Class 11 : Physics (In English) – Chapter 2: Motion in a Straight Line
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔶 1. Introduction
This chapter deals with motion in one dimension, i.e., along a straight line. It’s part of kinematics, the branch of mechanics that describes motion without regard to its causes.
🔶 2. Rest and Motion
A body is at rest if it does not change its position with time relative to a reference point.
A body is in motion if it changes its position with time.
Rest and motion are relative concepts depending on the observer’s frame of reference.
🔶 3. Position, Path Length, and Displacement
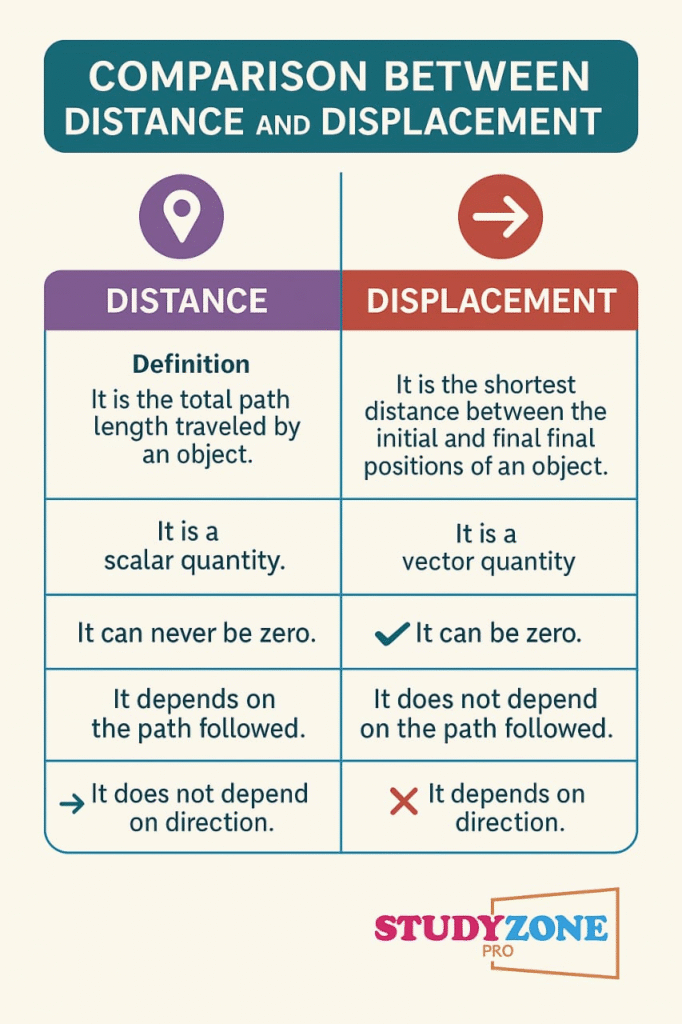
Position: Location of a particle at a given time, measured from a reference point (usually origin).
Path length: The actual length of the path traveled (scalar quantity).
Displacement: Change in position in a straight line with direction (vector quantity).
Example: For a round trip, displacement = 0 but path length > 0.
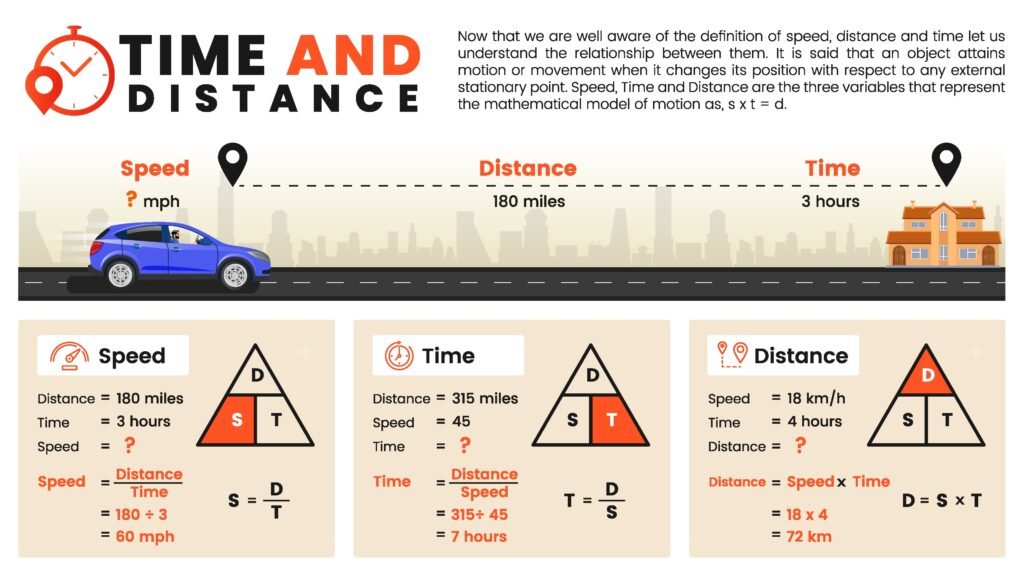
🔶 4. Speed and Velocity
Speed = Distance / Time (scalar)
Velocity = Displacement / Time (vector)
Types:
Average speed = Total distance / Total time
Average velocity = Total displacement / Total time
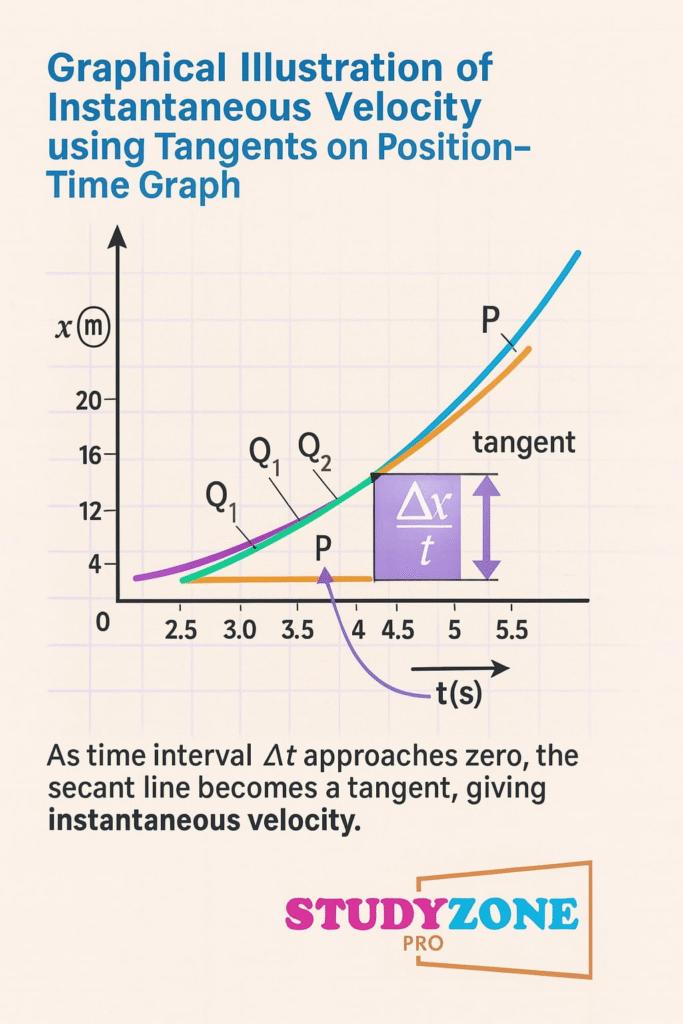
Instantaneous velocity = Limit of average velocity as time interval → 0
That is: v = dx/dt
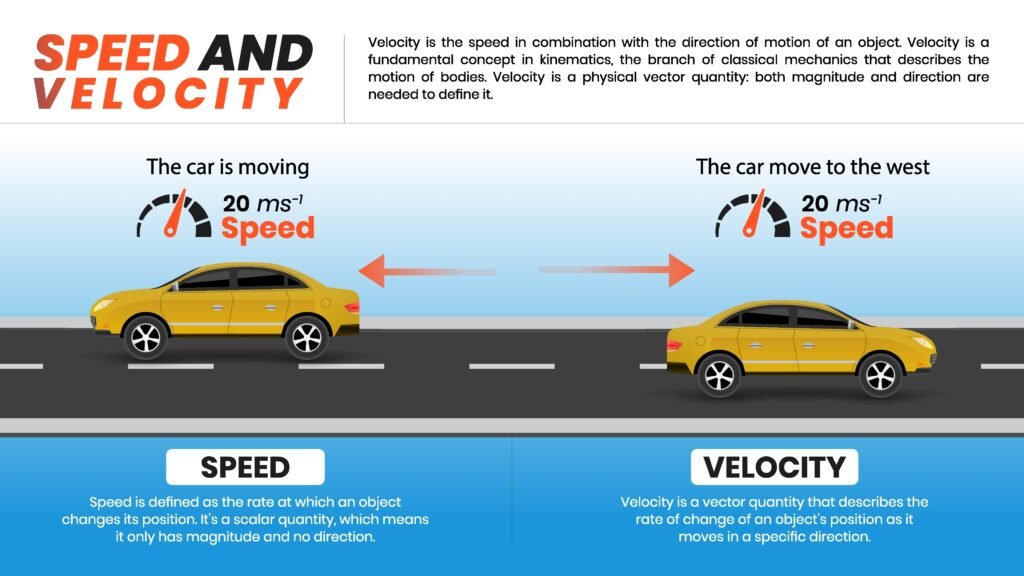
🔶 5. Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time:
a = dv/dt
Positive acceleration: speed increases
Negative acceleration (retardation): speed decreases
Zero acceleration: uniform velocity
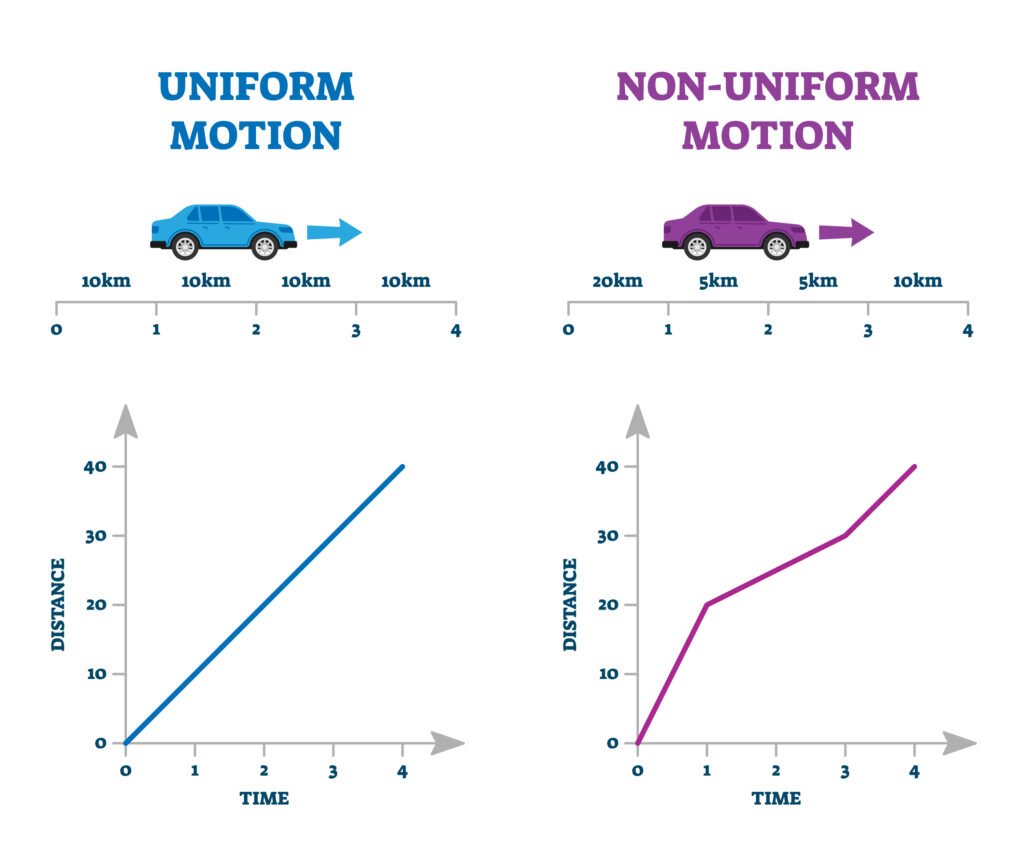
🔶 6. Uniform and Non-uniform Motion
Uniform motion: Constant velocity, zero acceleration
Uniformly accelerated motion: Acceleration is constant
Non-uniform motion: Variable velocity and/or variable acceleration
🔶 7. Equations of Motion for Uniform Acceleration
Let:
u = initial velocity
v = final velocity
a = acceleration
s = displacement
t = time
Then:
v = u + at
s = ut + (1/2)at²
v² = u² + 2as
These are valid only when a is constant.
