Class 11 : Biology (In English) – Lesson 8. Cell: The Unit of Life
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🌿✨ Introduction
🧠 All living organisms, from tiny microbes to giant trees and animals, are built of cells, which are the basic structural and functional units of life.
🧬 Every living being starts as a single cell — either remaining unicellular or dividing repeatedly to form multicellular bodies.
🌱 The cell performs all vital life processes: growth, metabolism, reproduction, and response to stimuli.
The discovery of the cell marked a turning point in biological understanding.
💡 Concept:
Cell theory forms the foundation of biology.
Structure and function of every organism depend on its cells.
🧭 Discovery of the Cell
🔹 Robert Hooke (1665) — observed cork slices under a microscope and coined the term “cell”.
🔹 Anton van Leeuwenhoek — first to observe living cells.
🔹 Schleiden (plants) and Schwann (animals) proposed Cell Theory (1838–39):
➤ All organisms are made of cells.
➤ Cell is the basic unit of structure and function.
🔹 Later, Rudolf Virchow (1855) added: “Omnis cellula-e-cellula” — all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
✏️ Note: The cell theory unified biology by linking all life forms through cellular organisation.
🌱 Characteristics of Cells
🪴 Smallest structural unit of life
🧠 Performs all life activities
⚙️ Has specific organelles for distinct functions
🧬 Stores genetic information (DNA/RNA)
🌿 Shows growth, division, energy transformation
🧫 Types of Cells
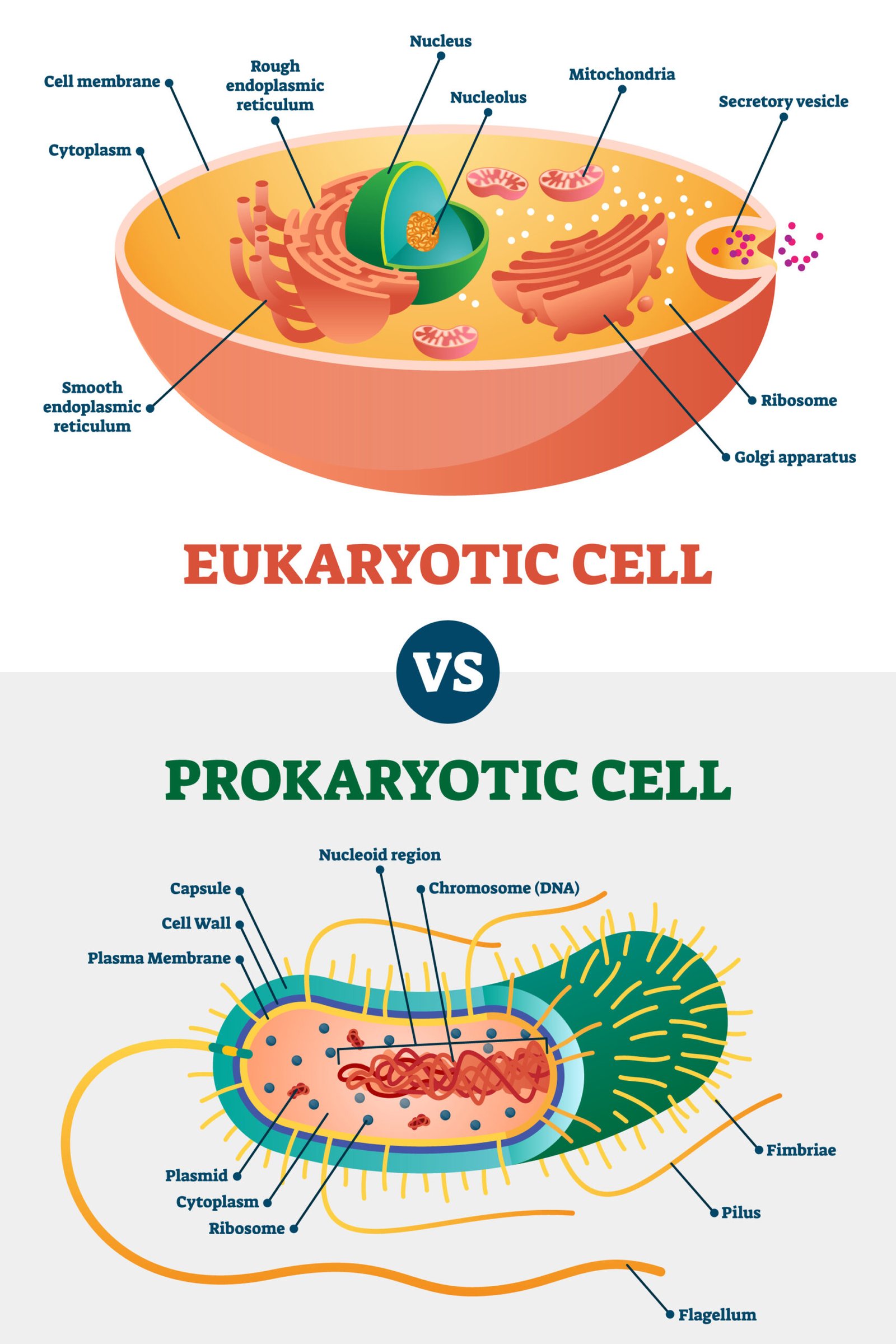
1️⃣ 🌿 Prokaryotic Cells
