SAARC).
Globalisation reduces war probability but increases vulnerability to global crises.
🔹 16. Debates on Globalisation
🧠 Supporters say:
✔️ Promotes growth, technology, and cooperation.
✔️ Reduces poverty and improves living standards.
⚠️ Critics say:
❌ Increases inequality, environmental damage, and cultural loss.
❌ Benefits MNCs more than people.
🧭 Middle view: Globalisation must be managed ethically.
🔹 17. Globalisation and Nationalism
🏳️🌈 Rise of nationalism in response (e.g., Brexit, America First).
Countries reassert local identity while engaging globally.
Balanced approach: Glocalisation — thinking globally, acting locally.
🔹 18. Key International Events
📌 1991 – India’s Economic Reforms
📌 1995 – Formation of WTO
📌 1999 – Seattle Protests
📌 2015 – Paris Climate Agreement
These shaped the direction of globalisation.
🔹 19. Role of MNCs
🏢 Multinational corporations (e.g., Apple, Toyota, Infosys) integrate global production. ✔️ Spread technology, jobs, and trade. ⚠️ But dominate markets and influence politics.
🔹 20. Future of Globalisation
📈 Increasing due to AI, digital trade, and global finance. ⚠️ Faces backlash from protectionism, wars, and pandemics. 🌏 Needs reform to ensure equity, sustainability, and inclusion.
🧾 Summary (≈200 words)
🌍 Globalisation is a process of increasing interconnectedness across the world in economic, political, cultural, and technological spheres.
It has deep historical roots but accelerated after the 1990s due to liberalisation and technological progress.
Economically, it encourages free trade and investment; politically, it reshapes sovereignty and governance; culturally, it spreads global values and hybrid lifestyles.
Institutions like WTO, IMF, and World Bank promote globalisation, but often favour developed countries.
India embraced globalisation in 1991, witnessing growth in services and technology sectors but also facing inequality and cultural changes.
Debates surround its benefits and harms: while it fosters innovation and cooperation, it also widens the gap between rich and poor.
Environmental concerns, resistance movements, and nationalist responses shape the ongoing discourse.
Sustainable and fair globalisation requires balancing economic progress with social justice and ecological protection.
📝 Quick Recap (≈100 words)
🔹 Meaning: Interconnected world through trade, ideas, culture.
🔹 Dimensions: Economic, political, cultural.
🔹 Drivers: Technology, liberalisation, MNCs.
🔹 Institutions: WTO, IMF, World Bank.
🔹 Impact on India: Growth + inequality.
🔹 Benefits: Development, innovation, cooperation.
🔹 Issues: Inequality, cultural erosion, environmental harm.
🔹 Resistance: Fair trade, protests, localisation.
🔹 Goal: Ethical and sustainable globalisation.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1: Which of the statements are TRUE about globalisation?
1️⃣ Globalisation is purely an economic phenomenon.
2️⃣ Globalisation began in 1991.
3️⃣ Globalisation is the same thing as westernisation.
4️⃣ Globalisation is a multi-dimensional phenomenon.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Option 4 is correct.
💡 Globalisation is multi-dimensional — it covers economic, political, cultural, and technological aspects.
❌ It is not limited to economy or westernisation, and though it expanded in 1991, its roots are much older.
🔵 Question 2: Which of the statements are TRUE about the impact of globalisation?
1️⃣ Globalisation has been uneven in its impact on states and societies.
2️⃣ Globalisation has had a uniform impact on all states and societies.
3️⃣ The impact of globalisation has been confined to the political sphere.
4️⃣ Globalisation inevitably results in cultural homogeneity.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Option 1 is correct.
💡 Globalisation affects countries differently — developed nations benefit more than developing ones; within societies, urban rich gain more than rural poor.
🔵 Question 3: Which of the statements are TRUE about the causes of globalisation?
1️⃣ Technology is an important cause of globalisation.
2️⃣ Globalisation is caused by a particular community of people.
3️⃣ Globalisation originated in the US.
4️⃣ Economic interdependence alone causes globalisation.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Option 1 is correct.
💡 Technological revolution, especially in communication, transport, and information, made the world interconnected.
Globalisation is driven by multiple factors, not a single nation or community.
🔵 Question 4: Which of the statements are TRUE about globalisation?
1️⃣ Globalisation is only about movement of commodities.
2️⃣ Globalisation does not involve a conflict of values.
3️⃣ Services are an insignificant part of globalisation.
4️⃣ Globalisation is about worldwide interconnectedness.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Option 4 is correct.