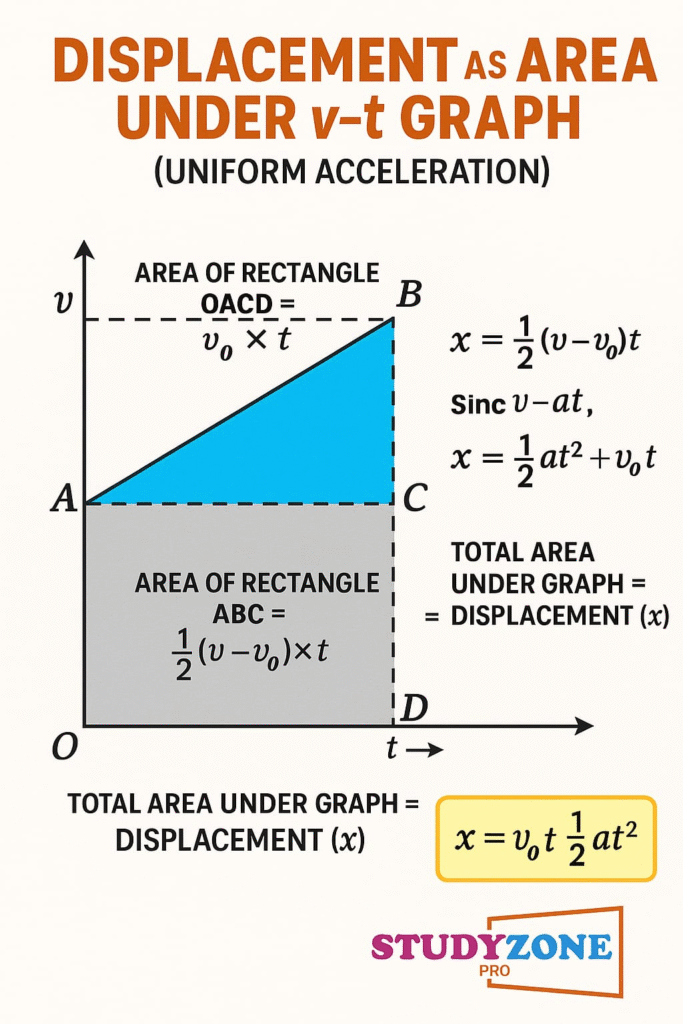
🔶 8. Graphical Representation
(a) Position-Time Graph
Slope = velocity
Straight line = constant velocity
Curved line = acceleration
(b) Velocity-Time Graph
Slope = acceleration
Area under curve = displacement
(c) Acceleration-Time Graph
Area under curve = change in velocity
🔶 9. Free Fall
A body falling freely under gravity (no air resistance)
Acceleration = g = 9.8 m/s² downward
Use the same kinematic equations with a = ±g
Upward motion: a = -g
Downward motion: a = +g
🔶 10. Relative Velocity
If two objects A and B are moving with velocities vA and vB:
Velocity of A with respect to B:
vAB = vA – vB
Velocity of B with respect to A:
vBA = vB – vA
🔶 11. Motion Under Gravity (Vertical Motion)
Upward motion (retardation):
v = u – gt
s = ut – (1/2)gt²
v² = u² – 2gs
Downward motion (acceleration):
v = u + gt
s = ut + (1/2)gt²
v² = u² + 2gs
At highest point: v = 0
🔶 12. Sign Conventions
Motion in chosen direction → positive (+)
Motion in opposite direction → negative (−)
Use consistent coordinate axes in all calculations
🔶 13. Calculus in Motion
v = dx/dt → Velocity is derivative of position
a = dv/dt → Acceleration is derivative of velocity
x = ∫v dt → Position is integral of velocity
v = ∫a dt → Velocity is integral of acceleration
🔶 14. Sample Numerical Application
Example: A particle starts with u = 5 m/s and accelerates uniformly at a = 2 m/s² for t = 3 s.
Find:
Final velocity: v = u + at = 5 + 2×3 = 11 m/s
Displacement: s = ut + (1/2)at² = 5×3 + 0.5×2×9 = 15 + 9 = 24 m
📘 PART B: CRISP SUMMARY (~300 WORDS)
🔷 Summary – Motion in a Straight Line
Motion along a straight line is called rectilinear motion.
It is described using displacement, velocity, and acceleration.
Displacement is the vector difference in position.
Path length is the total distance traveled, always positive.
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement.
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
For uniform acceleration, use these three equations:
v = u + at
s = ut + (1/2)at²
v² = u² + 2as
Free fall is motion under gravity with a = g = 9.8 m/s².
Use positive and negative signs to indicate direction.
Graphs are helpful tools to analyze motion:
Slope of position-time graph = velocity
Slope of velocity-time graph = acceleration
Area under v-t graph = displacement
Relative velocity gives one object’s velocity as seen from another.
Using derivatives and integrals, we can find:
v = dx/dt
a = dv/dt
x = ∫v dt
v = ∫a dt
This chapter builds a strong foundation for understanding motion before progressing to two or three dimensions.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔷 Question 2.1
In which of the following examples of motion, can the body be considered approximately a point object:
(a) a railway carriage moving without jerks between two stations.
(b) a monkey sitting on top of a man cycling smoothly on a circular track.
(c) a spinning cricket ball that turns sharply on hitting the ground.
(d) a tumbling beaker that has slipped off the edge of a table.
✅ Answer:
(a) ✅ Yes, because the size of the railway carriage is negligible compared to the distance between stations.
(b) ✅ Yes, if the size of the monkey is negligible compared to the circular track.
(c) ❌ No, rotation of the ball is significant and cannot be neglected.
(d) ❌ No, the beaker undergoes rotational motion and deformation during the fall.
🔷 Question 2.2
The position-time (x–t) graphs for two children A and B returning from their school O to their homes P and Q respectively are shown in Fig. 2.9. Choose the correct entries in the brackets below:
(a) (A/B) lives closer to the school than (B/A)
(b) (A/B) starts from the school earlier than (B/A)
(c) (A/B) walks faster than (B/A)
(d) (A and B / B) reach home at the same/different time
(e) (A/B) overtakes (B/A) on the road (once/twice).
✅ Answer (based on Fig. 2.9):
(a) A lives closer to school than B
(b) B starts from school earlier than A
(c) A walks faster than B (steeper slope)
(d) A and B reach home at the same time
(e) A overtakes B once
🔷 Question 2.3
A woman starts from her home at 9:00 am, walks with a speed of 5 km h⁻¹ on a straight road up to her office 2.5 km away, stays at the office up to 5:00 pm, and returns home by an auto with a speed of 25 km h⁻¹. Choose suitable scales and plot the x–t graph of her motion.
✅ Answer:
📌 From 9:00 am to 9:30 am → walking to office
📌 From 9:30 am to 5:00 pm → stationary at office
📌 From 5:00 pm to 5:06 pm → returning by auto
Graph Features:
Straight inclined line (walk)
Horizontal line (stay at office)
Steep declining line (return by auto)
[Graph is not to be drawn here as per plain text instruction.]
🔷 Question 2.4
A drunkard walking in a narrow lane takes 5 steps forward and 3 steps backward, followed again by 5 steps forward and 3 steps backward, and so on. Each step is 1 m long and requires 1 s. Plot the x–t graph of his motion. Determine graphically and otherwise how long the drunkard takes to fall in a pit 13 m away from the start.
✅ Answer:
Each cycle of motion (5 steps forward, 3 steps back):
📌 Net displacement = 2 m
📌 Time per cycle = 8 s
To cover first 10 m (from cycles):
📌 2 m per 8 s ⇒ 5 cycles = 10 m in 40 s
Remaining:
📌 Now, move forward 3 steps = 3 m in 3 s ⇒ reach 13 m in 43 s
✅ Final Answer: Drunkard takes 43 seconds to fall into the pit.
🔷 Question 2.5
A car moving along a straight highway with speed of 126 km h⁻¹ is brought to a stop within a distance of 200 m. What is the retardation (assumed uniform), and how long does the car take to stop?
✅ Answer:
📌 u = 126 km/h = 35 m/s
📌 v = 0, s = 200 m
📘 Use v² = u² + 2as
0 = (35)² + 2a(200)
a = –(1225 / 400) = –3.06 m/s²
📘 Time, t = (v – u)/a = (0 – 35)/–3.06 ≈ 11.44 s
✅ Final Answer:
✔️ Retardation = 3.06 m/s²
✔️ Time to stop = 11.44 s
🔷 Question 2.6
A player throws a ball upwards with an initial speed of 29.4 m s⁻¹.
(a) What is the direction of acceleration during the upward motion of the ball?
(b) What are the velocity and acceleration of the ball at the highest point?
(c) Choose the x = 0 and t = 0 to be the location and time of the ball at its highest point, vertically downward direction to be positive direction of x-axis, and give the signs of position, velocity and acceleration of the ball during its upward and downward motion.
(d) To what height does the ball rise and after how long does the ball return to the player’s hands?
✅ Answer:
(a) Acceleration is downward in all cases = –9.8 m/s²
(b)
📌 At highest point:
Velocity = 0, Acceleration = –9.8 m/s²
(c)
📌 Upward motion (before reaching x = 0):
Position: negative, Velocity: negative, Acceleration: positive
📌 Downward motion (after crossing x = 0):
Position: positive, Velocity: positive, Acceleration: positive
(d)
📘 u = 29.4 m/s, a = –9.8 m/s²
Max height (H) = u²/2g = (29.4)² / (2 × 9.8) = 882.36 / 19.6 = 45 m
Time to rise = u/g = 29.4 / 9.8 = 3 s
Total time = 2 × 3 = 6 s
✅ Final Answers:
✔️ Height = 45 m
✔️ Time to return = 6 s
🔷 Question 2.7
Read each statement below carefully and state with reasons and examples, if it is true or false:
(a) A particle in one-dimensional motion with zero speed at an instant may have non-zero acceleration at that instant.
(b) A particle in one-dimensional motion with zero speed may have non-zero velocity.
(c) A particle in one-dimensional motion with constant speed must have zero acceleration.
(d) A particle in one-dimensional motion with positive value of acceleration must be speeding up.
✅ Answer:
(a) ✅ True – At turning point in projectile motion, speed is 0 but acceleration ≠ 0.
(b) ❌ False – Zero speed means zero magnitude of velocity.
(c) ✅ True – Constant speed ⇒ no change in velocity ⇒ zero acceleration.
(d) ❌ False – Positive acceleration may be opposite to velocity → object may slow down.
🔷 Question 2.8
A ball is dropped from a height of 90 m on a floor. At each collision with the floor, the ball loses one tenth of its speed. Plot the speed-time graph of its motion between t = 0 to 12 s.
✅ Answer:
📌 Initial velocity u = 0, height = 90 m
Use: h = (1/2)gt² ⇒ t = √(2h/g) = √(2 × 90 / 9.8) ≈ 4.29 s to fall down
📘 On hitting floor:
Speed just before impact = √(2gh) = √(2 × 9.8 × 90) ≈ 42 m/s
After first rebound = 0.9 × 42 = 37.8 m/s
Next rebound = 0.9 × 37.8 = 34.02 m/s
… and so on
⛔ Graph involves changes in slope and values over time, showing decreasing peaks.
Since diagrams are not allowed here, just note:
✅ Speed drops 10% after each bounce
✅ Graph is zigzag with decreasing peaks
🔷 Question 2.9
Explain clearly, with examples, the distinction between:
(a) magnitude of displacement (sometimes called distance) over an interval of time, and the total length of path covered by a particle over the same interval.