🧪 Simple, primitive; found in bacteria and cyanobacteria
📦 No membrane-bound organelles
🧠 DNA lies in nucleoid region, not enclosed by membrane
⚙️ Functions occur in cytoplasm; ribosomes (70S) small
💧 Cell wall made of peptidoglycan
2️⃣ 🌸 Eukaryotic Cells
🌿 Found in protists, fungi, plants, animals
🧠 Have true nucleus with nuclear membrane
📦 Membrane-bound organelles present (mitochondria, ER, etc.)
🧬 Complex and compartmentalised
🧪 Ribosomes are larger (80S)
💡 Concept:
Prokaryotes = primitive, simple
Eukaryotes = advanced, organised
🌿 Cell Shape and Size
🌱 Shape varies with function: spherical (WBC), spindle (muscle), polygonal (epidermal), elongated (nerve).
📏 Size varies: from 0.1 µm (mycoplasma) to 170 mm (ostrich egg).
✏️ Note: Function influences structure; form follows function.
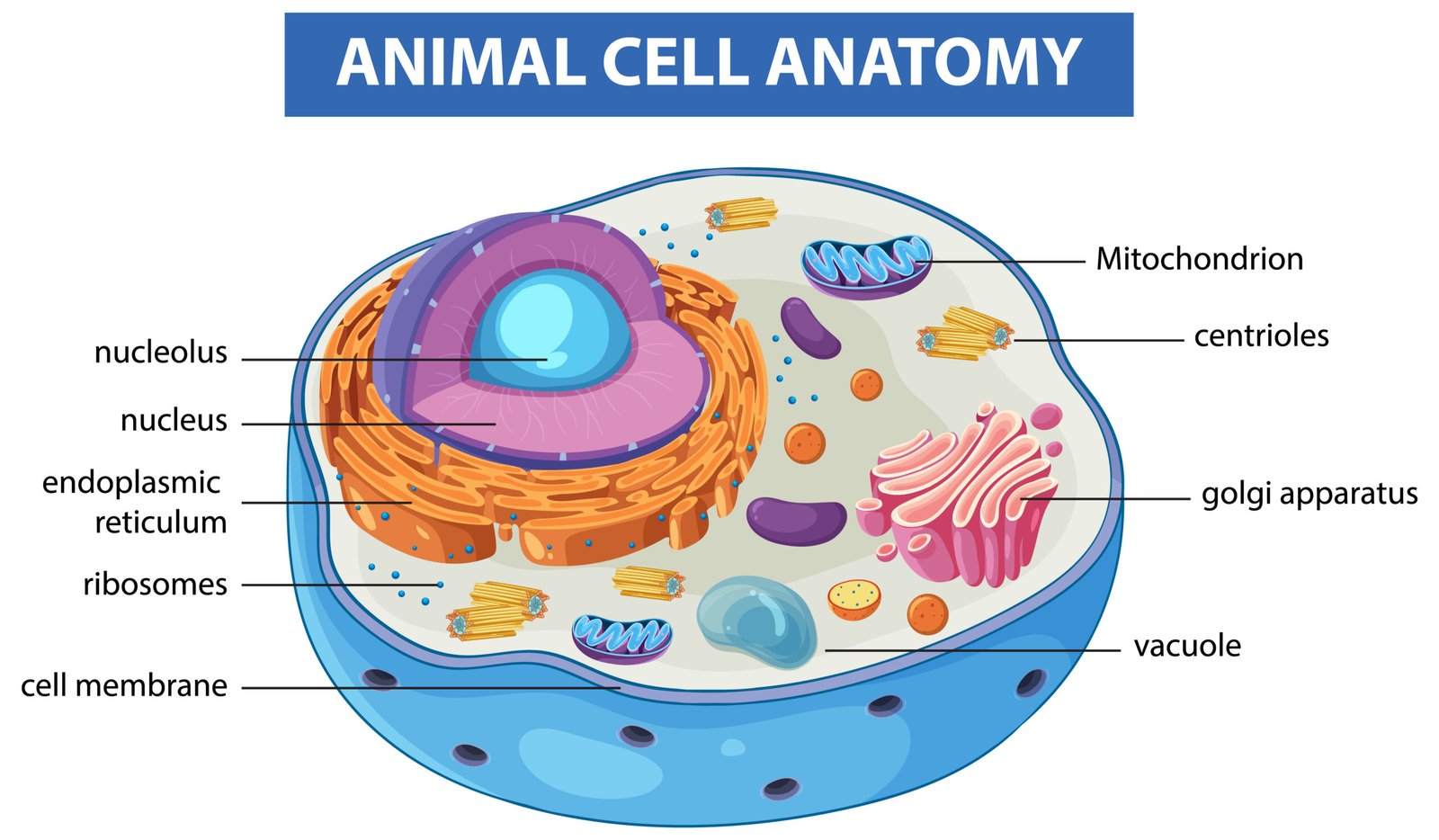
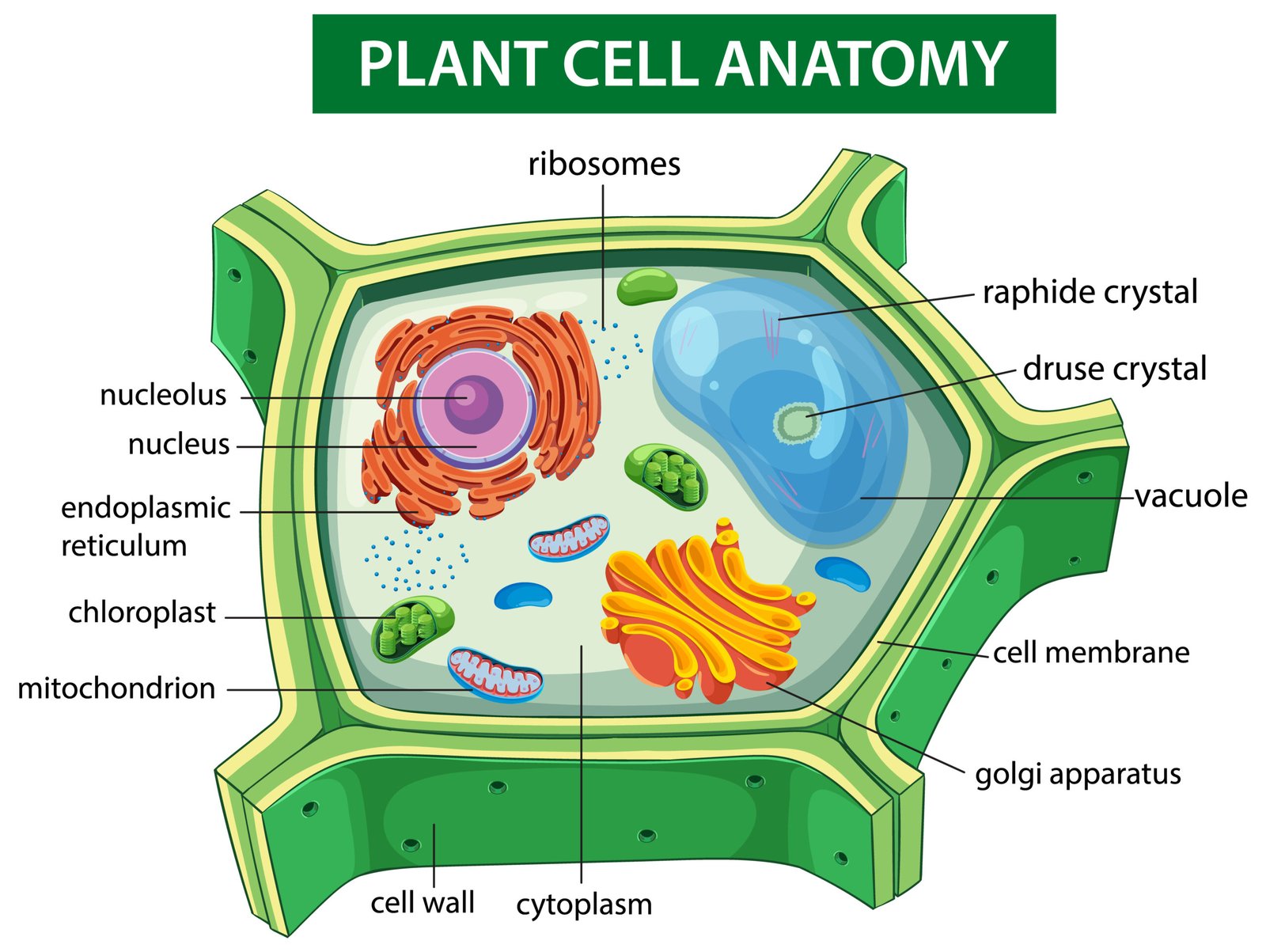
🍃 Cell Structure — Overview
Eukaryotic cells consist of:
1️⃣ Plasma membrane
2️⃣ Cytoplasm
3️⃣ Nucleus
4️⃣ Cell organelles
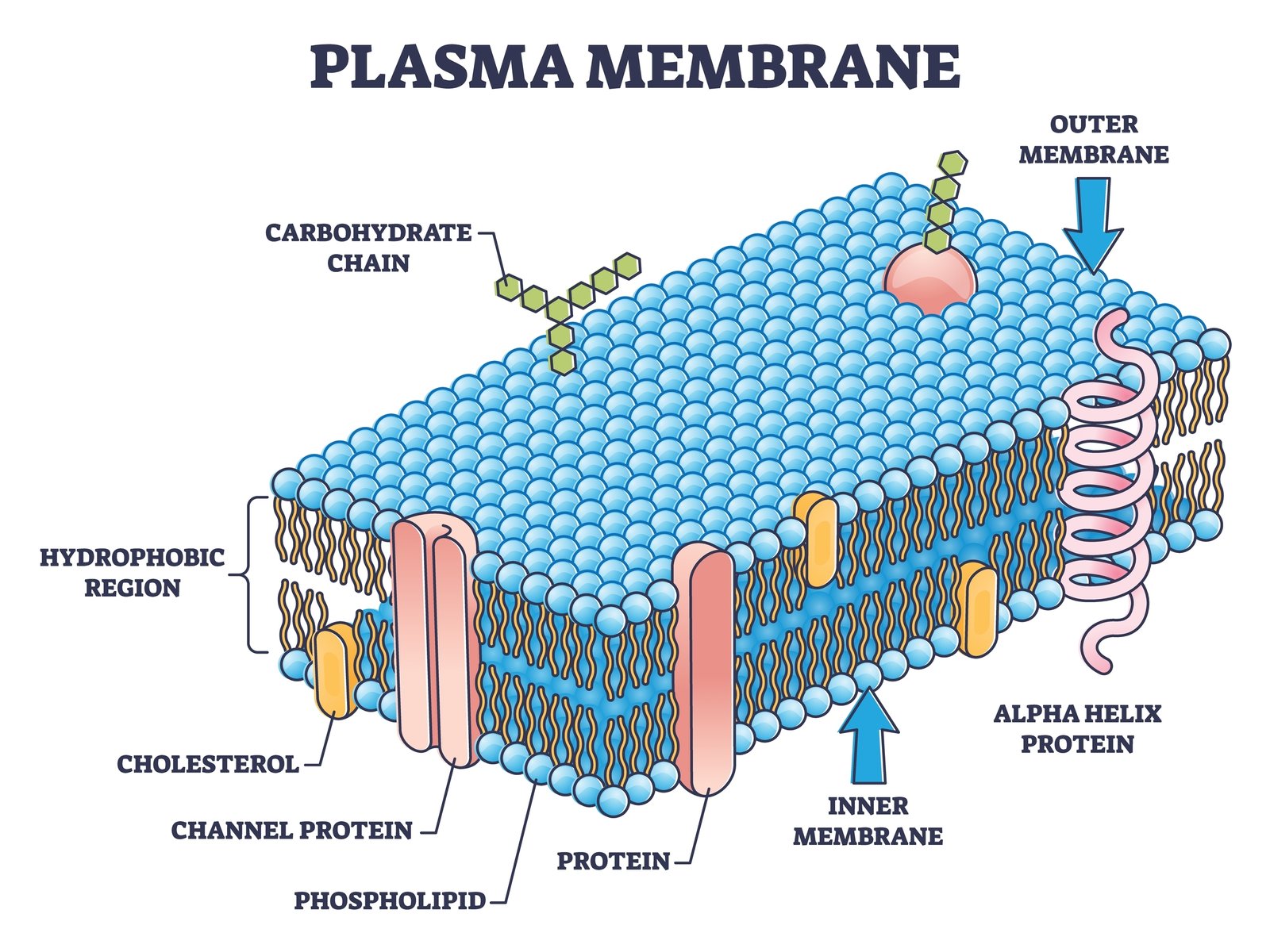
🧱 1️⃣ Plasma Membrane
🧠 Structure: Semi-permeable lipid bilayer (phospholipids + proteins)
💡 Described by Fluid Mosaic Model (Singer & Nicolson)
⚙️ Functions:
Selective transport (osmosis, diffusion, active transport)
Maintains internal environment
Communication and recognition
🧪 In plants, covered by cell wall (cellulose) for rigidity.
🧫 In bacteria, wall of peptidoglycan.
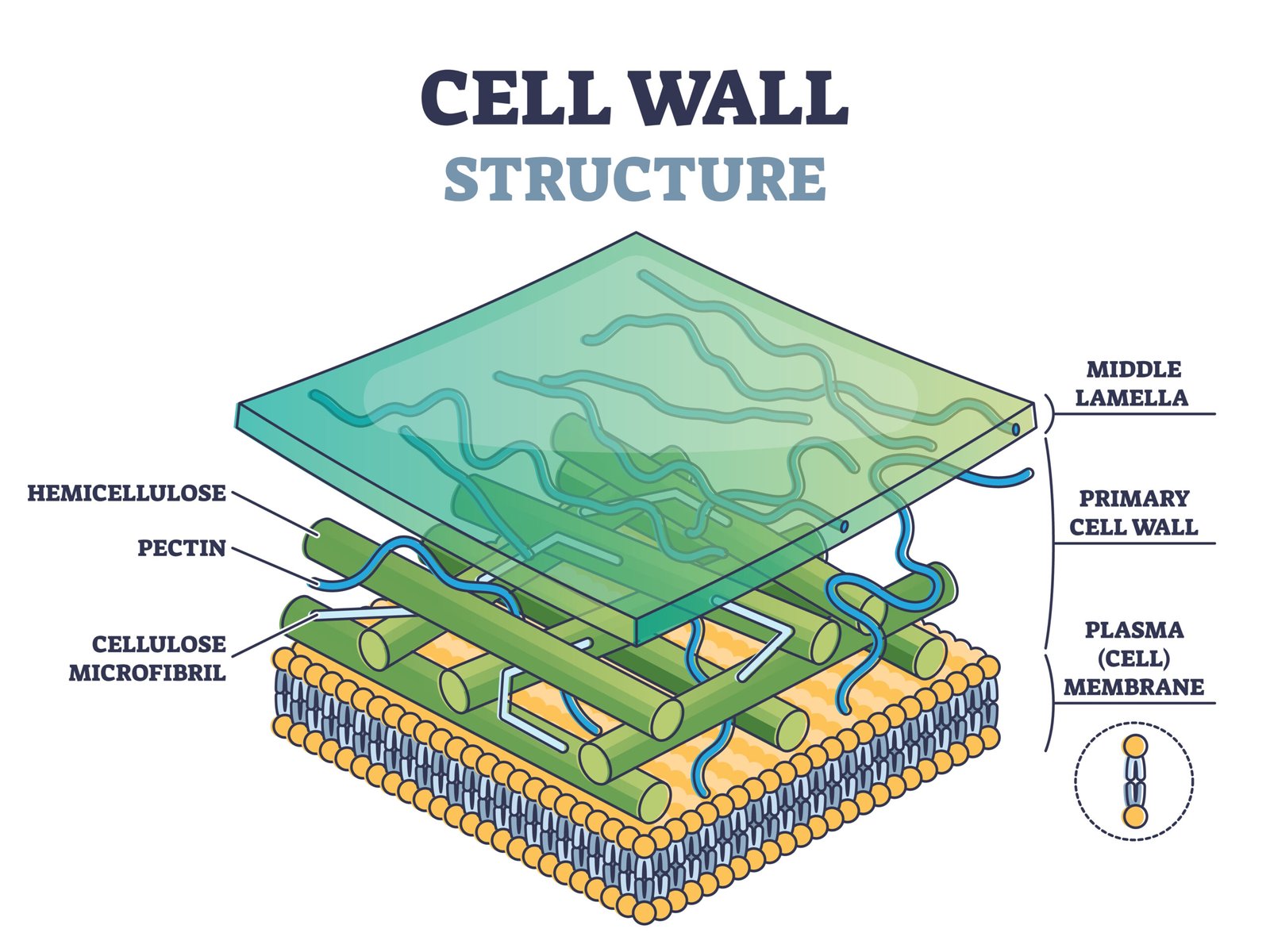
🧱 2️⃣ Cell Wall (in Plants)
🌿 Rigid outer covering made of cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin.