💡 Globalisation is about worldwide interconnectedness in economy, culture, technology, and politics, not limited to goods.
🔵 Question 5: Which of the statements are FALSE about globalisation?
1️⃣ Advocates of globalisation argue that it will result in greater economic growth.
2️⃣ Critics of globalisation argue that it will result in greater economic disparity.
3️⃣ Advocates of globalisation argue that it will result in cultural homogenisation.
4️⃣ Critics of globalisation argue that it will result in cultural homogenisation.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Option 3 is False.
💡 Advocates claim it promotes growth and cooperation, not uniform culture.
⚠️ Critics warn of economic inequality and cultural dominance.
🔵 Question 6: What is worldwide interconnectedness? What are its components?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Meaning: Worldwide interconnectedness refers to integration of countries through flows of goods, capital, ideas, technology, and people.
✔️ Components:
🌍 Trade – exchange of goods and services
💰 Capital – cross-border investments
🧑💼 People – migration and travel
💡 Ideas – spread of knowledge and values
🧭 Institutions – global organisations like WTO, IMF
🔵 Question 7: How has technology contributed to globalisation?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Communication technology (internet, mobile, satellites) enables instant exchange of information.
✔️ Transport innovations reduce distance and cost of trade.
✔️ Automation and logistics allow global production chains.
✔️ Technology links markets, media, and people globally — making integration faster.
🔵 Question 8: Critically evaluate the impact of the changing role of the state in developing countries in light of globalisation.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Globalisation reduced state control over economy.
✔️ Governments shifted from regulation to facilitation.
✔️ Private sector and MNCs gained influence.
✔️ States still handle social welfare, environment, and security.
✔️ In developing countries, state power adapts rather than disappears.
🔵 Question 9: What are the economic implications of globalisation? How has globalisation impacted India in this dimension?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Economic Implications:
🌏 Free trade, competition, liberalisation, foreign investment.
💰 Integration of domestic with global economy.
✔️ Impact on India:
📈 Growth in IT, services, exports.
🧠 Employment in global sectors.
⚠️ Inequality, dependence on foreign capital.
🔵 Question 10: Do you agree that globalisation leads to cultural heterogeneity?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Yes. Globalisation spreads foreign culture but local cultures adapt and blend.
✔️ Examples: Indian cuisine abroad, Western clothes in India, Bollywood worldwide.
✔️ Instead of uniformity, it creates hybrid cultures.
🔵 Question 11: How has globalisation impacted India and how is India in turn impacting globalisation?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Impact on India:
🌐 Economic growth, foreign investment, access to global goods.
⚠️ Inequality and cultural change.
✔️ India’s impact:
📱 Exports of IT and services,
🎬 Spread of Indian culture, yoga, cinema.
💡 Participation in global governance (WTO, UN).
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
🌍 Section A – Multiple Choice Questions (1 mark each)
(Each question carries 1 mark. Choose the correct option.)
🔵 Question 1: Which of the statements are TRUE about globalisation?
🟣 a. Globalisation is purely an economic phenomenon.
🟢 b. Globalisation began in 1991.
🟠 c. Globalisation is the same thing as westernisation.
🔴 d. Globalisation is a multi-dimensional phenomenon.
🟩 Answer: d
🔵 Question 2: Which of the statements are TRUE about the impact of globalisation?
🟣 a. Globalisation has been uneven in its impact on states and societies.
🟢 b. Globalisation has had a uniform impact on all states and societies.
🟠 c. The impact of globalisation has been confined to the political sphere.
🔴 d. Globalisation inevitably results in cultural homogeneity.
🟩 Answer: a
🔵 Question 3: Which of the statements are TRUE about the causes of globalisation?
🟣 a. Technology is an important cause of globalisation.
🟢 b. Globalisation is caused by a particular community of people.
🟠 c. Globalisation originated in the US.
🔴 d. Economic interdependence alone causes globalisation.
🟩 Answer: a
🔵 Question 4: Which of the statements are TRUE about globalisation?
🟣 a. Globalisation is only about movement of commodities.
🟢 b. Globalisation does not involve a conflict of values.
🟠 c. Services are an insignificant part of globalisation.
🔴 d. Globalisation is about worldwide interconnectedness.
🟩 Answer: d
🔵 Question 5: Which of the statements are FALSE about globalisation?
🟣 a. Advocates of globalisation argue that it will result in greater economic growth.
🟢 b. Critics of globalisation argue that it will result in greater economic disparity.
🟠 c. Advocates of globalisation argue that it will result in cultural homogenisation.