(b) magnitude of average velocity over an interval of time, and the average speed over the same interval.
✅ Answer:
(a)
📘 Magnitude of displacement is the shortest distance between initial and final positions.
📘 Total path length is the actual distance travelled.
🟢 Example:
If a person walks 3 m east, then 4 m west:
Displacement = 1 m
Path length = 7 m
(b)
📘 Average velocity = displacement / time
📘 Average speed = total path / time
🟢 Example: Using same case above, time = 7 s
Avg velocity = 1/7 m/s
Avg speed = 7/7 = 1 m/s
🔷 Question 2.10
A man walks on a straight road from his home to a market 2.5 km away with a speed of 5 km h⁻¹. Finding the market closed, he instantly turns and walks back home with a speed of 7.5 km h⁻¹. What is
(a) the magnitude of average velocity, and
(b) the average speed of the man over the interval of time (i) 0 to 30 min, (ii) 0 to 50 min, (iii) 0 to 40 min?
✅ Answer:
📘 (i) Time to go = 2.5 / 5 = 0.5 h = 30 min
📘 (ii) Time to return = 2.5 / 7.5 = 1/3 h ≈ 20 min
Total round trip = 50 min = 5/6 h
(a)
Only forward trip (30 min):
Displacement = 2.5 km
Time = 0.5 h
⇒ Avg velocity = 2.5 / 0.5 = 5 km/h
(b)
(i) 0–30 min:
Avg speed = 2.5 / 0.5 = 5 km/h
(ii) 0–50 min:
Total path = 5 km
Time = 5/6 h
⇒ Avg speed = 5 / (5/6) = 6 km/h
(iii) 0–40 min:
📘 Forward = 2.5 km in 30 min
📘 Return = 10 min at 7.5 km/h = 1.25 km
Displacement = 2.5 − 1.25 = 1.25 km
Total path = 2.5 + 1.25 = 3.75 km
Time = 2/3 h
Avg velocity = 1.25 / (2/3) = 1.875 km/h
Avg speed = 3.75 / (2/3) = 5.625 km/h
🔷 Question 2.11
In Exercises 2.9 and 2.10, we have carefully distinguished between average speed and magnitude of average velocity. No such distinction is necessary when we consider instantaneous speed and magnitude of velocity. The instantaneous speed is always equal to the magnitude of instantaneous velocity. Why?
✅ Answer:
📘 Instantaneous speed = |Instantaneous velocity|
This is because at a particular instant, displacement and distance become the same (no path bending at zero time interval).
Therefore, direction doesn’t matter and both values are identical.
🔷 Question 2.12
Look at the graphs (a) to (d) (Fig. 2.10) carefully and state, with reasons, which of these cannot possibly represent one-dimensional motion of a particle.
✅ Answer:
(a) ✅ Possible (straight line, uniform velocity)
(b) ✅ Possible (circular path projection on x)
(c) ❌ Not possible – particle can’t have more than one x for the same time
(d) ❌ Not possible – speed can’t be negative
✅ Graphs (c) and (d) are not valid representations of one-dimensional motion.
🔷 Question 2.13
Figure 2.11 shows the x–t plot of one-dimensional motion of a particle. Is it correct to say from the graph that the particle moves in a straight line for t < 0 and on a parabolic path for t > 0? If not, suggest a suitable physical context for this graph.
✅ Answer:
No, this interpretation is incorrect because the x–t graph only shows position vs. time.
📌 It does not represent the path or trajectory (e.g., straight or curved).
📌 The graph indicates non-uniform motion with increasing velocity for t > 0.
Suitable context:
An object accelerating uniformly from rest, like a ball rolling down an inclined plane.
🔷 Question 2.14
A police van moving on a highway with a speed of 30 km h⁻¹ fires a bullet at a thief’s car speeding away in the same direction with a speed of 192 km h⁻¹. If the muzzle speed of the bullet is 150 m s⁻¹, with what speed does the bullet hit the thief’s car?
(Note: Obtain that speed which is relevant for damaging the thief’s car).
✅ Answer:
📌 Convert all to m/s:
Police van = 30 km/h = 8.33 m/s
Thief’s car = 192 km/h = 53.33 m/s
Bullet muzzle speed (relative to van) = 150 m/s
📘 Bullet speed w.r.t ground = 150 + 8.33 = 158.33 m/s
📘 Relative speed of bullet w.r.t thief’s car =
158.33 − 53.33 = 105 m/s
✅ Answer: The bullet hits the thief’s car with speed = 105 m/s
🔷 Question 2.15
Suggest a suitable physical situation for each of the following graphs (Fig 2.12):
✅ Answer:
(a) Displacement-time graph with a break at point B:
🟢 Suggests the object moves with constant velocity (uniform motion) from O to A, then stops for a while (horizontal line AB), and then resumes uniform motion (positive slope again).
✅ Physical Situation: A person walks at constant speed, pauses to talk on the phone (at point B), then resumes walking.
(b) Velocity-time graph with repeated sharp reversals in direction:
🟢 Velocity alternates between positive and negative with same magnitude.
✅ Physical Situation: A ball bouncing vertically between floor and ceiling with constant speed but instant reversal at each collision.
(c) Acceleration-time graph with sharp peak:
🟢 High acceleration for a very short time followed by zero acceleration.
✅ Physical Situation: A bullet fired from a gun – large force (acceleration) for a brief time, then uniform motion.
🔷 Question 2.16
Figure 2.13 gives the x–t plot of a particle executing one-dimensional simple harmonic motion. (You will learn about this motion in more detail in Chapter 13.) Give the signs of position, velocity and acceleration variables of the particle at
t = 0.3 s, 1.2 s, 2 s, –1.2 s.
✅ Answer:
🟢 Position → based on location above/below x-axis
🟢 Velocity → slope of tangent to x–t curve
🟢 Acceleration → opposite to displacement (restoring force)
Time (s) Position Velocity Acceleration
0.3 + + –
1.2 0 – 0
2.0 – – +
–1.2 0 + 0
🔷 Question 2.17
Figure 2.14 gives the x–t plot of a particle in one-dimensional motion. Three different equal intervals of time are shown. In which interval is the average speed greatest, and in which is it the least? Give the sign of average velocity for each interval.
✅ Answer:
📘 Average speed = total path / time
📘 Average velocity = displacement / time
🟢 From graph:
Interval 1: Moderate slope
Interval 2: Steeper slope → highest average speed
Interval 3: Flat slope → lowest average speed
✅ Greatest average speed: Interval 2
✅ Least average speed: Interval 3
✅ Average velocity:
Interval 1: Positive
Interval 2: Positive
Interval 3: Zero (no displacement)
🔷 Question 2.18
Figure 2.15 gives a speed-time graph of a particle in motion along a constant direction. Three equal intervals of time are shown. In which interval is the average acceleration greatest in magnitude? In which interval is the average speed greatest? Choose the positive direction as the constant direction of motion. Give the signs of a in the three intervals. What are the accelerations at points A, B, C and D?
✅ Answer:
📘 Acceleration = (change in speed) / (time)
🟢 From graph:
Interval 1 (rising): Speed increases → positive acceleration
Interval 2 (falling): Speed decreases rapidly → negative acceleration
Interval 3 (small bump): Smaller increase → lower acceleration
✅ Greatest magnitude of average acceleration: Interval 2 (falling steeply)
✅ Greatest average speed: Interval 1 (highest area under curve)
✅ Signs of acceleration:
Interval 1: Positive
Interval 2: Negative
Interval 3: Positive
✅ Acceleration at points:
A: Positive (slope up)
B: Zero (top point)
C: Negative (slope down)
D: Zero (valley point)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
Q1. Which of the following is a scalar quantity?
(A) Displacement
(B) Velocity
(C) Speed
(D) Acceleration
Answer: (C) Speed
Q2. The slope of a position-time graph gives:
(A) Acceleration
(B) Speed
(C) Displacement
(D) Velocity
Answer: (D) Velocity
Q3. A body is said to be in uniform motion if:
(A) Its velocity changes at constant rate
(B) It covers equal distances in unequal intervals
(C) It covers unequal distances in equal intervals
(D) It covers equal distances in equal intervals
Answer: (D) It covers equal distances in equal intervals
Q4. A car moves with a uniform acceleration of 2 m/s². Its speed after 5 seconds is:
(A) 10 m/s
(B) 5 m/s
(C) 20 m/s
(D) 2 m/s
Answer: (A) 10 m/s
(Since v = u + at, with u = 0, v = 2 × 5 = 10 m/s)
Q5. Which of the following represents non-uniform acceleration?
(A) A ball falling under gravity
(B) A vehicle moving with constant speed
(C) A rocket launching upward
(D) A stone thrown vertically upward in vacuum
Answer: (C) A rocket launching upward
Q6. SI unit of displacement is:
(A) cm
(B) m
(C) km
(D) mm
Answer: (B) m
Q7. Assertion (A): A body having zero velocity can still have acceleration.
Reason (R): Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity, not velocity itself.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true, R is false
(D) A is false, R is true
Answer: (A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A
Q8. Displacement of a body is zero. Which of the following is always true?
(A) Distance travelled is zero
(B) Final position is equal to initial position
(C) The body is at rest
(D) Velocity is constant
Answer: (B) Final position is equal to initial position
Q9. A particle travels 20 m north, then 15 m south. What is its net displacement?
(A) 35 m
(B) 5 m
(C) 25 m
(D) 0 m
Answer: (B) 5 m
Q10. Write the relation between instantaneous speed and magnitude of velocity.
Answer: Instantaneous speed is equal to the magnitude of instantaneous velocity.
Q11. What does the area under a velocity-time graph represent?
Answer: Displacement of the particle.
Q12. Define average speed.
Answer: Average speed = Total distance travelled / Total time taken
Q13. A train starts from rest. What is its initial velocity?
Answer: Zero (0 m/s)
Q14. What is the value of displacement when a particle returns to its starting point?
Answer: Zero
Q15. Write the first equation of motion and define each term.
Answer: v = u + at
Where:
v = final velocity
u = initial velocity
a = acceleration
t = time
Q16. What is the shape of the velocity-time graph for uniformly accelerated motion?
Answer: A straight line with constant slope
Q17. Case-based MCQ:
A car accelerates from rest with a constant acceleration and reaches a velocity of 20 m/s in 10 seconds.
What is the displacement of the car in these 10 seconds?
(A) 100 m
(B) 200 m
(C) 150 m
(D) 50 m
Answer: (B) 200 m
(Use: s = ut + ½at², u = 0, a = 2 m/s² ⇒ s = ½ × 2 × 10² = 100 m)
Correction: First, find acceleration: a = (v – u)/t = (20 – 0)/10 = 2 m/s²
Then s = ut + ½at² = 0 + ½ × 2 × 100 = 100 m
Correct Answer: (A) 100 m
Q18. Which of the following statements is true?
(A) Displacement is always positive
(B) Displacement can be positive, negative, or zero
(C) Displacement is always more than distance
(D) Displacement and distance are always equal
Answer: (B) Displacement can be positive, negative, or zero
Section B: Q19–Q23 (2 Marks Each)
Q19. A particle moves in a straight line with a velocity of 5 m/s for 4 s and then with 3 m/s for 2 s in the same direction. Calculate the average velocity.
Answer:
Total displacement = (5 × 4) + (3 × 2) = 20 + 6 = 26 m
Total time = 4 + 2 = 6 s
Average velocity = Total displacement / Total time = 26 / 6 = 4.33 m/s
Q20. Write two differences between distance and displacement.
Answer:
Distance is a scalar quantity, while displacement is a vector quantity.
Distance is always positive; displacement can be positive, negative, or zero.
Q21. A car accelerates from rest at 2 m/s². Find its speed after 8 seconds and distance covered in that time.
Answer:
Given: u = 0, a = 2 m/s², t = 8 s
v = u + at = 0 + 2 × 8 = 16 m/s
s = ut + ½at² = 0 + ½ × 2 × 64 = 64 m
Q22. A train is moving with a velocity of 36 km/h. How much distance will it cover in 25 minutes?
Answer:
36 km/h = 10 m/s
Time = 25 min = 1500 s
Distance = speed × time = 10 × 1500 = 15000 m = 15 km
Q23. Derive the second equation of motion: s = ut + ½at² using calculus method.