⚙️ Functions:
Provides mechanical support
Prevents bursting in hypotonic medium
Allows transport via plasmodesmata (cytoplasmic bridges)
🧪 3️⃣ Cytoplasm
💧 Fluid matrix between nucleus and membrane.
🌿 Contains organelles and cytosol.
⚙️ Site of metabolic reactions.
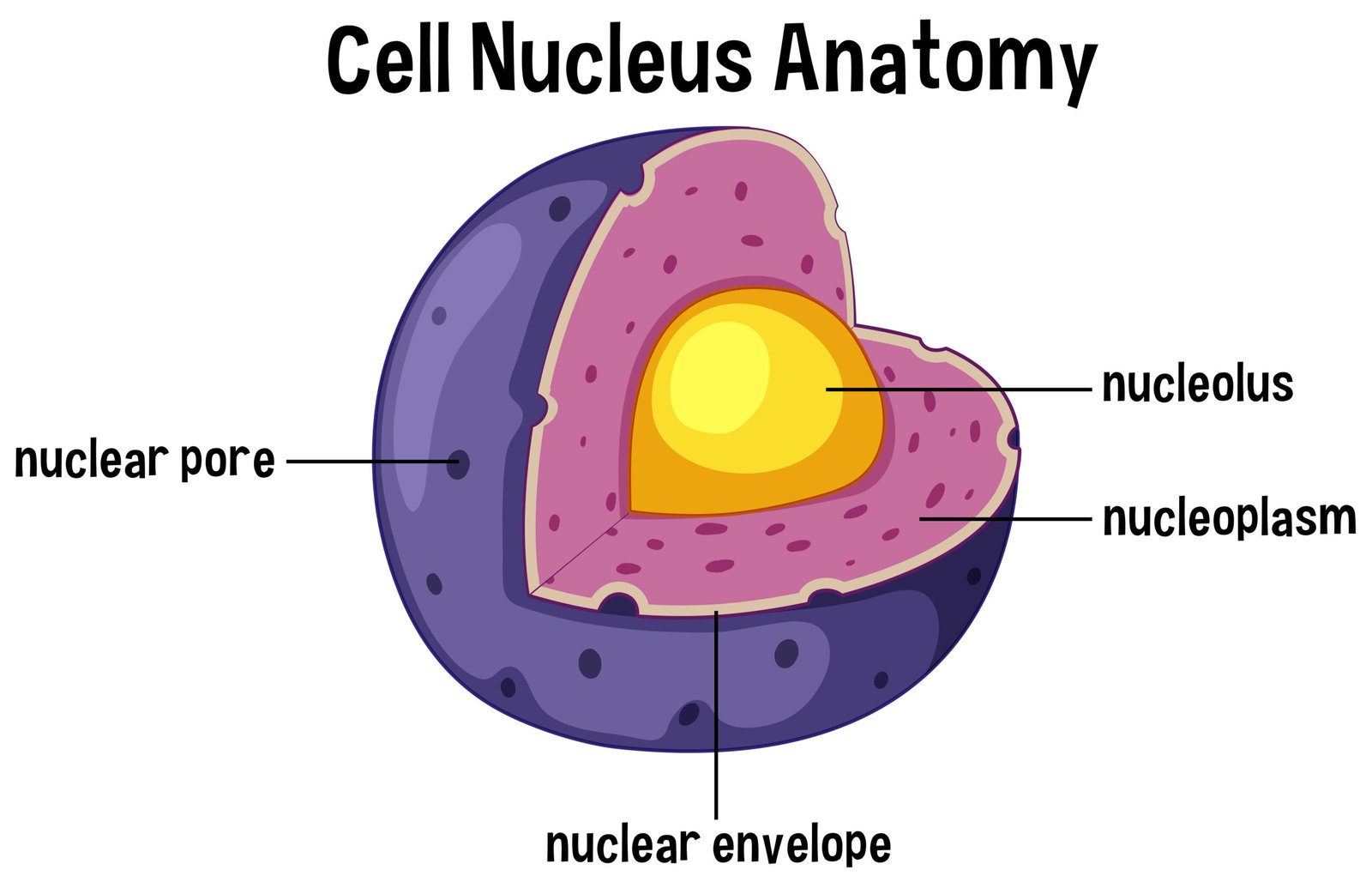
🧠 4️⃣ Nucleus
🧬 Control centre of cell.
🧫 Surrounded by nuclear envelope with pores.
📦 Contains nucleoplasm, chromatin (DNA + protein), nucleolus.
⚙️ Functions:
Controls cell activities
Stores genetic material
Regulates cell division
🧪 During cell division, chromatin condenses into chromosomes.
⚙️ Cell Organelles
🌿 1. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
🧬 Network of membranes; connects nucleus to cytoplasm
🔹 Rough ER – ribosomes attached; protein synthesis
🔹 Smooth ER – lipid synthesis, detoxification
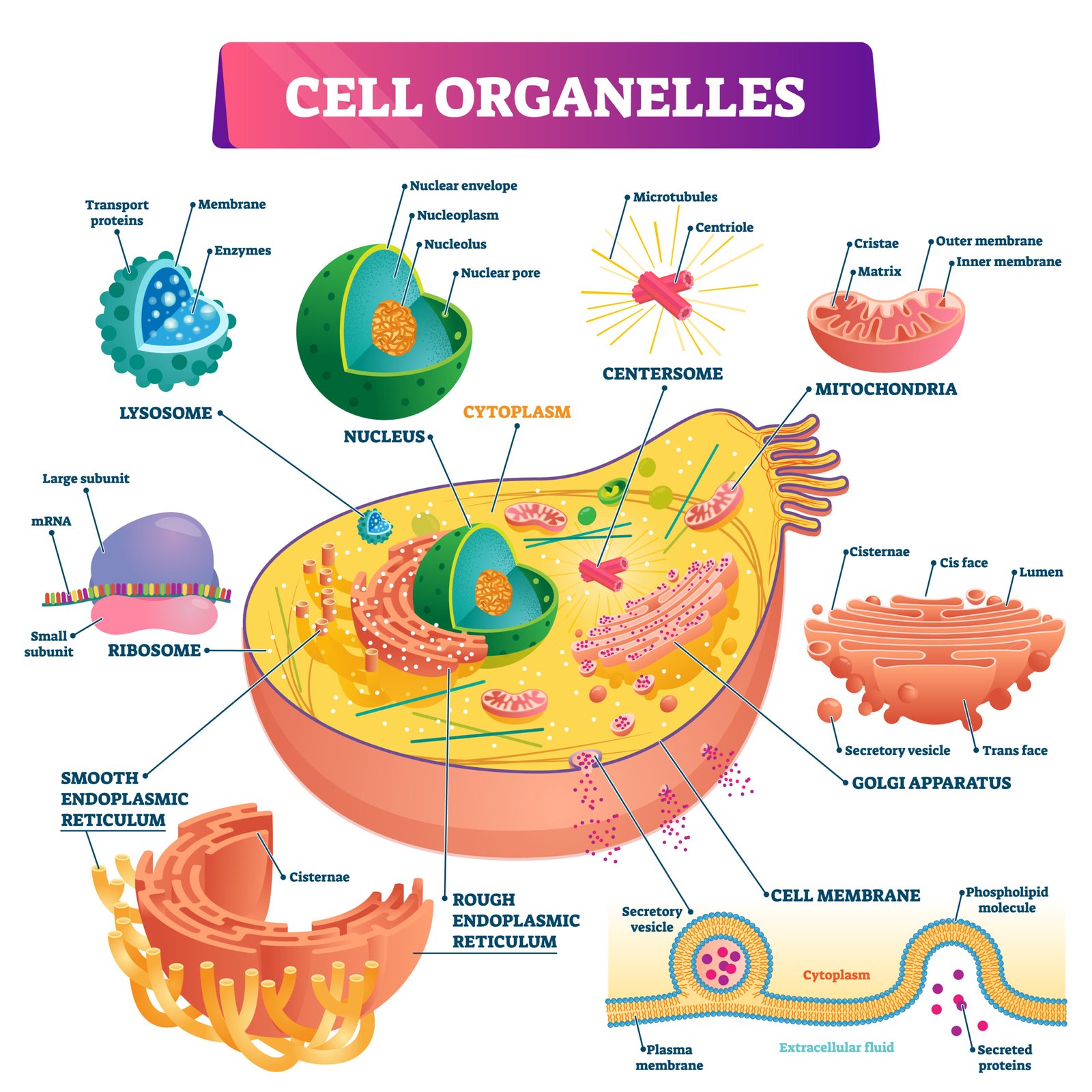