🔴 d. Critics of globalisation argue that it will result in cultural homogenisation.
🟩 Answer: c
🔵 Question 6: Globalisation has been mainly facilitated by—
🟣 a. Development of technology and communication
🟢 b. Colonial expansion
🟠 c. Military alliances
🔴 d. Regionalism
🟩 Answer: a
🔵 Question 7: Which of the following is NOT a feature of globalisation?
🟣 a. Free trade
🟢 b. Cultural exchange
🟠 c. Isolationism
🔴 d. Capital mobility
🟩 Answer: c
🔵 Question 8: Which institution promotes free trade among countries?
🟣 a. WTO
🟢 b. WHO
🟠 c. UNESCO
🔴 d. IMF
🟩 Answer: a
🔵 Question 9: Which dimension of globalisation influences fashion, food, and music?
🟣 a. Economic
🟢 b. Political
🟠 c. Cultural
🔴 d. Technological
🟩 Answer: c
🔵 Question 10: Which of the following statements is TRUE?
🟣 a. Globalisation leads to uniform benefits for all.
🟢 b. Globalisation affects all countries equally.
🟠 c. Globalisation creates both opportunities and inequalities.
🔴 d. Globalisation has ended poverty.
🟩 Answer: c
🔵 Question 11: Which of the following is an advantage of globalisation?
🟣 a. Decrease in competition
🟢 b. Decline in innovation
🟠 c. Increase in trade and technology exchange
🔴 d. Isolation of nations
🟩 Answer: c
🔵 Question 12: Which of the following reflects cultural heterogeneity?
🟣 a. Adoption of only Western culture
🟢 b. Mixture of local and global cultures
🟠 c. Complete cultural uniformity
🔴 d. Rejection of local cultures
🟩 Answer: b
🧠 End of Section A (12 × 1 = 12 marks)
🌏 Section B – Short Answer Type (2 marks each)
(Answer each in 50–60 words)
🔵 Question 13: What is meant by worldwide interconnectedness?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ It refers to the growing linkages between countries in terms of trade, technology, culture, and politics.
✔️ It includes the free flow of goods, services, capital, people, and ideas.
✔️ It reflects how events in one part of the world affect others instantly.
🔵 Question 14: What are the main components of worldwide interconnectedness?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Trade – Exchange of goods and services across borders.
✔️ Capital – Flow of money and investment globally.
✔️ People – Migration for work, education, and tourism.
✔️ Ideas – Spread of knowledge, culture, and values.
🔵 Question 15: How has technology contributed to globalisation?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Technology revolutionised communication (internet, phones) and transport (aviation, shipping).
✔️ It reduced distance and cost, enabling faster exchange of goods and ideas.
✔️ Created global media and digital platforms for instant interaction.
🔵 Question 16: Mention any two economic implications of globalisation.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Expansion of international trade and investment.
✔️ Integration of national economies into global markets.
✔️ Growth of multinational corporations and global competition.
🔵 Question 17: Explain the cultural impact of globalisation.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Promotes exchange of ideas, music, food, and fashion across borders.
✔️ Leads to cultural hybridisation — mixing of global and local cultures.
✔️ May also cause cultural homogenisation where one culture dominates others.
🔵 Question 18: What are the arguments of critics against globalisation?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ It increases inequality between nations and within societies.
✔️ Favors rich countries and MNCs.
✔️ Threatens local industries and cultures.
✔️ Reduces state control over economy.
🌿 Section C – Long Answer Type I (4 marks each)
(Answer each in 100–120 words)
🔵 Question 19: What is meant by worldwide interconnectedness? Explain its key components.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Worldwide interconnectedness refers to growing linkages between nations in multiple fields such as economy, culture, technology, and politics.
✔️ It represents the reality that events in one country can influence others instantly.
✔️ Key Components:
🌍 Trade and Commerce – Exchange of goods/services between countries.
💰 Capital Flow – Cross-border investments by individuals, firms, or governments.
👥 People – Migration, tourism, and cultural exchange.
💡 Ideas – Movement of innovations, values, and knowledge.
✔️ Together, these create a web of mutual dependence among states.
🔵 Question 20: How has technology contributed to the process of globalisation?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Technological advancements have been the most powerful driving force behind globalisation.
✔️ Modern communication tools (internet, mobiles, satellites) enable instant global contact.
✔️ Transportation innovations (aircraft, container ships) reduce distance and cost.
✔️ Technology supports e-commerce, global supply chains, and digital trade.
✔️ It allows global flow of information, ideas, and products, thus integrating economies and cultures worldwide.