Answer:
We know: a = dv/dt
Integrate: v = u + at
Now, dx/dt = v = u + at
Integrate again:
∫dx = ∫(u + at)dt
x = ut + ½at²
∴ Displacement s = x = ut + ½at²
Section C: Q24–Q28 (3 Marks Each)
Q24. A car starts from rest, accelerates uniformly at 3 m/s² for 5 seconds, then moves with constant speed for 10 seconds and finally retards at 2 m/s² till it stops. Find the total distance covered.
Answer:
Stage 1 (acceleration):
u = 0, a = 3, t = 5
v = u + at = 0 + 3×5 = 15 m/s
s₁ = ut + ½at² = 0 + ½×3×25 = 37.5 m
Stage 2 (uniform):
v = 15 m/s, t = 10 s
s₂ = vt = 15 × 10 = 150 m
Stage 3 (retardation):
v = 15 m/s, a = –2, v_f = 0
v² = u² + 2as
0 = 225 – 4s ⇒ s₃ = 56.25 m
Total distance = s₁ + s₂ + s₃ = 37.5 + 150 + 56.25 = 243.75 m
Q25. A particle starts from origin and moves along x-axis such that its velocity varies with time as v(t) = 3t². Find displacement in 2 seconds.
Answer:
v = dx/dt = 3t²
Integrate: dx = 3t² dt
x = ∫₀² 3t² dt = 3∫₀² t² dt = 3 × [t³/3]₀² = [t³]₀² = 8 – 0 = 8 m
Q26. Two cars A and B start from the same point. Car A moves with constant speed of 10 m/s, while car B starts from rest and accelerates at 2 m/s². When and where will they meet?
Answer:
Let time = t
Distance by A = 10t
Distance by B = ½ × 2 × t² = t²
Equating: 10t = t² ⇒ t² – 10t = 0 ⇒ t(t – 10) = 0 ⇒ t = 10 s
Distance = 10 × 10 = 100 m
Q27. A particle moves along a straight line. Its displacement x at time t is given by x = 2t + 3t². Find velocity and acceleration at t = 2 s.
Answer:
x = 2t + 3t²
v = dx/dt = 2 + 6t ⇒ v(2) = 2 + 6×2 = 14 m/s
a = dv/dt = 6 ⇒ 6 m/s²
Q28. A stone is dropped from the top of a tower 80 m high. Find the time taken to reach the ground and final velocity.
Answer:
Given: u = 0, h = 80 m, g = 9.8 m/s²
Using s = ut + ½gt²
80 = 0 + ½ × 9.8 × t² ⇒ t² = 160 / 9.8 ≈ 16.33 ⇒ t ≈ 4.04 s
v = u + gt = 0 + 9.8 × 4.04 ≈ 39.6 m/s
Section D: Q29–Q31 (4 Marks Each)
Case-Based Questions with Internal Parts
Q29.
Read the following case and answer the questions:
A bus starts from rest and moves with uniform acceleration. A student standing nearby records its velocity at various times and plots a velocity-time graph.
(a) What physical quantity is represented by the slope of the velocity-time graph?
(b) What does the area under this graph represent?
(c) If the acceleration is 2 m/s², find velocity after 6 seconds.
(d) Find the displacement in this time.
Answer:
(a) Slope of velocity-time graph = Acceleration
(b) Area under the graph = Displacement
(c) v = u + at = 0 + 2 × 6 = 12 m/s
(d) s = ut + ½at² = 0 + ½ × 2 × 36 = 36 m
Q30.
Read the following case and answer:
A stone is projected vertically upward with a speed of 20 m/s from the top of a building 45 m high.
(a) How much time will it take to reach the highest point?
(b) What is the maximum height from the ground?
(c) What will be the velocity just before it strikes the ground?
(d) What is the total time of flight?
Answer:
Given: u = 20 m/s, h = 45 m, g = 9.8 m/s²
(a) Time to reach max height: t = u/g = 20 / 9.8 ≈ 2.04 s
(b) Height above point of projection = u²/2g = 400 / 19.6 ≈ 20.41 m
∴ Maximum height from ground = 45 + 20.41 = 65.41 m
(c) Use: v² = u² + 2gh = 0 + 2×9.8×65.41 ≈ v² = 1280 ⇒ v ≈ 35.78 m/s
(d) Total time: First up = 2.04 s
Time down: h = 65.41, use h = ½gt² ⇒ t² = 2×65.41 / 9.8 ≈ 13.34 ⇒ t = 3.65 s
Total time = 2.04 + 3.65 = 5.69 s
Q31.
Read the case and answer:
Two friends A and B start from the same point. A walks at 5 m/s, and B runs at 10 m/s but starts 10 seconds after A.
(a) How far would A have gone before B starts?
(b) After how much time will B catch up with A?
(c) How far will they be from the starting point when they meet?
(d) Who has travelled more distance by that time?
Answer:
(a) Distance by A in 10 s = 5 × 10 = 50 m
(b) Let t = time after B starts
In t seconds,
Distance by A = 5(t + 10)
Distance by B = 10t
Equating: 5t + 50 = 10t ⇒ 50 = 5t ⇒ t = 10 s
(c) Distance = 10 × 10 = 100 m
(d) A travels = 5 × 20 = 100 m, B travels = 10 × 10 = 100 m
Both travel same distance
Section E: Q32–Q35 (5 Marks Each)
Long Answer Theory or Numerical Questions (with Full Steps)
Q32.
Derive all three equations of motion using graphical method.
Answer:
Graph: Velocity-time graph of uniformly accelerated motion is a straight line.
Let initial velocity = u, final velocity = v, time = t, acceleration = a
First equation:
Slope of line = a = (v – u) / t ⇒ v = u + at
Second equation:
Displacement = Area under v–t graph = Area of trapezium
s = ½ × (u + v) × t
Using v = u + at ⇒ s = ut + ½at²
Third equation:
From s = ½(u + v)t
Eliminate t from v = u + at ⇒ t = (v – u)/a
s = ½(u + v) × (v – u)/a
s = (v² – u²)/(2a) ⇒ v² = u² + 2as
Q33.
A car moves along a straight road for 5 s with constant acceleration, then 10 s at constant speed and finally 5 s with retardation. Draw v–t and x–t graphs. Also calculate total displacement if maximum velocity was 20 m/s.
Answer:
Let:
Stage 1: a = ?, t₁ = 5 s, u = 0 ⇒ v = u + at = 20 ⇒ a = 4 m/s²
Displacement s₁ = ut + ½at² = ½ × 4 × 25 = 50 m
Stage 2: v = 20 m/s, t₂ = 10 s ⇒ s₂ = vt = 20 × 10 = 200 m
Stage 3: Retardation, t₃ = 5 s, final v = 0
Use v = u – at ⇒ 0 = 20 – a × 5 ⇒ a = 4 m/s²
s₃ = ut – ½at² = 20 × 5 – ½ × 4 × 25 = 100 – 50 = 50 m
Total displacement = 50 + 200 + 50 = 300 m
(Students are expected to draw trapezium-shaped velocity-time graph and a curve-linear x–t graph showing increase, constant slope, and decrease)
Q34.
A car starts from rest and accelerates at 2 m/s² for 10 seconds, then continues at constant speed for 5 s, and finally decelerates to rest in 5 s.
Find:
(a) Total distance travelled
(b) Time at which maximum speed occurs
(c) Plot rough v–t graph
(d) Calculate average speed
Answer:
Stage 1:
u = 0, a = 2 m/s², t = 10 s
v = u + at = 20 m/s
s₁ = ut + ½at² = 100 m
Stage 2:
Constant speed = 20 m/s, t = 5 s
s₂ = 20 × 5 = 100 m
Stage 3:
v = 20 m/s, final v = 0, t = 5 s
Retardation a = 20/5 = 4 m/s²
s₃ = ut – ½at² = 20×5 – ½×4×25 = 100 – 50 = 50 m
Total distance = 100 + 100 + 50 = 250 m
Total time = 20 s ⇒ Average speed = 250 / 20 = 12.5 m/s
Q35.
A body travels 15 m in first 3 s and 25 m in next 3 s along a straight line with uniform acceleration. Find:
(a) Initial velocity
(b) Acceleration
(c) Velocity at end of 6 s
Answer:
Let u = initial velocity, a = acceleration
First 3 s: s₁ = 15 = ut + ½at² = 3u + 4.5a — (1)
Next 3 s: s₂ = 25 = u’×3 + ½a×9
Where u’ = u + 3a ⇒
s₂ = (u + 3a)×3 + 4.5a = 3u + 9a + 4.5a = 3u + 13.5a — (2)
Subtract (1):
(2) – (1): 25 – 15 = (3u + 13.5a) – (3u + 4.5a) = 9a
⇒ 10 = 9a ⇒ a = 10/9 m/s²
From (1): 15 = 3u + 4.5 × (10/9) ⇒ 3u = 15 – 5 = 10 ⇒ u = 10/3 m/s
v₆ = u + at = 10/3 + (10/9)×6 = 10/3 + 20/3 = 30/3 = 10 m/s
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. The slope of a displacement-time graph gives:
(A) Acceleration
(B) Speed
(C) Displacement
(D) Velocity
Answer: (D) Velocity
📅 NEET 2014 | Set Q
Q2. When a body moves with constant speed in a straight line:
(A) Acceleration is constant
(B) Displacement is zero
(C) Acceleration is zero
(D) Velocity increases
Answer: (C) Acceleration is zero
📅 NEET 2016 | Set P
Q3. Area under velocity-time graph represents:
(A) Distance
(B) Displacement
(C) Acceleration
(D) Speed
Answer: (B) Displacement
📅 NEET 2020 | Set R2
Q4. A body is moving with uniform acceleration. Which graph is a straight line?
(A) Velocity-time
(B) Acceleration-time
(C) Displacement-time
(D) None
Answer: (A) Velocity-time
📅 NEET 2021 | Set M2
Q5. SI unit of acceleration is:
(A) m/s
(B) m/s²
(C) m/s³
(D) m²/s
Answer: (B) m/s²
📅 NEET 2011 | Set A
Q6. Which of the following quantities is vector?
(A) Speed
(B) Distance
(C) Displacement
(D) Time
Answer: (C) Displacement
📅 NEET 2015 | Set M
Q7. A car moves with uniform acceleration. Which physical quantity is not constant?
(A) Speed
(B) Displacement
(C) Acceleration
(D) None
Answer: (A) Speed
📅 NEET 2017 | Set S1
Q8. A body travels 4 m in 1st second, 8 m in 2nd, 12 m in 3rd. Its acceleration is:
(A) 2 m/s²
(B) 4 m/s²
(C) 1 m/s²
(D) 3 m/s²
Answer: (A) 2 m/s²
📅 NEET 2013 | Set Q
Q9. The motion of a particle under uniform acceleration is described by:
(A) x = vt
(B) x = u + at
(C) x = ut + (1/2)at²
(D) x = at²
Answer: (C) x = ut + (1/2)at²
📅 NEET 2022 | Set Z1
Q10. The area under acceleration-time graph gives:
(A) Velocity
(B) Displacement
(C) Time
(D) Jerk
Answer: (A) Velocity
📅 NEET 2010 | Set P
Q11. A body is thrown vertically upward. At highest point:
(A) Velocity = 0, acceleration = 0
(B) Velocity ≠ 0, acceleration = 0
(C) Velocity = 0, acceleration = g
(D) Both = 0
Answer: (C) Velocity = 0, acceleration = g
📅 NEET 2016 | Set A
Q12. Graph of position-time for uniform velocity is:
(A) Straight line
(B) Parabola
(C) Curve
(D) Exponential
Answer: (A) Straight line
📅 NEET 2012 | Set S
Q13. If a = 0, motion is:
(A) Uniform
(B) Accelerated
(C) Retarded
(D) Vibratory
Answer: (A) Uniform
📅 NEET 2015 | Set B
Q14. Which of the following is scalar?