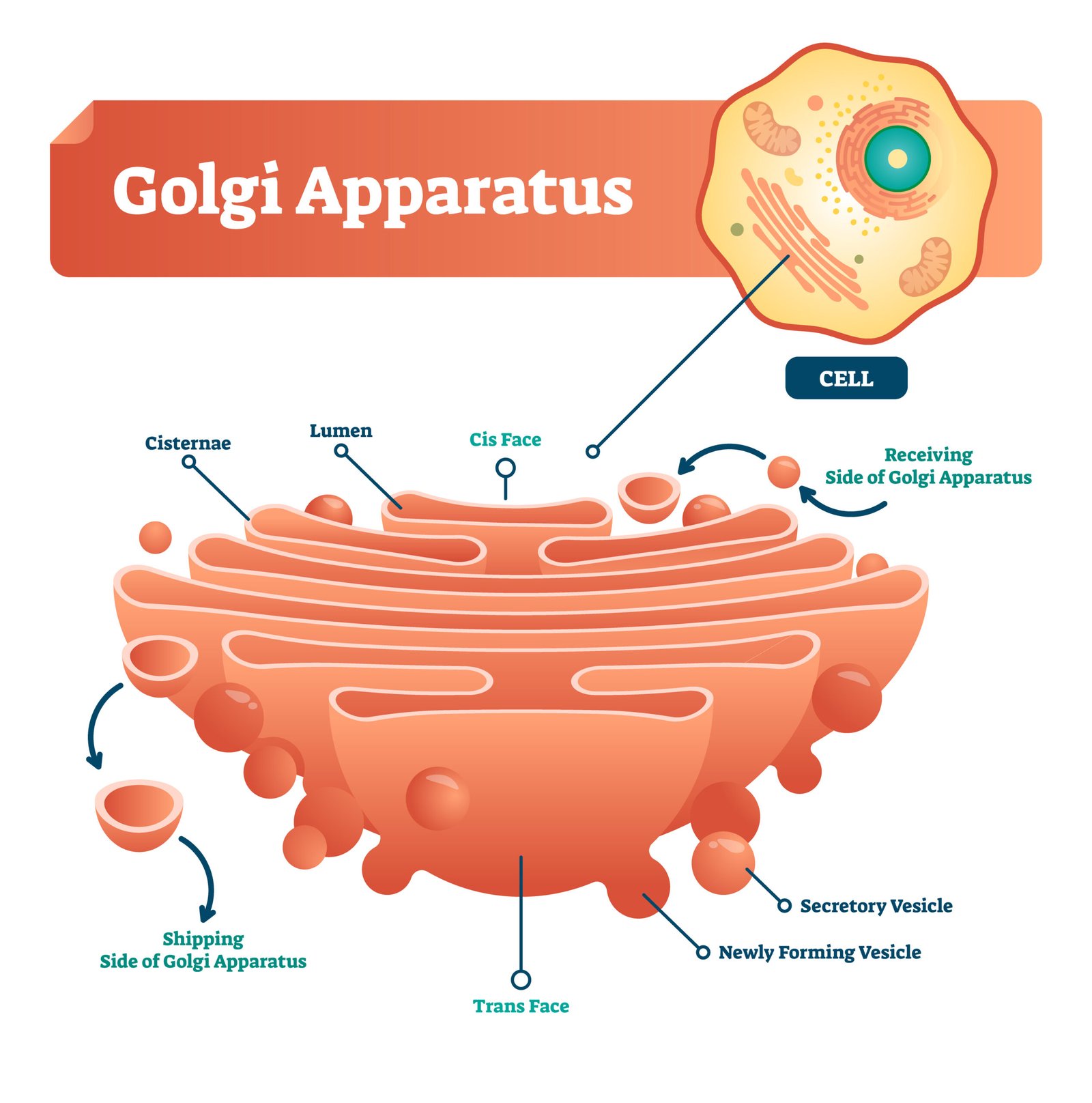
🌸 2. Golgi Apparatus
📦 Stack of cisternae; modifies, packages materials from ER
⚙️ Forms lysosomes and secretory vesicles
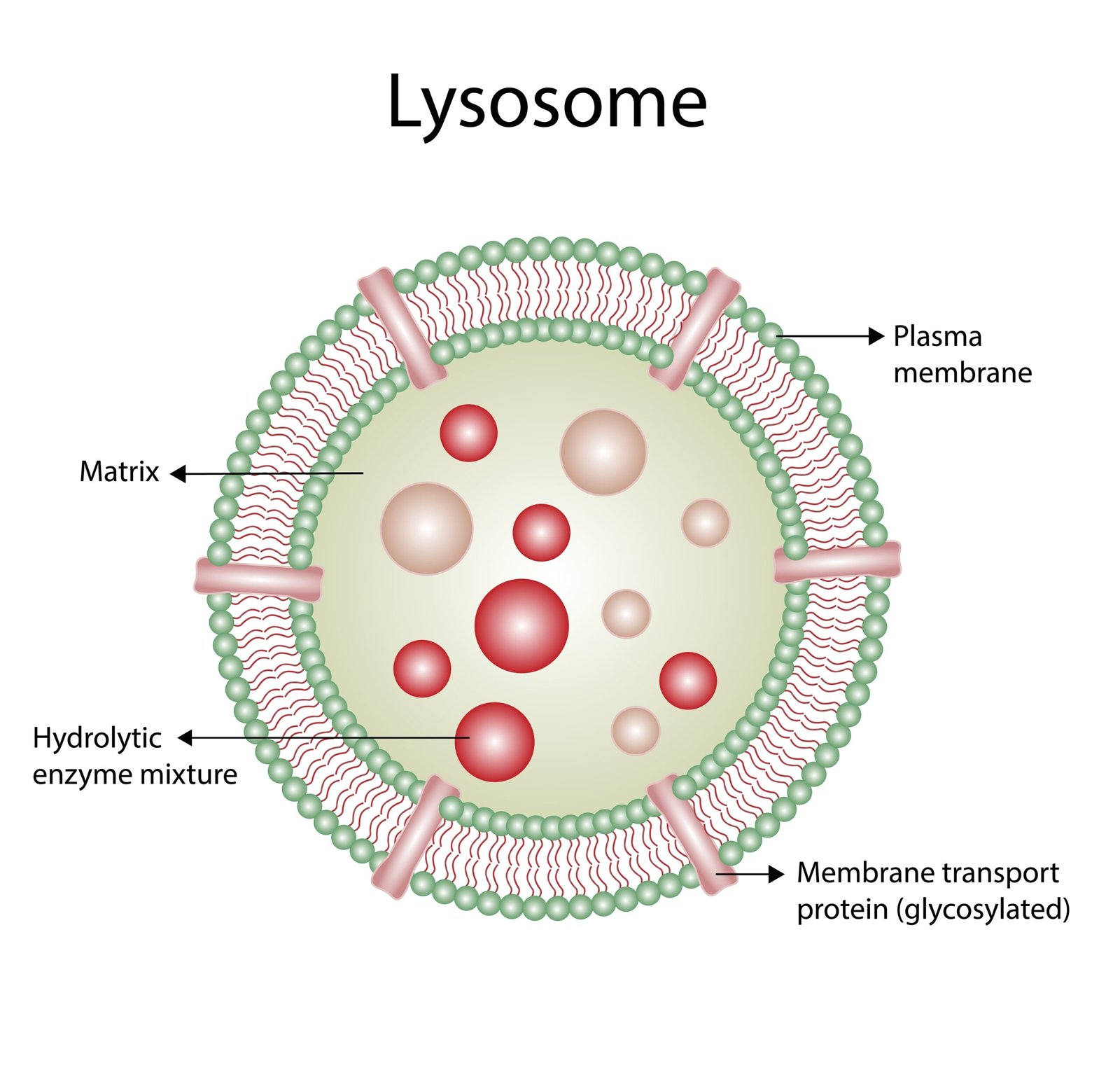
🧫 3. Lysosomes
💣 Membrane sacs with hydrolytic enzymes
⚡ Perform intracellular digestion, remove waste
🧠 Called suicidal bags
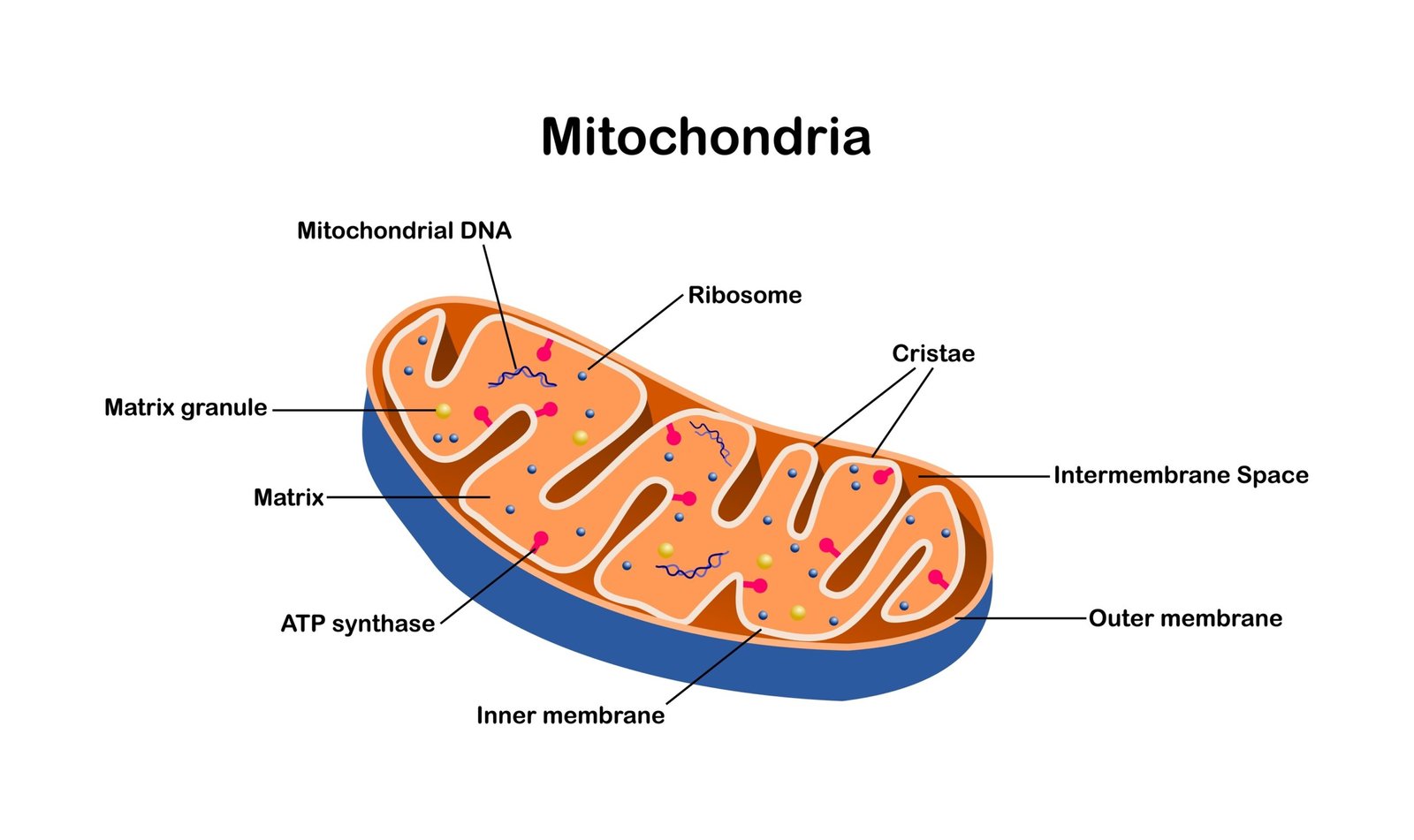
⚡ 4. Mitochondria
🧬 Double membrane; inner folded into cristae
🌿 Contain own DNA and ribosomes
⚙️ Site of aerobic respiration → ATP generation
💡 Known as powerhouse of cell
🪴 5. Plastids (Plants only)
🧪 Double membrane organelles
🟢 Chloroplasts – with chlorophyll, perform photosynthesis
🟡 Chromoplasts – coloured pigments
⚪ Leucoplasts – store food
💧 6. Vacuoles
📦 Fluid-filled, membrane-bound sacs
🌿 Plant cells: large central vacuole, stores water & solutes