🔵 Question 21: Explain the economic implications of globalisation.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Positive Impacts:
🌐 Increase in international trade and foreign investment.
📈 Growth of multinational corporations (MNCs).
💡 Exchange of technology and skills.
✔️ Negative Impacts:
⚠️ Greater inequality between rich and poor nations.
⚠️ Threat to local industries and small producers.
✔️ Overall, it connects national economies to global markets, creating both opportunities and challenges.
🔵 Question 22: Critically evaluate the impact of globalisation on developing countries.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Globalisation has brought economic growth and foreign investment in developing countries.
✔️ It opened access to global markets and technology.
✔️ However, it increased economic dependence on developed nations.
✔️ It widened income inequality and reduced control of governments over economies.
✔️ For example, in India, globalisation boosted IT and service sectors but affected small-scale industries and farmers.
🔵 Question 23: What are the cultural consequences of globalisation?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Globalisation spreads cultural ideas, products, and lifestyles across borders.
✔️ It leads to cultural homogenisation (similarity) through global media, brands, and entertainment.
✔️ Simultaneously, it creates cultural heterogenisation, blending global and local traditions (e.g., Bollywood + Hollywood styles).
✔️ It promotes multiculturalism but may also threaten local identities.
🧠 End of Section C (5 × 4 = 20 Marks)
🌎 Section D – Source/Map/Cartoon-Based (4 marks each)
🔵 Question 24: Study the statement:
“Globalisation has led to both opportunities and inequalities.”
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Opportunities include global trade, access to technology, and employment.
✔️ Inequalities arise because developed countries benefit more.
✔️ Poor nations face exploitation and dependency.
✔️ Hence, globalisation must be managed to ensure equitable gains.
🔵 Question 25: Interpretation Question:
A map shows growing global trade routes. What does it reveal?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Trade networks connect continents, reflecting economic interdependence.
✔️ Regions like North America, Europe, and Asia dominate trade.
✔️ Developing countries integrate as suppliers or markets.
✔️ Trade reflects global cooperation but also inequality.
🔵 Question 26: Cartoon Analysis:
Cartoon showing people from different countries linked by trade, culture, and media.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ The cartoon symbolises interconnectedness of societies through globalisation.
✔️ It shows shared prosperity and common challenges.
✔️ It highlights loss of cultural uniqueness yet growing cooperation.
✔️ The message: globalisation unites but also transforms societies.
🧠 End of Section D (3 × 4 = 12 Marks)
🌱 Section E – Long Answer Type II (6 marks each)
(Answer each in 170–180 words)
🔵 Question 27: Examine how globalisation has impacted India.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Economic Impact:
🌍 Increased FDI, trade liberalisation, and growth of IT and service sectors.
💼 Boosted employment in urban areas.
✔️ Social Impact:
🎓 Exposure to global education, lifestyles, and consumer culture.
✔️ Political Impact:
⚖️ Policies aligned with global institutions (IMF, WTO).
✔️ Challenges:
⚠️ Rising inequality between urban and rural sectors.
⚠️ Threat to small-scale industries and farmers.
✔️ Positive: Strengthened India’s global presence, enhanced competitiveness.
✔️ Conclusion: Globalisation transformed India’s economy and society, demanding inclusive policies.
🔵 Question 28: Do you agree that globalisation leads to cultural heterogeneity?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Yes, globalisation spreads global culture but interacts with local values.
✔️ Creates hybrid forms—Indian pop with Western beats, McAloo Tikki at McDonald’s.
✔️ Enhances diversity and exchange of traditions.
✔️ Example: Yoga, Bollywood gaining global popularity.
✔️ Hence, rather than uniformity, it results in cultural blending.
🔵 Question 29: How has technology transformed globalisation?
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Communication Revolution: Internet, mobile phones enable instant contact.
✔️ Transportation: Air cargo, container ships reduced trade barriers.
✔️ Digital Economy: E-commerce, online banking, outsourcing.
✔️ Media and Culture: Global platforms spread music, films, ideas.
✔️ Technology connects markets, cultures, and communities, accelerating globalisation.
🔵 Question 30: Evaluate the arguments for and against globalisation.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ In Favour:
🌐 Increases growth, investment, employment.
💡 Promotes technology transfer and innovation.
🤝 Encourages cooperation and understanding.
✔️ Against:
⚠️ Increases inequality, cultural dominance.
⚠️ Reduces national sovereignty.
✔️ Conclusion: Globalisation is beneficial if made inclusive, ethical, and sustainable.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