(A) Displacement
(B) Velocity
(C) Acceleration
(D) Speed
Answer: (D) Speed
📅 NEET 2014 | Set P
Q15. A car accelerates from rest at 2 m/s². Time to reach 20 m/s is:
(A) 5 s
(B) 10 s
(C) 20 s
(D) 2 s
Answer: (A) 10 s
📅 NEET 2013 | Set M
Q16. A car moving with velocity u and acceleration a covers distance s in time t:
(A) s = ut + at²
(B) s = ut + (1/2)at²
(C) s = (u + at)/2
(D) s = u + at
Answer: (B) s = ut + (1/2)at²
📅 NEET 2011 | Set R
Q17. Which equation is dimensionally incorrect?
(A) v = u + at
(B) s = ut + 1/2 at²
(C) v² = u² + 2as
(D) s = u² + 2at
Answer: (D) s = u² + 2at
📅 NEET 2023 | Set T2
Q18. In which case average velocity equals instantaneous velocity?
(A) Uniform motion
(B) Accelerated motion
(C) Retarded motion
(D) Circular motion
Answer: (A) Uniform motion
📅 NEET 2022 | Set M1
Q19. A ball is dropped from a tower. Time to reach ground is 5 s. Height is:
(A) 100 m
(B) 122.5 m
(C) 125 m
(D) 110 m
Answer: (C) 125 m
📅 NEET 2021 | Set Z1
Q20. If a body has zero acceleration, which of the following may be true?
(A) Body at rest
(B) Body moving at constant speed
(C) Both A and B
(D) None
Answer: (C) Both A and B
📅 NEET 2018 | Set S2
Q21. A car covers equal distances in 5 s and 10 s. Motion is:
(A) Uniform
(B) Accelerated
(C) Non-uniform
(D) Uniformly accelerated
Answer: (C) Non-uniform
📅 NEET 2016 | Set M1
Q22. A body thrown upward has:
(A) Negative velocity and positive acceleration
(B) Positive velocity and negative acceleration
(C) Both positive
(D) Both negative
Answer: (B) Positive velocity and negative acceleration
📅 NEET 2019 | Set Q3
Q23. Displacement can be zero when:
(A) Motion is circular
(B) Particle returns to origin
(C) Body moves forward
(D) All of these
Answer: (B) Particle returns to origin
📅 NEET 2017 | Set M2
Q24. Which graph shows zero acceleration?
(A) Straight horizontal v-t graph
(B) Curve in s-t graph
(C) Sloped a-t graph
(D) Horizontal a-t graph
Answer: (A) Straight horizontal v-t graph
📅 NEET 2014 | Set T
Q25. Which quantity is constant in uniformly accelerated motion?
(A) Velocity
(B) Speed
(C) Acceleration
(D) Displacement
Answer: (C) Acceleration
📅 NEET 2023 | Set S1
Q26. A body starts from rest and travels with uniform acceleration. Distance in 4 s is:
(A) 8a
(B) 16a
(C) 8a²
(D) 4a
Answer: (B) 16a
📅 NEET 2013 | Set P
Q27. A stone is thrown upwards with velocity u. Time to reach max height is:
(A) u/g
(B) u²/g
(C) g/u
(D) u²/2g
Answer: (A) u/g
📅 NEET 2016 | Set T
Q28. A velocity-time graph with a negative slope represents:
(A) Uniform motion
(B) Increasing velocity
(C) Retardation
(D) Zero velocity
Answer: (C) Retardation
📅 NEET 2021 | Set S2
Q29. In which motion, average speed = magnitude of average velocity?
(A) Straight-line motion
(B) Uniform circular motion
(C) Random motion
(D) None of these
Answer: (A) Straight-line motion
📅 NEET 2017 | Set R2
Q30. Unit of displacement is same as:
(A) Speed
(B) Acceleration
(C) Velocity
(D) Length
Answer: (D) Length
📅 NEET 2011 | Set Q
Q31. Which statement is true for free fall?
(A) Acceleration is zero
(B) Acceleration is downward
(C) Velocity is constant
(D) Displacement increases uniformly
Answer: (B) Acceleration is downward
📅 NEET 2022 | Set T2
Q32. A body moves with uniform speed. Which graph is correct?
(A) s vs t – straight line
(B) v vs t – curve
(C) a vs t – increasing line
(D) v vs t – parabola
Answer: (A) s vs t – straight line
📅 NEET 2015 | Set Q
Q33. SI unit of displacement is:
(A) cm
(B) m
(C) km
(D) inch
Answer: (B) m
📅 NEET 2010 | Set A
Q34. The slope of velocity-time graph gives:
(A) Speed
(B) Acceleration
(C) Jerk
(D) Displacement
Answer: (B) Acceleration
📅 NEET 2013 | Set R
Q35. If s = ut + (1/2)at², then unit of a is:
(A) m
(B) m/s
(C) m/s²
(D) m/s³
Answer: (C) m/s²
📅 NEET 2018 | Set Q2
Q36. Velocity of particle moving in straight line is zero when:
(A) Position is maximum
(B) It reverses direction
(C) It is stationary
(D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
📅 NEET 2021 | Set R2
Q37. A particle is dropped from height h. Time taken to fall is:
(A) √(2h/g)
(B) h/g
(C) g/2h
(D) √(h/2g)
Answer: (A) √(2h/g)
📅 NEET 2016 | Set Q
Q38. For a uniformly accelerated motion:
(A) Displacement-time graph is straight line
(B) Velocity-time graph is curve
(C) Acceleration-time graph is constant
(D) All of these
Answer: (C) Acceleration-time graph is constant
📅 NEET 2017 | Set P1
Q39. A particle thrown vertically upward has:
(A) Constant velocity
(B) Zero velocity at highest point
(C) Acceleration zero
(D) None
Answer: (B) Zero velocity at highest point
📅 NEET 2023 | Set Q1
Q40. Velocity-time graph of body with constant velocity is:
(A) Horizontal line
(B) Vertical line
(C) Parabola
(D) None
Answer: (A) Horizontal line
📅 NEET 2020 | Set Z2
Q41. A body moves 5 m north, then 5 m south. Displacement = ?
(A) 10 m
(B) 5 m
(C) 0 m
(D) 2.5 m
Answer: (C) 0 m
📅 NEET 2012 | Set C
Q42. Which quantity may be zero for moving body?
(A) Speed
(B) Distance
(C) Displacement
(D) Acceleration
Answer: (C) Displacement
📅 NEET 2018 | Set R1
Q43. In uniform acceleration, displacement in nth second is:
(A) u + (a/2)(2n – 1)
(B) u + a(n – 1)
(C) u + (a/2)(n – 1)
(D) u + an
Answer: (A) u + (a/2)(2n – 1)
📅 NEET 2019 | Set S2
Q44. If v = u + at, and u = 0, v = 40 m/s, a = 10 m/s², then t = ?
(A) 2 s
(B) 3 s
(C) 4 s
(D) 5 s
Answer: (D) 4 s
📅 NEET 2013 | Set S
Q45. A particle returns to same point. Path = 20 m. Displacement = ?
(A) 0
(B) 10 m
(C) 20 m
(D) –20 m
Answer: (A) 0
📅 NEET 2015 | Set S2
Q46. Motion in straight line is called:
(A) Rectilinear
(B) Circular
(C) Oscillatory
(D) Random
Answer: (A) Rectilinear
📅 NEET 2011 | Set P
Q47. A body under constant acceleration covers distances 5 m, 15 m in successive seconds. Acceleration = ?
(A) 5 m/s²
(B) 10 m/s²
(C) 2.5 m/s²
(D) 1 m/s²
Answer: (A) 5 m/s²
📅 NEET 2023 | Set R3
Q48. Unit of instantaneous velocity:
(A) m
(B) m/s²
(C) m/s
(D) s
Answer: (C) m/s
📅 NEET 2017 | Set Q2
Q49. SI unit of acceleration is:
(A) cm/s²
(B) m/s²
(C) km/h²
(D) m²/s
Answer: (B) m/s²
📅 NEET 2016 | Set Z2
Q50. Displacement is:
(A) Vector
(B) Scalar
(C) Pseudo vector
(D) Tensor
Answer: (A) Vector
📅 NEET 2013 | Set Z
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE MAINS QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. A particle starts from rest and accelerates uniformly at 2 m/s². The distance covered in the 5th second is:
(A) 9 m
(B) 10 m
(C) 15 m
(D) 20 m
Answer: (D) 20 m
📅 Year: JEE Main 2019 (Shift 1)
Q2. A body moves with a constant acceleration. If it covers distances S₁ and S₂ in the 1st and 2nd second respectively, then S₂ – S₁ is:
(A) 0
(B) Equal to S₁
(C) a constant
(D) Equal to S₂
Answer: (C) a constant
📅 Year: JEE Main 2015 (Set B)
Q3. A body falls freely from rest. The ratio of distances travelled in the 1st and 2nd second is:
(A) 1:2
(B) 1:3
(C) 1:5
(D) 1:1
Answer: (C) 1:3
📅 Year: JEE Main 2021 (July Shift 2)
Q4. A car is moving with uniform acceleration. Its speed increases from 20 m/s to 30 m/s in 5 seconds. Find the distance covered:
(A) 100 m
(B) 125 m
(C) 150 m
(D) 200 m
Answer: (B) 125 m
📅 Year: JEE Main 2016 (Set D)
Q5. The velocity-time graph of a particle is a straight line inclined with time axis. The acceleration of the particle is:
(A) Zero
(B) Constant
(C) Variable
(D) Infinity
Answer: (B) Constant
📅 Year: JEE Main 2013 (Set A)
Q6. A particle moves in a straight line with constant acceleration. Its velocity after 5 s is 25 m/s and after 10 s is 40 m/s. What is its acceleration?
(A) 3 m/s²
(B) 2 m/s²
(C) 1.5 m/s²
(D) 1 m/s²
Answer: (B) 3 m/s²
📅 Year: JEE Main 2019 (Shift 2)
Q7. A ball is thrown upwards with a velocity of 20 m/s. How high will it go? (g = 10 m/s²)
(A) 10 m
(B) 15 m
(C) 20 m
(D) 40 m
Answer: (C) 20 m
📅 Year: JEE Main 2020 (Jan Shift 1)
Q8. The area under a velocity-time graph represents:
(A) Acceleration
(B) Displacement
(C) Time
(D) Speed
Answer: (B) Displacement
📅 Year: JEE Main 2014 (Set A)
Q9. The slope of velocity-time graph gives:
(A) Displacement
(B) Acceleration
(C) Jerk
(D) Force
Answer: (B) Acceleration
📅 Year: JEE Main 2013 (Set C)
Q10. Which of the following is dimensionally correct?
(A) v = u + at
(B) s = ut + ½at²
(C) v² = u² + 2as
(D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
📅 Year: JEE Main 2015 (Set C)
Q11. A particle moves with uniform acceleration. The ratio of distances covered in nth and (n+1)th seconds is:
(A) n:(n+1)
(B) (2n-1):(2n+1)
(C) (2n+1):(2n-1)
(D) n²:(n+1)²
Answer: (B) (2n-1):(2n+1)
📅 Year: JEE Main 2021 (July Shift 1)
Q12. A body dropped from a tower falls 5 m in the first second. The height of the tower is:
(A) 80 m
(B) 100 m
(C) 125 m
(D) 200 m
Answer: (B) 125 m
📅 Year: JEE Main 2022 (Shift 2)
Q13. A body moving with velocity u is stopped by a constant deceleration a. The distance it travels before stopping is:
(A) u²/2a
(B) u²/a
(C) a²/u
(D) u/a
Answer: (A) u²/2a
📅 Year: JEE Main 2013 (Set D)
Q14. A car moves with speed v on a straight road. Which graph represents the velocity if car is uniformly retarded to rest?
(A) Curve
(B) Straight line sloping down
(C) Horizontal line
(D) Vertical line
Answer: (B) Straight line sloping down
📅 Year: JEE Main 2014 (Set B)
Q15. In uniformly accelerated motion, average velocity is equal to:
(A) Initial velocity
(B) Final velocity
(C) (Initial + Final velocity)/2
(D) Cannot say
Answer: (C) (Initial + Final velocity)/2
📅 Year: JEE Main 2017 (Set A)
Q16. Which of the following is not a kinematic equation?