🐾 Animal cells: small, temporary vacuoles
⚙️ Maintain turgor pressure
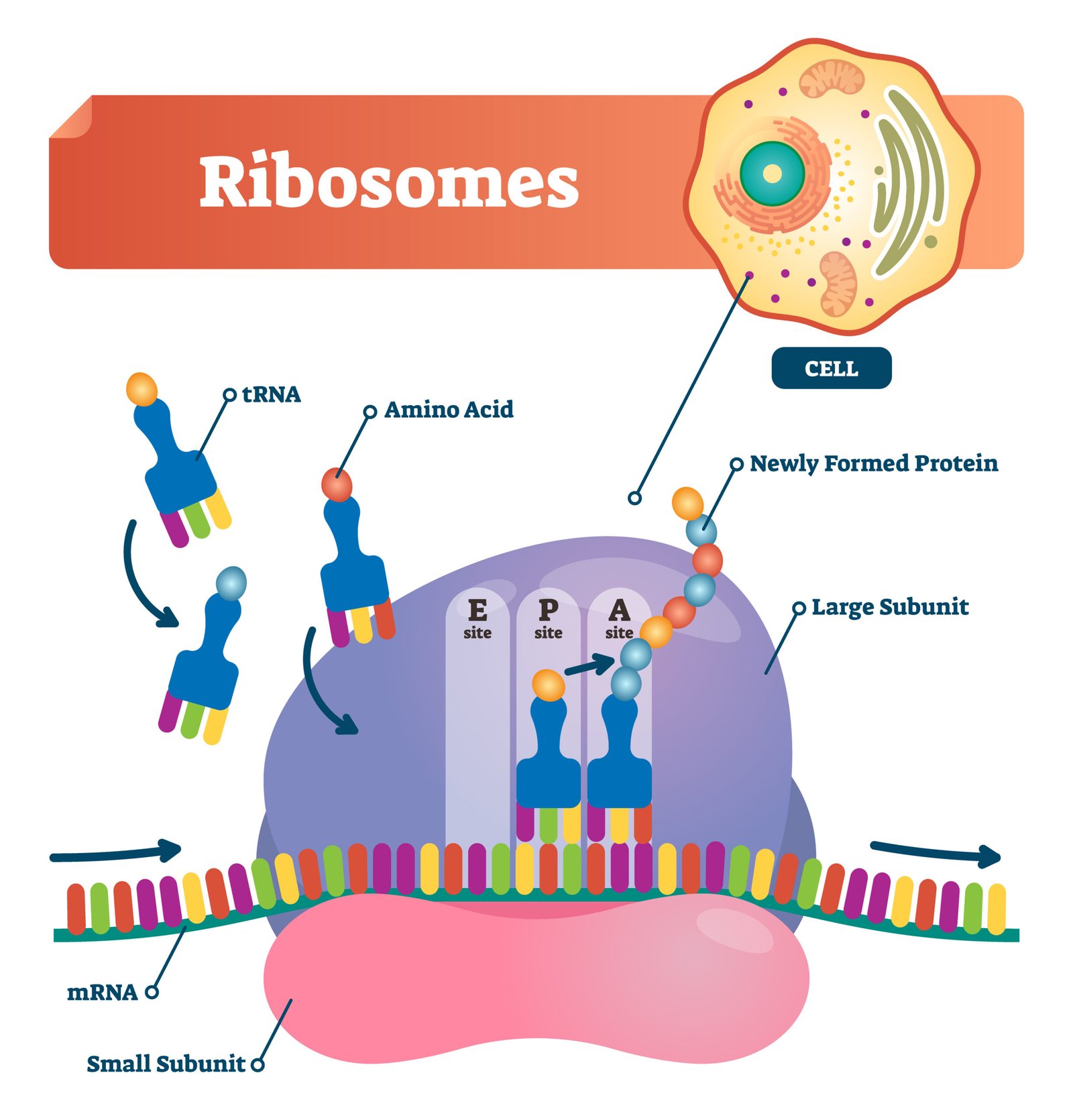
⚙️ 7. Ribosomes
🧠 Non-membranous
🧬 Site of protein synthesis
📏 Two subunits: 70S (prokaryote), 80S (eukaryote)
🧬 8. Centrosome and Centrioles (Animals)
🌿 Located near nucleus
🧭 Form spindle fibres during division
⚙️ Help in chromosome movement
🧠 Chromosomes
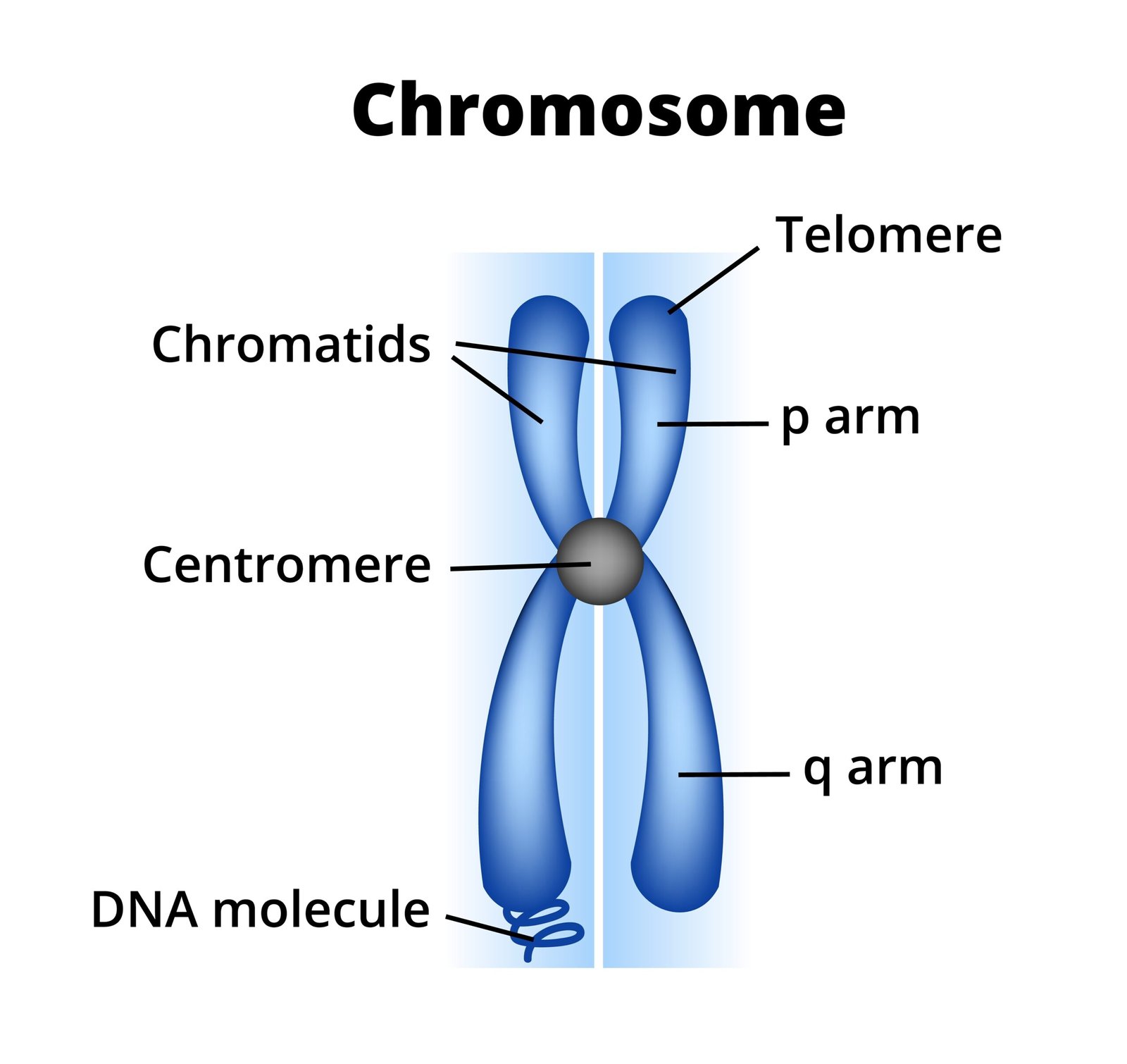
🌿 Thread-like structures carrying genetic information
🧬 Made of DNA + protein
📈 Visible during cell division
🧪 Types: Autosomes, sex chromosomes
💡 Function: Pass traits from parents to offspring
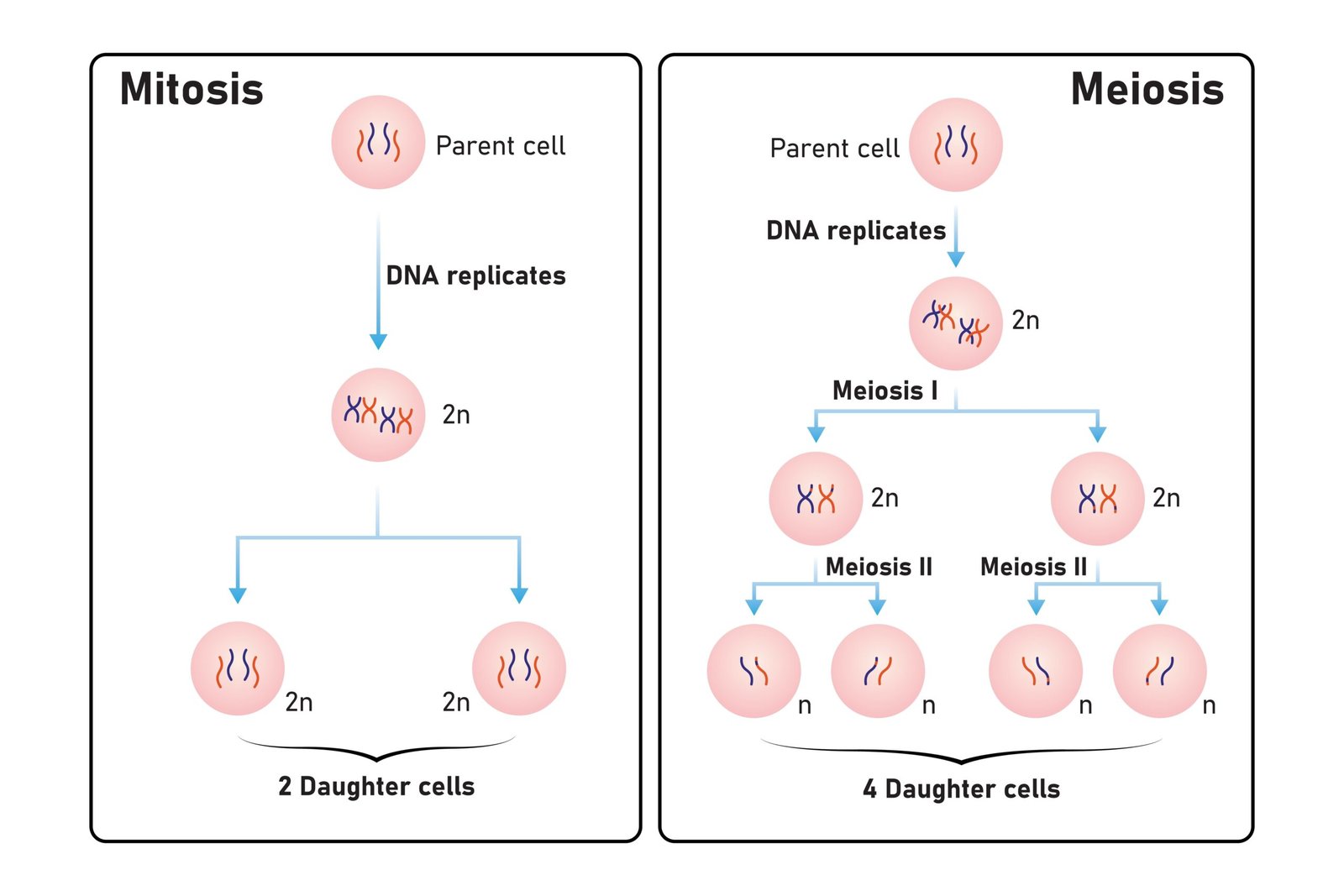
🌱 Cell Division (Brief Overview)
💡 Purpose: Growth, repair, reproduction
📘 Types:
1️⃣ Mitosis – equational division (growth)
2️⃣ Meiosis – reductional division (gametes)
✏️ Note: Cell division maintains genetic continuity.