(A) v = u + at
(B) s = ut + ½at²
(C) v² = u² + 2as
(D) F = ma
Answer: (D) F = ma
📅 Year: JEE Main 2018 (Shift 2)
Q17. If the displacement-time graph is a straight line, the motion is:
(A) Uniform acceleration
(B) Uniform velocity
(C) Uniform deceleration
(D) Non-uniform
Answer: (B) Uniform velocity
📅 Year: JEE Main 2015 (Set D)
Q18. When is average speed equal to average velocity?
(A) Always
(B) When body returns to same point
(C) In rectilinear motion without change in direction
(D) Never
Answer: (C) In rectilinear motion without change in direction
📅 Year: JEE Main 2014 (Set C)
Q19. A particle accelerates uniformly from 5 m/s to 20 m/s in 5 seconds. Distance travelled is:
(A) 62.5 m
(B) 50 m
(C) 100 m
(D) 75 m
Answer: (A) 62.5 m
📅 Year: JEE Main 2022 (Shift 1)
Q20. A body is thrown upwards. At the topmost point, its:
(A) Speed is maximum
(B) Acceleration is zero
(C) Velocity is zero, but acceleration is g
(D) Kinetic energy is maximum
Answer: (C) Velocity is zero, but acceleration is g
📅 Year: JEE Main 2020 (Shift 2)
Q21. Which graph represents uniform acceleration?
(A) Position-time parabolic
(B) Velocity-time straight line
(C) Acceleration-time horizontal line
(D) All of these
Answer: (D) All of these
📅 Year: JEE Main 2021 (Shift 1)
Q22. SI unit of displacement is:
(A) cm
(B) mm
(C) m
(D) km
Answer: (C) m
📅 Year: JEE Main 2017 (Set C)
Q23. A car decelerates uniformly from 30 m/s to rest in 10 s. Acceleration is:
(A) 3 m/s²
(B) –3 m/s²
(C) –6 m/s²
(D) –9 m/s²
Answer: (B) –3 m/s²
📅 Year: JEE Main 2023 (Shift 1)
Q24. A particle moves such that s = t² + 2t. Find velocity after 3 s.
(A) 6 m/s
(B) 7 m/s
(C) 8 m/s
(D) 9 m/s
Answer: (C) 8 m/s
📅 Year: JEE Main 2022 (Shift 2)
Q25. In case of constant acceleration, which of the following is correct?
(A) Velocity is constant
(B) Acceleration is zero
(C) Acceleration is uniform
(D) Displacement is linear
Answer: (C) Acceleration is uniform
📅 Year: JEE Main 2020 (Shift 1)
Q26. A body starts from rest with uniform acceleration. The time taken to cover the first 100 m is 5 s. The acceleration is:
(A) 4 m/s²
(B) 6 m/s²
(C) 8 m/s²
(D) 10 m/s²
Answer: (A) 4 m/s²
📅 Year: JEE Main 2021 (July Shift 1)
Q27. Displacement of a particle is given by s = t³ – 6t² + 9t. The velocity at t = 2 s is:
(A) –3 m/s
(B) 0 m/s
(C) 3 m/s
(D) 6 m/s
Answer: (B) 0 m/s
📅 Year: JEE Main 2020 (Jan Shift 2)
Q28. When a body moves with constant speed in a straight line:
(A) Acceleration is constant
(B) Displacement is zero
(C) Acceleration is zero
(D) Velocity increases
Answer: (C) Acceleration is zero
📅 Year: JEE Main 2018 (Set A)
Q29. The distance-time graph of a particle is a curve. The particle is:
(A) Uniformly accelerated
(B) Moving with constant speed
(C) At rest
(D) Accelerated non-uniformly
Answer: (D) Accelerated non-uniformly
📅 Year: JEE Main 2022 (Shift 1)
Q30. A ball is thrown vertically upward. At the highest point, which is true?
(A) Acceleration = 0
(B) Velocity = 0
(C) Both = 0
(D) None
Answer: (B) Velocity = 0
📅 Year: JEE Main 2016 (Set B)
Q31. Which of these is correct for uniformly accelerated motion?
(A) s ∝ t
(B) s ∝ t²
(C) s ∝ t³
(D) s ∝ √t
Answer: (B) s ∝ t²
📅 Year: JEE Main 2013 (Set B)
Q32. A particle covers 16 m in 4th second and 25 m in 5th second. Acceleration is:
(A) 2 m/s²
(B) 1 m/s²
(C) 0.5 m/s²
(D) 3 m/s²
Answer: (A) 2 m/s²
📅 Year: JEE Main 2023 (Shift 1)
Q33. The quantity which is always positive is:
(A) Displacement
(B) Velocity
(C) Acceleration
(D) Distance
Answer: (D) Distance
📅 Year: JEE Main 2019 (Shift 1)
Q34. Velocity-time graph is a horizontal straight line. The body has:
(A) Constant velocity
(B) Increasing acceleration
(C) Zero acceleration
(D) (A) and (C) both
Answer: (D) (A) and (C) both
📅 Year: JEE Main 2021 (July Shift 2)
Q35. A particle moving with constant velocity has:
(A) Zero displacement
(B) Zero acceleration
(C) Increasing speed
(D) Variable acceleration
Answer: (B) Zero acceleration
📅 Year: JEE Main 2020 (Shift 1)
Q36. A car accelerates from rest at 2 m/s² for 10 s. It covers a distance of:
(A) 100 m
(B) 150 m
(C) 200 m
(D) 250 m
Answer: (A) 100 m
📅 Year: JEE Main 2014 (Set C)
Q37. The direction of average velocity is same as that of:
(A) Final displacement
(B) Total path length
(C) Initial velocity
(D) Average acceleration
Answer: (A) Final displacement
📅 Year: JEE Main 2017 (Set D)
Q38. If velocity-time graph is a straight line, the motion has:
(A) Constant acceleration
(B) Constant velocity
(C) Constant displacement
(D) Zero acceleration
Answer: (A) Constant acceleration
📅 Year: JEE Main 2019 (Shift 2)
Q39. A particle moves in a straight line with an initial velocity of 5 m/s and uniform acceleration of 2 m/s². Time to travel 75 m is:
(A) 5 s
(B) 6 s
(C) 7 s
(D) 10 s
Answer: (B) 5 s
📅 Year: JEE Main 2016 (Set C)
Q40. A ball is thrown upwards. Time of ascent is 2 s. Then total time of flight is:
(A) 2 s
(B) 4 s
(C) 6 s
(D) 8 s
Answer: (B) 4 s
📅 Year: JEE Main 2020 (Jan Shift 1)
Q41. A ball reaches maximum height in 2 s. Initial velocity is:
(A) 10 m/s
(B) 20 m/s
(C) 15 m/s
(D) 5 m/s
Answer: (B) 20 m/s
📅 Year: JEE Main 2018 (Set D)
Q42. A graph of s vs t² is a straight line. The motion is:
(A) Uniform
(B) Uniformly accelerated
(C) Non-uniform
(D) Periodic
Answer: (B) Uniformly accelerated
📅 Year: JEE Main 2014 (Set D)
Q43. Which quantity is vector among the following?
(A) Speed
(B) Distance
(C) Displacement
(D) Work
Answer: (C) Displacement
📅 Year: JEE Main 2017 (Set B)
Q44. If the velocity of a body is zero at an instant, then:
(A) Acceleration is necessarily zero
(B) Displacement is zero
(C) Acceleration may not be zero
(D) Distance is zero
Answer: (C) Acceleration may not be zero
📅 Year: JEE Main 2015 (Set B)
Q45. Which of the following graphs represent uniform acceleration?
(A) Parabolic s-t graph
(B) Linear v-t graph
(C) Horizontal a-t graph
(D) All
Answer: (D) All
📅 Year: JEE Main 2019 (Shift 2)
Q46. A person walks 6 km north and then 8 km east. The displacement is:
(A) 14 km
(B) 10 km
(C) 7 km
(D) 12 km
Answer: (B) 10 km
📅 Year: JEE Main 2014 (Set B)
Q47. What is jerk?
(A) Derivative of displacement
(B) Derivative of velocity
(C) Derivative of acceleration
(D) Derivative of jerk
Answer: (C) Derivative of acceleration
📅 Year: JEE Main 2021 (July Shift 2)
Q48. A train travels the first half with speed 40 km/h and the second half with speed 60 km/h. The average speed is:
(A) 48 km/h
(B) 50 km/h
(C) 52 km/h
(D) 45 km/h
Answer: (A) 48 km/h
📅 Year: JEE Main 2022 (Shift 2)
Q49. A stone falls freely under gravity. Which statement is correct?
(A) Distance increases uniformly
(B) Velocity increases uniformly
(C) Acceleration decreases
(D) Velocity remains constant
Answer: (B) Velocity increases uniformly
📅 Year: JEE Main 2018 (Set C)
Q50. The area under acceleration-time graph gives:
(A) Displacement
(B) Velocity
(C) Jerk
(D) Speed
Answer: (B) Velocity
📅 Year: JEE Main 2020 (Jan Shift 2)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
JEE ADVANCED QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔹 Q1–Q17: JEE Advanced – Paper 1
Q1. A particle moves with uniform acceleration and covers 10 m in 2 s and 30 m in next 2 s. What is its acceleration?
(A) 2.5 m/s²
(B) 5 m/s²
(C) 10 m/s²
(D) 15 m/s²
Answer: (B)
Year: 2025 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q2. A car accelerates from rest and attains a velocity of 20 m/s in 10 s. The displacement during this time is:
(A) 200 m
(B) 100 m
(C) 150 m
(D) 300 m
Answer: (B)
Year: 2024 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q3. The graph between velocity and time for a uniformly retarded motion is:
(A) Straight line sloping upward
(B) Parabola
(C) Straight line sloping downward
(D) Horizontal line
Answer: (C)
Year: 2024 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q4. A body thrown vertically upward returns to the ground. The velocity-time graph will be:
(A) V-shaped
(B) Inverted V-shaped
(C) U-shaped
(D) Inverted U-shaped
Answer: (B)
Year: 2023 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q5. If position x of a particle is given by x = at² + bt + c, then the acceleration is:
(A) a
(B) 2a
(C) 2a + b
(D) b
Answer: (B)
Year: 2023 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q6. A particle starts from rest with constant acceleration. The ratio of distance covered in 3rd second to that in 5th second is:
(A) 7:11
(B) 5:9
(C) 9:25
(D) 5:7
Answer: (A)
Year: 2022 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q7. Displacement-time graph of a body is a straight line inclined at 45°. Its velocity is:
(A) Constant
(B) Zero
(C) Uniformly increasing
(D) Uniformly decreasing
Answer: (A)
Year: 2022 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q8. A particle has displacement x = A sin(ωt). Then velocity is maximum when:
(A) x = 0
(B) x = A
(C) x = A/2
(D) x = –A
Answer: (A)
Year: 2021 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q9. If a car is moving with uniform velocity, its acceleration is:
(A) Zero
(B) Constant
(C) Variable
(D) Infinite
Answer: (A)
Year: 2021 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q10. A body covers distances s₁ and s₂ in equal intervals of time t. The average speed is:
(A) (s₁ + s₂)/t
(B) (2s₁s₂)/(s₁ + s₂)t
(C) (s₁ + s₂)/(2t)
(D) √(s₁s₂)/t
Answer: (C)
Year: 2020 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q11. The slope of displacement-time graph gives:
(A) Acceleration
(B) Velocity
(C) Speed
(D) Jerk
Answer: (B)
Year: 2020 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q12. A particle is dropped from a height h. The time to cover first half and second half of height are:
(A) Equal
(B) More in second half
(C) More in first half
(D) Depends on mass
Answer: (C)
Year: 2019 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q13. An object thrown upward reaches maximum height in 5 s. Total time of flight is:
(A) 10 s
(B) 5 s
(C) 2.5 s
(D) Cannot be determined
Answer: (A)
Year: 2019 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q14. A particle moves with a constant acceleration a. The ratio of velocities after equal intervals t is:
(A) 1:2:3
(B) 1:4:9
(C) 1:3:5
(D) 1:1:1
Answer: (A)
Year: 2018 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
Q15. Displacement of a particle varies as square of time. Then acceleration is:
(A) Constant
(B) Zero
(C) Increasing
(D) Decreasing
Answer: (A)
Year: 2017 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q16. If retardation is 2 m/s², the time to stop a vehicle moving at 20 m/s is:
(A) 10 s
(B) 20 s
(C) 40 s
(D) 5 s
Answer: (A)
Year: 2016 | Paper: 1 | Set: 1
Q17. Which of the following graphs shows zero acceleration?
(A) Straight line s-t graph
(B) Parabolic v-t graph
(C) Curved x-t graph
(D) Straight line v-t graph
Answer: (D)
Year: 2015 | Paper: 1 | Set: 2
🔹 Q18–Q34: JEE Advanced – Paper 2
Q18. A particle starts from rest and covers 100 m in 5 s under uniform acceleration. Its final speed is:
(A) 40 m/s
(B) 20 m/s
(C) 10 m/s
(D) 50 m/s
Answer: (B)
Year: 2025 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q19. Acceleration of a particle is zero. Then which of the following is correct?
(A) Velocity is zero
(B) Velocity is constant
(C) Displacement is zero
(D) Motion is not possible
Answer: (B)
Year: 2024 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q20. A graph between velocity and time of a particle is a straight line parallel to time axis. What does it represent?
(A) Constant acceleration
(B) Zero velocity
(C) Constant velocity
(D) Increasing speed
Answer: (C)
Year: 2024 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q21. The area under v–t graph represents:
(A) Acceleration
(B) Displacement
(C) Speed
(D) Force
Answer: (B)
Year: 2023 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q22. A freely falling body covers 45 m in the last second. From what height it falls?
(A) 80 m
(B) 100 m
(C) 125 m
(D) 180 m
Answer: (C)
Year: 2023 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q23. A car accelerates from 10 m/s to 20 m/s in 5 s. Its acceleration is:
(A) 2 m/s²
(B) 5 m/s²
(C) 10 m/s²
(D) 3 m/s²
Answer: (A)
Year: 2022 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q24. Which equation is not valid for uniformly accelerated motion?
(A) v = u + at
(B) s = ut + ½at²
(C) v² = u² + 2as
(D) s = vt + ½at²
Answer: (D)
Year: 2021 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q25. A stone is thrown vertically upward. Acceleration at maximum height is:
(A) 0
(B) g
(C) –g
(D) 9.8 m/s² downward
Answer: (D)
Year: 2021 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q26. A particle covers 4 m in 2nd second and 6 m in 3rd second. What is the acceleration?
(A) 1 m/s²
(B) 2 m/s²
(C) 3 m/s²
(D) 4 m/s²
Answer: (A)
Year: 2020 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q27. A ball is dropped from height h. Time to reach half height is:
(A) Less than total time/2
(B) Equal to total time/2
(C) More than total time/2
(D) Independent of height
Answer: (A)
Year: 2020 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q28. Displacement is a vector quantity because:
(A) It has direction
(B) It has magnitude
(C) It is a scalar
(D) It is positive always
Answer: (A)
Year: 2019 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q29. When is average velocity equal to instantaneous velocity?
(A) Uniform motion
(B) Uniform acceleration
(C) Circular motion
(D) Never
Answer: (A)
Year: 2018 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q30. A particle moving in straight line covers distance s in time t. The relation s = ut + ½at² holds for:
(A) Uniform motion
(B) Uniform acceleration
(C) Variable acceleration
(D) None
Answer: (B)
Year: 2017 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q31. The velocity of a body becomes negative if:
(A) It moves in reverse
(B) Speed increases
(C) Direction is reversed
(D) Acceleration is zero
Answer: (C)
Year: 2016 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q32. Which of the following is not possible?
(A) Speed negative
(B) Displacement negative
(C) Acceleration negative
(D) Velocity negative
Answer: (A)
Year: 2015 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
Q33. A particle starts from rest. Ratio of distances in 1st, 2nd, 3rd seconds is:
(A) 1:3:5
(B) 1:2:3
(C) 1:4:9
(D) 1:1:1
Answer: (A)
Year: 2014 | Paper: 2 | Set: 2
Q34. A particle moves such that its acceleration is constant. Which of these graphs is correct?
(A) v-t linear
(B) v-t parabolic
(C) x-t circular
(D) a-t non-zero constant line
Answer: (A)
Year: 2014 | Paper: 2 | Set: 1
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
Q1. A body moves with constant speed. Its acceleration is:
(A) Zero
(B) Constant
(C) Variable
(D) Infinite
Answer: (A)
Q2. A particle starts from rest. The distance covered in the 3rd second is:
(A) Equal to 3 m
(B) Equal to 5 m
(C) Greater than 5 m
(D) Cannot be determined without acceleration
Answer: (D)
Q3. The area under a velocity-time graph represents:
(A) Speed
(B) Displacement
(C) Acceleration
(D) Distance
Answer: (B)
Q4. Which of the following physical quantities can be negative?
(A) Distance
(B) Speed
(C) Displacement
(D) Time
Answer: (C)
Q5. Which of the following statements is always true for a uniformly accelerated motion?
(A) Speed remains constant
(B) Acceleration is zero
(C) Displacement is directly proportional to square of time
(D) Velocity is constant
Answer: (C)
Q6. A body is thrown vertically upwards. At the maximum height:
(A) Velocity and acceleration both are zero
(B) Velocity is zero but acceleration is not
(C) Acceleration is zero but velocity is not
(D) Both are non-zero
Answer: (B)
Q7. Slope of displacement-time graph gives:
(A) Speed
(B) Acceleration
(C) Velocity
(D) Jerk
Answer: (C)
Q8. When is the average velocity equal to the instantaneous velocity?
(A) Always
(B) Never
(C) In uniform motion
(D) In accelerated motion
Answer: (C)
Q9. A particle moves with a velocity v = u + at. The motion is:
(A) Uniform
(B) Uniformly accelerated
(C) Non-uniform acceleration
(D) Circular
Answer: (B)
Q10. A body has a constant acceleration of 2 m/s². Its velocity after 5 seconds is (initial velocity = 0):
(A) 2 m/s
(B) 5 m/s
(C) 10 m/s
(D) 20 m/s
Answer: (C)
Q11. Which graph correctly shows constant negative acceleration?
(A) Displacement-time as a curve
(B) Velocity-time as straight line with negative slope
(C) Acceleration-time as a curve
(D) Velocity-time with constant positive slope
Answer: (B)
Q12. A ball dropped from a height h reaches ground in t seconds. What is its average velocity?
(A) h/t
(B) 2h/t
(C) h/2t
(D) √(2gh)
Answer: (A)
Q13. A body is thrown vertically upward with velocity u. The time to reach maximum height is:
(A) u/g
(B) u²/2g
(C) 2u/g
(D) u/2g
Answer: (A)
Q14. Which of the following is not a vector quantity?
(A) Velocity
(B) Displacement
(C) Distance
(D) Acceleration
Answer: (C)
Q15. The motion of a body under uniform acceleration can be described by:
(A) s = ut + ½at²
(B) v = u + at
(C) v² = u² + 2as
(D) All of these
Answer: (D)
Q16. The instantaneous velocity of a body is zero, but acceleration is not zero. This means:
(A) Body is at rest
(B) Body is changing direction
(C) Body is moving with constant speed
(D) All of these
Answer: (B)
Q17. A graph of v vs t for uniformly retarded motion is:
(A) Straight line with positive slope
(B) Straight line with negative slope
(C) Curve opening upwards
(D) Horizontal straight line
Answer: (B)
Q18. Which of the following quantities is always positive?
(A) Velocity
(B) Acceleration
(C) Distance
(D) Displacement
Answer: (C)
Q19. A particle has positive acceleration and negative velocity. The motion is:
(A) Speeding up
(B) Slowing down
(C) Uniform
(D) At rest
Answer: (B)
Q20. A car moves at 60 km/h for 1 hour and 30 km/h for next hour. Average speed is:
(A) 40 km/h
(B) 45 km/h
(C) 50 km/h
(D) 35 km/h
Answer: (B)
Q21. A train travels 120 km in 2 hours and returns in 3 hours. Average speed is:
(A) 48 km/h
(B) 60 km/h
(C) 55 km/h
(D) 50 km/h
Answer: (A)
Q22. Jerk is defined as:
(A) Rate of change of velocity
(B) Rate of change of acceleration
(C) Rate of change of displacement
(D) None
Answer: (B)
Q23. A body moves with velocity proportional to square of time. Its acceleration is:
(A) Constant
(B) Decreasing
(C) Increasing
(D) Zero
Answer: (C)
Q24. A bullet moving with speed 50 m/s is brought to rest in 0.1 s. Its acceleration is:
(A) –500 m/s²
(B) –50 m/s²
(C) –100 m/s²
(D) –5 m/s²
Answer: (A)
Q25. If displacement-time graph is a straight line passing through origin, the motion is:
(A) Uniform
(B) Accelerated
(C) Retarded
(D) At rest
Answer: (A)
🔸 JEE Main Level (Q26–Q40)
Q26. A body covers 10 m in the first second and 30 m in the next second. The acceleration is:
(A) 10 m/s²
(B) 5 m/s²
(C) 15 m/s²
(D) 20 m/s²
Answer: (A)
Q27. A car starts from rest and attains a velocity of 20 m/s in 10 s. Its displacement is:
(A) 200 m
(B) 100 m
(C) 150 m
(D) 300 m
Answer: (B)
Q28. If a body covers equal distances in equal intervals of time, its motion is:
(A) Non-uniform
(B) Uniform
(C) Accelerated
(D) Retarded
Answer: (B)
Q29. A particle moves along x-axis such that x = t² – 4t + 5. At t = 2 s, its acceleration is:
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) Constant
Answer: (C)
Q30. A body moves with v = 2t + 3. Displacement after 5 seconds is:
(A) 45 m
(B) 40 m
(C) 35 m
(D) 30 m
Answer: (A)
Q31. A velocity-time graph is a straight line with negative slope. The body is:
(A) At rest
(B) Moving with uniform speed
(C) Uniformly retarded
(D) Accelerating
Answer: (C)
Q32. A freely falling object covers 245 m. Time taken is:
(A) 5 s
(B) 6 s
(C) 7 s
(D) 8 s
Answer: (C)
Q33. Displacement of a particle is given by s = 4t – 2t². The particle:
(A) Moves forward
(B) Comes to rest and then reverses
(C) Moves backward
(D) Accelerates uniformly
Answer: (B)
Q34. Two bodies A and B move such that A: s = 5t and B: s = 10 – t². They meet when:
(A) t = 1 s
(B) t = 2 s
(C) t = 3 s
(D) t = 4 s
Answer: (A)
Q35. A train moving with 60 km/h is brought to rest by applying brakes in 10 s. Its acceleration is:
(A) –1.67 m/s²
(B) –3 m/s²
(C) –4 m/s²
(D) –2.5 m/s²
Answer: (A)
Q36. Displacement-time graph is a parabola. Motion is:
(A) Uniform
(B) Uniform acceleration
(C) Non-uniform acceleration
(D) Oscillatory
Answer: (B)
Q37. If a body moves such that velocity = 3t², then acceleration at t = 2 s is:
(A) 6 m/s²
(B) 12 m/s²
(C) 8 m/s²
(D) 9 m/s²
Answer: (B)
Q38. Which of the following is not a valid kinematic equation?