🌸 Differences: Plant vs Animal Cells
Feature Plant Cell Animal Cell
Cell wall Present (cellulose) Absent
Plastids Present Absent
Vacuole Large, central Small, temporary
Centrosome Absent Present
Shape Fixed, rectangular Variable
💡 Concept: Structural differences reflect functional needs.
🌿 Specialised Cells
🧠 Different cells perform unique roles:
🌾 RBC – transport oxygen
🪴 Muscle cell – movement
🧬 Neuron – impulse transmission
🌿 Guard cells – regulate stomata
🌍 Importance of Cell Biology
🌱 Explains growth, heredity, and disease
🧠 Forms basis of genetics, physiology, and medicine
⚙️ Understanding cell structure helps in biotechnology and research
🌍 Why This Lesson Matters
🧠 Introduces foundation of life’s organisation
🧬 Builds base for genetics and evolution
🌿 Essential for biomedical sciences
⚡ Crucial for NEET, JEE, and CBSE exams
📝 Quick Recap
🧫 Cell = structural & functional unit
🧠 Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic
🧱 Plasma membrane – selective barrier
🧬 Nucleus – genetic control
⚙️ Organelles: ER, Golgi, lysosomes, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, ribosomes
📈 Division: mitosis & meiosis
🌿 Plant vs Animal → cell wall, plastids, vacuoles
📘 Summary
The cell is the basic building block of all living organisms.
Prokaryotic cells are simple, lacking a true nucleus, while eukaryotic cells are complex with compartmentalisation.
The plasma membrane maintains internal environment, the nucleus controls heredity, and organelles perform specific functions.
Mitochondria produce energy, ER and Golgi handle synthesis and transport, lysosomes manage digestion, and plastids enable photosynthesis.
Cell differences between plants and animals reflect adaptations to lifestyle.
Understanding cell structure and functions is essential to grasp all biological processes — growth, reproduction, and inheritance.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1. Which of the following is not correct?
(a) Robert Brown discovered the cell.
(b) Schleiden and Schwann formulated the cell theory.
(c) Virchow explained that cells are formed from pre-existing cells.
(d) A unicellular organism carries out its life activities within a single cell.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Option (a) is not correct.
💡 Reason: Robert Brown discovered the nucleus, not the cell.
The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665.
🔵 Question 2. New cells generate from
(a) bacterial fermentation (b) regeneration of old cells
(c) pre-existing cells (d) abiotic materials
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Option (c) pre-existing cells.
💡 According to Rudolf Virchow, “Omnis cellula e cellula” — all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
🔵 Question 3. Match the following:
Column I Column II
(a) Cristae (ii) Infoldings in mitochondria
(b) Cisternae (iii) Disc-shaped sacs in Golgi apparatus
(c) Thylakoids (i) Flat membranous sacs in stroma
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Correct matching:
(a) → (ii), (b) → (iii), (c) → (i)
💡 Explanation:
Cristae: Folds of inner mitochondrial membrane.
Cisternae: Flattened sacs of Golgi apparatus.
Thylakoids: Flattened sacs in chloroplast stroma.
🔵 Question 4. Which of the following is correct?
(a) Cells of all living organisms have a nucleus.
(b) Both animal and plant cells have a well-defined cell wall.
(c) In prokaryotes, there are no membrane-bound organelles.
(d) Cells are formed de novo from abiotic materials.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Option (c) is correct.
💡 Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles like nucleus, mitochondria, etc.
🔵 Question 5. What is a mesosome in a prokaryotic cell? Mention the functions that it performs.
🟢 Answer:
🧫 Mesosomes are infoldings of the plasma membrane in prokaryotes (like bacteria).
🌿 Functions:
➡️ Help in cell wall formation during division.
➡️ Assist in DNA replication and distribution.
➡️ Help in respiration (contain enzymes).
➡️ Aid in enzyme secretion and cell compartmentalisation.
🔵 Question 6. How do neutral solutes move across the plasma membrane? Can the polar molecules also move across it in the same way? If not, then how are these transported across the membrane?
🟢 Answer:
🌸 Neutral solutes move by simple diffusion — from high concentration to low concentration across the membrane.
⚗️ Polar molecules cannot pass freely due to the lipid bilayer barrier. They are transported by:
Facilitated diffusion via carrier proteins (no energy used).
Active transport using energy (ATP) through pumps.
💡 Examples: Glucose via facilitated diffusion, Na⁺ via active transport.
🔵 Question 7. Name two cell-organelles that are double membrane-bound. What are the characteristics of these two organelles? State their functions and draw labelled diagrams of both.
🟢 Answer:
🧬 Organelles: Mitochondria and Chloroplast
🌿 Common characteristics:
Double membrane.
Contain DNA and ribosomes.
Capable of self-replication.
🧪 Mitochondria:
Inner membrane folded into cristae
Site of cellular respiration
Produces ATP (powerhouse of cell)
🌱 Chloroplast:
Present in plant cells, contains thylakoids arranged as grana
Site of photosynthesis
✏️ Diagram descriptions:
Mitochondrion: outer & inner membrane, cristae, matrix.
Chloroplast: outer & inner membrane, grana, stroma.
🔵 Question 8. What are the characteristics of prokaryotic cells?
🟢 Answer:
🧫 Prokaryotic cells (e.g. bacteria):
No true nucleus — nucleoid present.
No membrane-bound organelles.
Cell wall made of peptidoglycan.
Ribosomes are 70S type.
Reproduction: binary fission.
Genetic material: circular DNA.
✔️ Simple organisation, performs all vital functions.
🔵 Question 9. Multicellular organisms have division of labour. Explain.
🟢 Answer:
🌿 In multicellular organisms, cells are specialised for specific functions.
➡️ Example:
Nerve cells — conduction
Muscle cells — movement
RBCs — oxygen transport
💡 Division of labour improves efficiency and survival.
🔵 Question 10. Cell is the basic unit of life. Discuss in brief.
🟢 Answer:
🧬 The cell is the structural and functional unit of all living organisms.
➡️ All organisms are made of cells.
➡️ All functions — growth, metabolism, reproduction — occur in cells.
➡️ Cells arise from pre-existing cells.
✔️ Thus, cell = fundamental unit of life.
🔵 Question 11. What are nuclear pores? State their function.
🟢 Answer:
🧠 Nuclear pores are openings in the nuclear envelope.
🌿 Functions:
Allow exchange of materials (RNA, proteins) between nucleus and cytoplasm.
Maintain communication between nucleoplasm and cytoplasm.
🔵 Question 12. Both lysosomes and vacuoles are endomembrane structures, yet they differ in terms of their functions. Comment.
🟢 Answer:
🧫 Lysosomes:
Contain hydrolytic enzymes.
Function: intracellular digestion, destruction of worn-out organelles.
🌿 Vacuoles:
Contain cell sap (water, ions, sugars).
Function: storage, osmoregulation, turgidity.
✔️ Both are endomembrane structures but have different roles.
🔵 Question 13. Describe the structure of the following with the help of labelled diagrams:
(i) Nucleus (ii) Centrosome
🟢 Answer:
(i) 🧠 Nucleus:
Surrounded by double membrane with nuclear pores.
Contains nucleoplasm, chromatin, nucleolus.
Controls cell activities.
✏️ Diagram description: Circular body, double membrane, nucleolus, chromatin threads.
(ii) ⚙️ Centrosome:
Present near nucleus in animal cells.
Consists of two centrioles perpendicular to each other.
Helps in spindle formation during cell division.
✏️ Diagram description: Two cylindrical centrioles arranged at right angles.
🔵 Question 14. What is a centromere? How does the position of centromere form the basis of classification of chromosomes? Support your answer with a diagram showing the position of centromere on different types of chromosomes.
🟢 Answer:
🧬 Centromere:
Constricted region on chromosome dividing it into arms.
Helps attach chromosome to spindle during division.
🌿 Based on centromere position:
Metacentric: Centromere in middle; equal arms.
Sub-metacentric: Slightly off-centre; unequal arms.
Acrocentric: Near one end; one very short arm.
Telocentric: At terminal end; one arm.
✏️ Diagram description: Shows all four types with centromere positions.
✔️ Function: Segregation during cell division.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔴 Question 1:
The cell was discovered by:
🔴1️⃣ Robert Brown
🟢2️⃣ Robert Hooke
🟡3️⃣ Leeuwenhoek
🔵4️⃣ Schleiden
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Robert Hooke
🔴 Question 2:
Smallest living unit of life is:
🔴1️⃣ Atom
🟢2️⃣ Molecule
🟡3️⃣ Cell
🔵4️⃣ Organelle
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Cell
🔴 Question 3:
Prokaryotic cells lack:
🔴1️⃣ DNA
🟢2️⃣ Plasma membrane
🟡3️⃣ Nucleus
🔵4️⃣ Ribosomes
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Nucleus
🔴 Question 4:
Which of the following is a prokaryote?
🔴1️⃣ Fungi
🟢2️⃣ Algae
🟡3️⃣ Bacteria
🔵4️⃣ Protozoa
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Bacteria
🔴 Question 5:
The functional unit of endoplasmic reticulum is:
🔴1️⃣ Cisternae
🟢2️⃣ Ribosome
🟡3️⃣ Golgi body
🔵4️⃣ Lysosome
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ Cisternae
🔴 Question 6:
Which cell organelle is called powerhouse of cell?
🔴1️⃣ Lysosome
🟢2️⃣ Golgi apparatus
🟡3️⃣ Mitochondria
🔵4️⃣ Ribosome
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Mitochondria
🔴 Question 7:
Lysosomes are formed from:
🔴1️⃣ Ribosomes
🟢2️⃣ Endoplasmic reticulum
🟡3️⃣ Golgi apparatus
🔵4️⃣ Mitochondria
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Golgi apparatus
🔴 Question 8:
Which organelle is responsible for photosynthesis?
🔴1️⃣ Mitochondria
🟢2️⃣ Chloroplast
🟡3️⃣ Ribosome
🔵4️⃣ Golgi body
🟢 Answer: 2️⃣ Chloroplast
🔴 Question 9:
Ribosomes are sites of:
🔴1️⃣ Respiration
🟢2️⃣ Photosynthesis
🟡3️⃣ Protein synthesis
🔵4️⃣ Lipid synthesis
🟢 Answer: 3️⃣ Protein synthesis
🔴 Question 10:
Cell theory was proposed by:
🔴1️⃣ Schleiden and Schwann
🟢2️⃣ Hooke and Leeuwenhoek
🟡3️⃣ Virchow and Pasteur
🔵4️⃣ Brown and Schwann
🟢 Answer: 1️⃣ Schleiden and Schwann
🔴 Question 11:
Name the two main types of cells.
🟢 Answer:
1️⃣ Prokaryotic cells: Without membrane-bound organelles (e.g. Bacteria).
2️⃣ Eukaryotic cells: With true nucleus and organelles (e.g. Plant, Animal).
🔴 Question 12:
Define cell theory.
🟢 Answer:
Proposed by Schleiden and Schwann.