(A) v = u + at
(B) s = ut + ½at²
(C) v² = u² + 2as
(D) s = vt – ½at²
Answer: (D)
Q39. A bullet is fired vertically and reaches max height in 4 s. Total time of flight is:
(A) 4 s
(B) 8 s
(C) 6 s
(D) 2 s
Answer: (B)
Q40. A body falls freely from a height and covers 20 m in last second. Height is:
(A) 45 m
(B) 80 m
(C) 125 m
(D) 180 m
Answer: (C)
🔸 JEE Advanced Level (Q41–Q50)
Q41. A stone is thrown upward and returns to same point. The average velocity during entire journey is:
(A) Zero
(B) Non-zero
(C) g
(D) 2g
Answer: (A)
Q42. A body moves with uniform acceleration. If in 2 s it moves 6 m and in 4 s it moves 24 m, its initial velocity is:
(A) 0
(B) 1 m/s
(C) 2 m/s
(D) 3 m/s
Answer: (A)
Q43. The displacement s = t³ – 6t² + 9t + 1. Velocity becomes zero at:
(A) t = 1 s
(B) t = 2 s
(C) t = 3 s
(D) t = 0 s
Answer: (B)
Q44. For a particle with v = u + at, plot of v² vs s is:
(A) Straight line
(B) Parabola
(C) Hyperbola
(D) Circular
Answer: (A)
Q45. A ball dropped from a height H reaches ground in time T. The height reached in time T/2 is:
(A) H/2
(B) H/4
(C) H
(D) 3H/4
Answer: (D)
Q46. A particle has zero velocity and non-zero acceleration. This implies:
(A) Turning point
(B) Rest
(C) Uniform motion
(D) Oscillation
Answer: (A)
Q47. A ball dropped from height h, travels last half in 1 s. Total time of fall is:
(A) √(2h/g)
(B) 3 s
(C) 2 s
(D) 1 + √2 s
Answer: (C)
Q48. The time taken by a particle to fall through height h from rest is t. Time to fall first h/2 is:
(A) t
(B) t/2
(C) t/√2
(D) t√2
Answer: (C)
Q49. Displacement is zero but distance is not. This can happen if:
(A) Body returns to starting point
(B) Body is at rest
(C) Body moves uniformly
(D) Body moves on straight path
Answer: (A)
Q50. A particle moves with constant acceleration. If velocity at t = 0 is 5 m/s, and at t = 10 s is 25 m/s, displacement is:
(A) 150 m
(B) 200 m
(C) 100 m
(D) 250 m
Answer: (A)
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
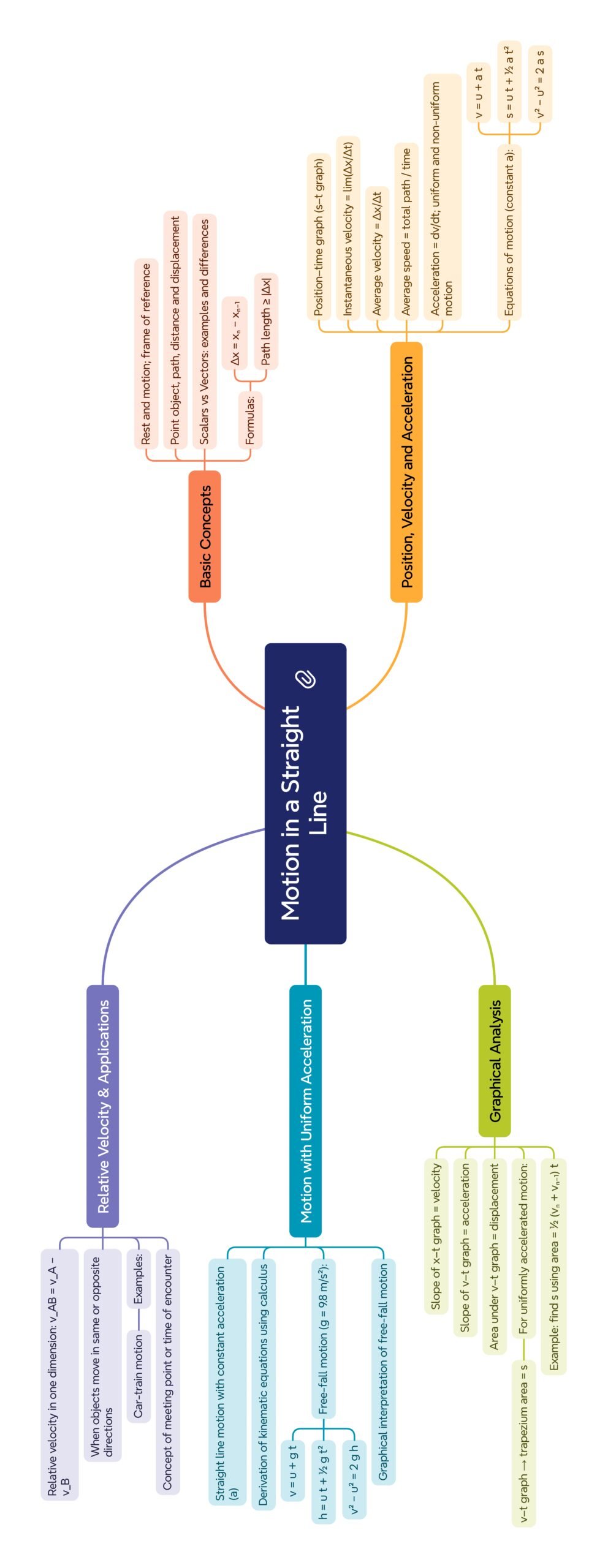
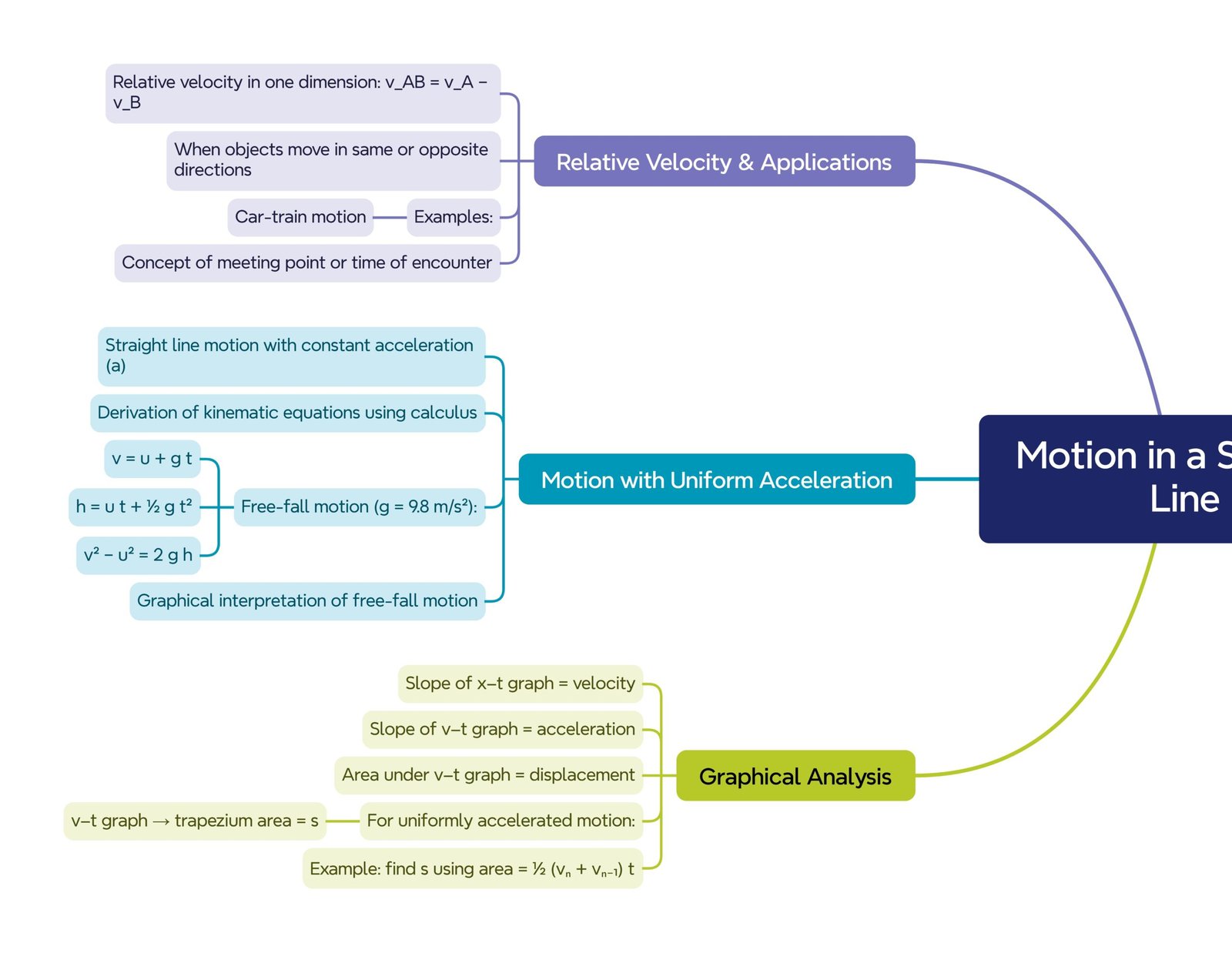
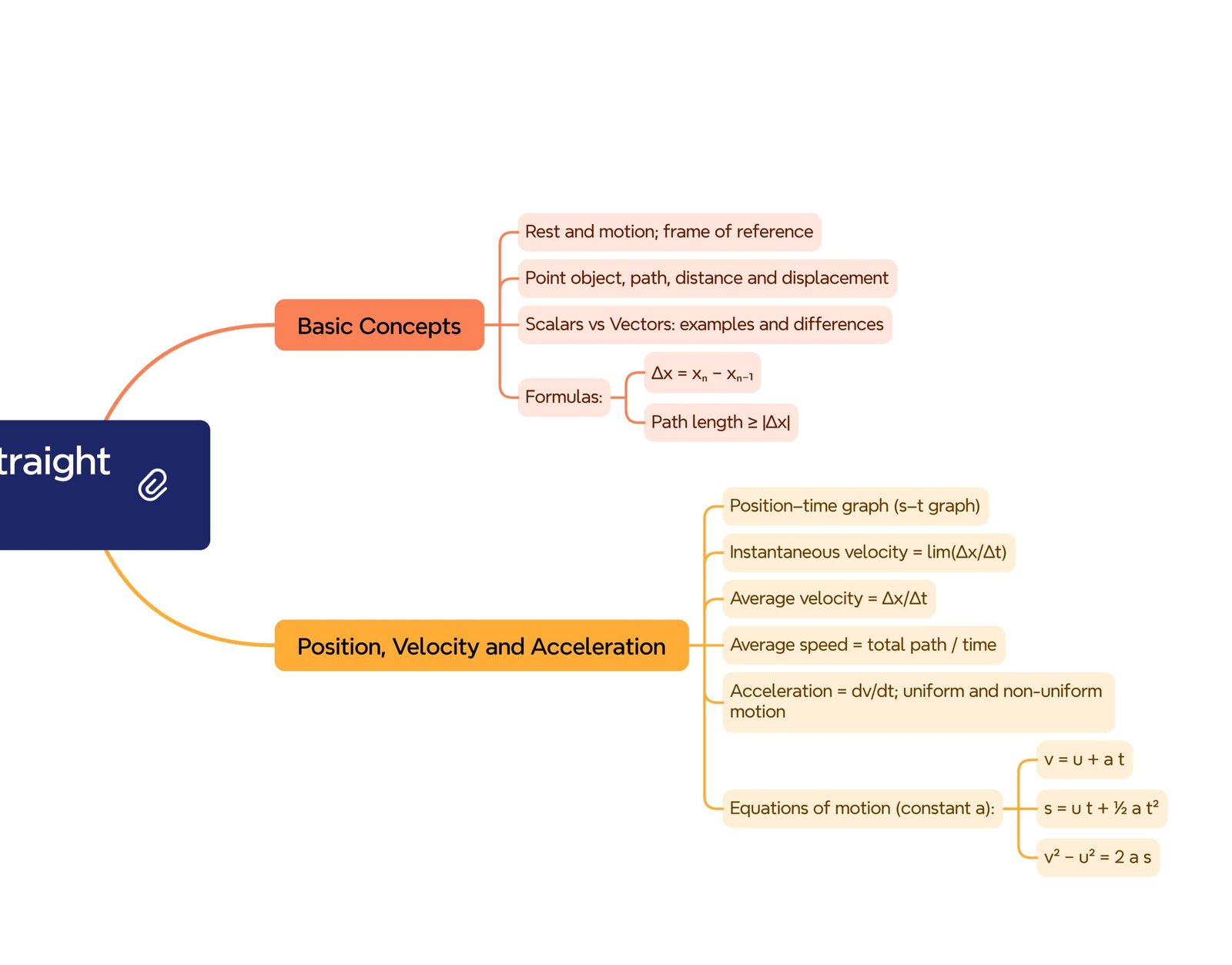
MIND MAP
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