States that:
1️⃣ All living organisms are composed of cells.
2️⃣ Cell is the structural and functional unit of life.
3️⃣ All cells arise from pre-existing cells (Virchow).
🔴 Question 13:
Write the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
🟢 Answer:
Feature Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell
Nucleus Absent (nucleoid) Present with nuclear membrane
Organelles No membrane-bound organelles Membrane-bound organelles present
Example Bacteria, Cyanobacteria Plants, Animals, Fungi
Size Small (1–10 µm) Large (10–100 µm)
💡 Eukaryotes show compartmentalisation and complexity.
🔴 Question 14:
Describe the structure and functions of plasma membrane.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
1️⃣ Composed of lipid bilayer (phospholipids + proteins).
2️⃣ Fluid Mosaic Model proposed by Singer and Nicolson.
3️⃣ Selectively permeable membrane.
Functions:
✔️ Regulates entry and exit of substances.
✔️ Maintains cell shape.
✔️ Helps in communication and recognition.
🔴 Question 15:
What are cell organelles? Name the membrane-bound and non-membrane-bound organelles.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Structures in cytoplasm performing specific functions.
Membrane-bound: Nucleus, ER, Golgi body, Lysosomes, Mitochondria, Plastids.
Non-membrane-bound: Ribosomes, Centrioles.
Function: Division of labour within cell.
🔴 Question 16:
Describe the structure and function of nucleus.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
1️⃣ Double membrane nuclear envelope with pores.
2️⃣ Contains nucleoplasm, chromatin, and nucleolus.
Functions:
✔️ Controls cellular activities.
✔️ Contains genetic material (DNA).
✔️ Regulates cell division and heredity.
🔴 Question 17:
What are ribosomes? Mention their types and functions.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Small, non-membranous organelles made of RNA & protein.
Types:
1️⃣ 70S: Found in prokaryotes.
2️⃣ 80S: Found in eukaryotes.
Function: Protein synthesis (called protein factories).
🔴 Question 18:
Describe the structure and functions of mitochondria.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
1️⃣ Double membrane — outer smooth, inner folded (cristae).
2️⃣ Matrix with DNA, RNA, enzymes.
Functions:
✔️ Powerhouse of cell — produces ATP.
✔️ Site of respiration.
✔️ Self-replicating due to DNA.
🔴 Question 19:
What is endoplasmic reticulum (ER)? Name its types and functions.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Network of membranes forming channels in cytoplasm.
Types:
1️⃣ Rough ER (RER): With ribosomes; protein synthesis.
2️⃣ Smooth ER (SER): No ribosomes; lipid synthesis, detoxification.
Functions: Transport and compartmentalisation.
🔴 Question 20:
Explain the structure and function of Golgi apparatus.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
• Stack of membrane-bound sacs called cisternae.
• Has cis (forming) and trans (maturing) faces.
Functions:
✔️ Modifies and packages proteins.
✔️ Forms lysosomes.
✔️ Secretes materials outside cell.
🔴 Question 21:
Describe the structure and function of lysosomes.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
• Single membrane-bound vesicles formed from Golgi apparatus.
• Contain hydrolytic enzymes.
Function:
✔️ Intracellular digestion.
✔️ Destroy damaged organelles (suicidal bags).
✔️ Defence against pathogens.
🔴 Question 22:
What are plastids? Write their types and functions.
🟢 Answer:
Definition: Double-membraned organelles found in plant cells 🌿.
Types:
1️⃣ Chloroplasts: Green; contain chlorophyll; photosynthesis.
2️⃣ Chromoplasts: Coloured pigments; attract pollinators 🌸.
3️⃣ Leucoplasts: Colourless; store food (amyloplast, elaioplast, aleuroplast).
Function: Photosynthesis and storage.
🔴 Question 23:
Explain the structure of a prokaryotic cell (bacterium 🦠) with labelled parts.
🟢 Answer:
Shape: Spherical (coccus), rod-shaped (bacillus), spiral, or comma-shaped.
Main parts:
1️⃣ Cell envelope:
• Glycocalyx (capsule/slime layer) → protection.
• Cell wall → rigidity.
• Plasma membrane → selectively permeable.
2️⃣ Cytoplasm: No membrane-bound organelles; contains ribosomes (70S).
3️⃣ Nucleoid: Single circular DNA molecule; no nuclear membrane.
4️⃣ Inclusions: Storage granules (phosphate, glycogen).
5️⃣ Flagella (for movement), pili and fimbriae (attachment).
Feature: Simple structure, fast reproduction, primitive nucleus.
🔴 Question 24:
Describe the structure of a eukaryotic cell.
🟢 Answer:
Shape: Varies — spherical, cuboidal, polygonal.
Main components:
1️⃣ Plasma membrane: Lipid bilayer; selectively permeable.
2️⃣ Cytoplasm: Contains organelles.
3️⃣ Nucleus: True nucleus with double membrane & DNA.
4️⃣ Cell organelles:
• Mitochondria — respiration.
• ER — transport & synthesis.
• Golgi apparatus — packaging.
• Lysosomes — digestion.
• Ribosomes — protein synthesis.
• Plastids (plants 🌿) — photosynthesis/storage.
• Centrioles (animals 🧫) — cell division.
Feature: High organisation, compartmentalisation, complex nucleus.
🔴 Question 25:
Explain the Fluid Mosaic Model of plasma membrane.
🟢 Answer:
Proposed by: Singer and Nicolson (1972).
Structure:
1️⃣ Lipid bilayer — phospholipids with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
2️⃣ Proteins —
• Integral proteins (span membrane)
• Peripheral proteins (surface).
3️⃣ Cholesterol — provides stability.
Features:
✔️ Fluid nature → lipids & proteins move laterally.
✔️ Mosaic → irregular arrangement of proteins.
Function:
• Selective transport.
• Cell recognition.
• Flexibility & stability.
🔴 Question 26:
Describe the structure of mitochondria and its functions.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
1️⃣ Double membrane: Outer smooth, inner folded (forms cristae).
2️⃣ Matrix: Contains DNA, RNA, ribosomes, enzymes.
3️⃣ Cristae: Increase surface area for enzyme activity.
Functions:
✔️ Site of aerobic respiration.
✔️ Produces ATP — “powerhouse of cell”.
✔️ Can replicate independently.
✔️ Stores enzymes for Krebs cycle and ETC.
🔴 Question 27:
Explain the structure of chloroplast 🌿 with labelled parts.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
1️⃣ Double membrane-bound organelle.
2️⃣ Stroma: Fluid containing DNA, RNA, ribosomes, enzymes.
3️⃣ Thylakoids: Flattened sacs arranged in stacks (grana).
4️⃣ Grana connected by stromal lamellae.
5️⃣ Chlorophyll pigments in thylakoid membranes capture light.
Function:
✔️ Site of photosynthesis.
✔️ Light reactions in grana; dark reactions in stroma.
✔️ Synthesises glucose and oxygen.
🔴 Question 28:
Describe the structure and functions of Golgi apparatus.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
• Series of flattened membrane sacs (cisternae) arranged parallel.
• Has cis face (receiving) and trans face (shipping).
Functions:
1️⃣ Modification and packaging of materials.
2️⃣ Formation of lysosomes.
3️⃣ Secretion of glycoproteins and mucilage.
4️⃣ Involved in cell wall formation in plants 🌿.
🔴 Question 29:
Describe the structure and functions of nucleus.
🟢 Answer:
Structure:
1️⃣ Nuclear envelope — double membrane with pores.
2️⃣ Nucleoplasm — fluid with enzymes & nucleotides.
3️⃣ Chromatin:
• Euchromatin — active DNA.
• Heterochromatin — inactive DNA.
4️⃣ Nucleolus — synthesises rRNA.
Functions:
✔️ Controls cell activities.
✔️ Contains hereditary material (DNA).
✔️ Directs protein synthesis.
✔️ Regulates cell division.
🔴 Question 30:
Write short notes on:
(a) Centrosome and Centrioles
(b) Cytoskeleton
🟢 Answer:
(a) Centrosome and Centrioles:
• Present in animal cells near nucleus.
• Contains two centrioles arranged perpendicular.
• Each centriole = 9 triplets of microtubules.
• Function: Spindle formation during cell division.
(b) Cytoskeleton:
• Network of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments.
• Provides shape, support, and movement of organelles.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
NEET QUESTIONS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Q1. The smallest living unit of an organism is
🟡 A. Tissue
🟡 B. Organelle
🟡 C. Cell
🟡 D. Organ
🟢 Answer: C. Cell
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q2. Cell theory was proposed by
🟡 A. Schleiden and Schwann
🟡 B. Robert Hooke and Leeuwenhoek
🟡 C. Watson and Crick
🟡 D. Virchow and Brown
🟢 Answer: A. Schleiden and Schwann
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q3. Who introduced the term “cell” for the first time?
🟡 A. Leeuwenhoek
🟡 B. Robert Hooke
🟡 C. Schwann
🟡 D. Schleiden
🟢 Answer: B. Robert Hooke
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q4. Cell theory was modified by Virchow with which concept?
🟡 A. Cells arise from crystalloids
🟡 B. Cells arise de novo
🟡 C. Cells arise from pre-existing cells
🟡 D. Cells arise from protoplasm only
🟢 Answer: C. Cells arise from pre-existing cells
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q5. Prokaryotic cells lack
🟡 A. Plasma membrane
🟡 B. DNA
🟡 C. Membrane-bound organelles
🟡 D. Ribosomes
🟢 Answer: C. Membrane-bound organelles
📅 NEET 2020
🔵 Q6. The 70S ribosomes occur in
🟡 A. Eukaryotic cytoplasm
🟡 B. Prokaryotes and eukaryotic organelles
🟡 C. Nucleolus only
🟡 D. Golgi bodies
🟢 Answer: B. Prokaryotes and eukaryotic organelles
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q7. In prokaryotic cells, DNA is
🟡 A. Linear with histones
🟡 B. Circular and naked
🟡 C. Linear and wrapped on histones
🟡 D. Segmented and membrane bound
🟢 Answer: B. Circular and naked
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q8. The plasma membrane model proposed by Singer and Nicolson is called
🟡 A. Sandwich model
🟡 B. Fluid mosaic model
🟡 C. Unit membrane model
🟡 D. Lipoprotein model
🟢 Answer: B. Fluid mosaic model
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q9. Mesosomes in prokaryotes are involved in
🟡 A. Respiration and cell wall formation
🟡 B. Protein synthesis only
🟡 C. Photosynthesis only
🟡 D. Digestion of waste
🟢 Answer: A. Respiration and cell wall formation
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q10. The organelle responsible for packaging and secretion of proteins is
🟡 A. Mitochondria
🟡 B. Lysosome
🟡 C. Golgi apparatus
🟡 D. Ribosome
🟢 Answer: C. Golgi apparatus
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q11. Lysosomes are formed from
🟡 A. Endoplasmic reticulum
🟡 B. Golgi apparatus
🟡 C. Ribosomes
🟡 D. Nucleus
🟢 Answer: B. Golgi apparatus
📅 NEET 2014
🔵 Q12. The double membrane-bound organelle with its own DNA and ribosomes is
🟡 A. Peroxisome
🟡 B. Mitochondrion
🟡 C. Lysosome
🟡 D. Ribosome
🟢 Answer: B. Mitochondrion
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q13. Plasmodesmata in plant cells are meant for
🟡 A. Passage of water only
🟡 B. Cytoplasmic connections between cells
🟡 C. Transport of hormones only
🟡 D. Storage of starch
🟢 Answer: B. Cytoplasmic connections between cells
📅 NEET 2021
🔵 Q14. Which of these is absent in animal cells?
🟡 A. Mitochondria
🟡 B. Centrosome
🟡 C. Plastids
🟡 D. Ribosomes
🟢 Answer: C. Plastids
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q15. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is primarily involved in
🟡 A. Protein synthesis
🟡 B. Lipid synthesis
🟡 C. Packaging of proteins
🟡 D. Photosynthesis
🟢 Answer: B. Lipid synthesis
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q16. In eukaryotic cells, ribosomal subunits are synthesized in
🟡 A. Cytoplasm
🟡 B. Nucleolus
🟡 C. Nuclear envelope
🟡 D. Endoplasmic reticulum
🟢 Answer: B. Nucleolus
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q17. The organelle which helps in photorespiration is
🟡 A. Peroxisome
🟡 B. Lysosome
🟡 C. Golgi body
🟡 D. Ribosome
🟢 Answer: A. Peroxisome
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q18. Which of the following possesses 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules?
🟡 A. Centriole
🟡 B. Basal body
🟡 C. Flagella
🟡 D. Nuclear spindle
🟢 Answer: C. Flagella
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q19. Tonoplast is the membrane of
🟡 A. Mitochondria
🟡 B. Vacuole
🟡 C. Nucleus
🟡 D. Lysosome
🟢 Answer: B. Vacuole
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q20. The cytoskeleton maintains cell shape and is composed mainly of
🟡 A. Cellulose fibres
🟡 B. Microtubules and microfilaments
🟡 C. Chitin fibrils
🟡 D. Peptidoglycan
🟢 Answer: B. Microtubules and microfilaments
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q21. The site of ribosomal RNA synthesis is
🟡 A. Nucleolus
🟡 B. Nuclear pore
🟡 C. Rough ER
🟡 D. Cytoplasm
🟢 Answer: A. Nucleolus
📅 NEET 2020
🔵 Q22. Cristae are characteristic features of
🟡 A. Chloroplast
🟡 B. Mitochondria
🟡 C. Nucleus
🟡 D. Golgi complex
🟢 Answer: B. Mitochondria
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q23. The cell organelle responsible for detoxification of harmful substances is
🟡 A. Smooth ER
🟡 B. Golgi apparatus
🟡 C. Peroxisome
🟡 D. Ribosome
🟢 Answer: A. Smooth ER
📅 NEET 2013
🔵 Q24. In plant cells, cytokinesis occurs by
🟡 A. Furrow method
🟡 B. Cell plate formation
🟡 C. Binary fission
🟡 D. Constriction
🟢 Answer: B. Cell plate formation
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q25. The major site for synthesis of ATP is
🟡 A. Chloroplast
🟡 B. Mitochondria
🟡 C. Golgi body
🟡 D. Peroxisome
🟢 Answer: B. Mitochondria
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q26. The energy currency of the cell is
🟡 A. GTP
🟡 B. ATP
🟡 C. NADH
🟡 D. FADH₂
🟢 Answer: B. ATP
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q27. The function of ribosomes is
🟡 A. Lipid synthesis
🟡 B. Protein synthesis
🟡 C. DNA replication
🟡 D. Carbohydrate storage
🟢 Answer: B. Protein synthesis
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q28. Which of the following is not a double-membrane-bound organelle?
🟡 A. Mitochondria
🟡 B. Plastid
🟡 C. Lysosome
🟡 D. Nucleus
🟢 Answer: C. Lysosome
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q29. The cell organelle involved in the formation of lysosomes is
🟡 A. Ribosome
🟡 B. Golgi apparatus
🟡 C. Smooth ER
🟡 D. Nucleus
🟢 Answer: B. Golgi apparatus
📅 AIPMT 2011
🔵 Q30. The fluid-filled space inside the endoplasmic reticulum is called
🟡 A. Cisternae
🟡 B. Thylakoid lumen
🟡 C. Matrix
🟡 D. Grana
🟢 Answer: A. Cisternae
📅 NEET 2020
🔵 Q31. The primary wall of plant cells is mainly composed of
🟡 A. Lignin
🟡 B. Cellulose
🟡 C. Pectin
🟡 D. Hemicellulose only
🟢 Answer: B. Cellulose
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q32. The structure that regulates the entry and exit of molecules into and out of the nucleus is
🟡 A. Nuclear pore
🟡 B. Nucleolus
🟡 C. Nuclear matrix
🟡 D. Nucleoplasm
🟢 Answer: A. Nuclear pore
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q33. The cisternae of the Golgi apparatus are involved in
🟡 A. Packaging of materials
🟡 B. DNA replication
🟡 C. Photosynthesis
🟡 D. Transcription
🟢 Answer: A. Packaging of materials
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q34. The 80S ribosomes are composed of
🟡 A. 40S and 60S subunits
🟡 B. 50S and 30S subunits
🟡 C. 60S and 20S subunits
🟡 D. 70S and 10S subunits
🟢 Answer: A. 40S and 60S subunits
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q35. Centrioles help in the formation of
🟡 A. Spindle fibres
🟡 B. Golgi bodies
🟡 C. Mitochondria
🟡 D. Nucleolus
🟢 Answer: A. Spindle fibres
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q36. The organelle that provides turgidity and rigidity to plant cells is
🟡 A. Lysosome
🟡 B. Plastid
🟡 C. Vacuole
🟡 D. Peroxisome
🟢 Answer: C. Vacuole
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q37. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is abundant in cells active in
🟡 A. Lipid metabolism
🟡 B. Protein synthesis
🟡 C. Cell division
🟡 D. Photosynthesis
🟢 Answer: A. Lipid metabolism
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q38. The cell organelle responsible for oxidative phosphorylation is
🟡 A. Chloroplast
🟡 B. Lysosome
🟡 C. Mitochondrion
🟡 D. Peroxisome
🟢 Answer: C. Mitochondrion
📅 NEET 2018
🔵 Q39. Plastids that store starch, oils, and proteins are collectively called
🟡 A. Chromoplasts
🟡 B. Leucoplasts
🟡 C. Chloroplasts
🟡 D. Etioplasts
🟢 Answer: B. Leucoplasts
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q40. The structural and functional unit of the Golgi apparatus is
🟡 A. Cisternae
🟡 B. Cristae
🟡 C. Grana
🟡 D. Vesicles only
🟢 Answer: A. Cisternae
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q41. Which organelle in plant cells captures light energy for photosynthesis?
🟡 A. Mitochondria
🟡 B. Plastid (Chloroplast)
🟡 C. Golgi body
🟡 D. Ribosome
🟢 Answer: B. Plastid (Chloroplast)
📅 AIPMT 2013
🔵 Q42. The small openings in the nuclear envelope that regulate nucleocytoplasmic exchange are called
🟡 A. Nuclear pores
🟡 B. Plasmodesmata
🟡 C. Tonoplasts
🟡 D. Desmosomes
🟢 Answer: A. Nuclear pores
📅 NEET 2016
🔵 Q43. The powerhouses of the cell are
🟡 A. Chloroplasts
🟡 B. Golgi bodies
🟡 C. Mitochondria
🟡 D. Lysosomes
🟢 Answer: C. Mitochondria
📅 AIPMT 2015
🔵 Q44. The chlorophyll-containing organelles in plant cells are
🟡 A. Mitochondria
🟡 B. Chromoplasts
🟡 C. Chloroplasts
🟡 D. Leucoplasts
🟢 Answer: C. Chloroplasts
📅 NEET 2019
🔵 Q45. The ribosomes found on rough ER are involved in
🟡 A. Lipid synthesis
🟡 B. Protein synthesis for export
🟡 C. DNA replication
🟡 D. Cell wall formation
🟢 Answer: B. Protein synthesis for export
📅 AIPMT 2012
🔵 Q46. The primary function of peroxisomes is
🟡 A. Photosynthesis
🟡 B. Lipid synthesis
🟡 C. Detoxification and photorespiration
🟡 D. Protein transport
🟢 Answer: C. Detoxification and photorespiration
📅 NEET 2017
🔵 Q47. The nuclear envelope is continuous with
🟡 A. Golgi apparatus
🟡 B. Endoplasmic reticulum
🟡 C. Mitochondria
🟡 D. Plasma membrane
🟢 Answer: B. Endoplasmic reticulum
📅 AIPMT 2010
🔵 Q48. The large central vacuole of mature plant cells is filled with
🟡 A. Stroma
🟡 B. Cell sap
🟡 C. Plasma
🟡 D. Cytosol
🟢 Answer: B. Cell sap
📅 NEET 2015
🔵 Q49. Microtubules are composed of
🟡 A. Actin
🟡 B. Tubulin
🟡 C. Myosin
🟡 D. Keratin
🟢 Answer: B. Tubulin
📅 AIPMT 2014
🔵 Q50. The nucleolus is mainly concerned with
🟡 A. DNA replication
🟡 B. Ribosomal RNA synthesis
🟡 C. Lipid metabolism
🟡 D. Protein degradation
🟢 Answer: B. Ribosomal RNA synthesis
📅 NEET 2018
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
PRACTICE SETS FROM THIS LESSON
🔵 Question 1:
Who discovered the cell?
🔴 1️⃣ Robert Brown
🟢 2️⃣ Robert Hooke
🟡 3️⃣ Leeuwenhoek
🔵 4️⃣ Schleiden
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Robert Hooke
🔵 Question 2:
Cell theory was proposed by:
🔴 1️⃣ Schleiden and Schwann
🟢 2️⃣ Hooke and Brown
🟡 3️⃣ Virchow and Leeuwenhoek
🔵 4️⃣ Darwin and Lamarck
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Schleiden and Schwann
🔵 Question 3:
“Omnis cellula-e-cellula” was stated by:
🔴 1️⃣ Robert Hooke
🟢 2️⃣ Rudolf Virchow
🟡 3️⃣ Schwann
🔵 4️⃣ Schleiden
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Rudolf Virchow
🔵 Question 4:
Prokaryotic cells lack:
🔴 1️⃣ DNA
🟢 2️⃣ Nucleus
🟡 3️⃣ Plasma membrane
🔵 4️⃣ Cytoplasm
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Nucleus
🔵 Question 5:
Which of the following is a prokaryote?
🔴 1️⃣ Amoeba
🟢 2️⃣ Bacterium
🟡 3️⃣ Euglena
🔵 4️⃣ Paramecium
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Bacterium
🔵 Question 6:
Largest cell in the human body is:
🔴 1️⃣ Nerve cell
🟢 2️⃣ Ovum
🟡 3️⃣ Muscle cell
🔵 4️⃣ RBC
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Ovum
🔵 Question 7:
Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell?
🔴 1️⃣ Ribosome
🟢 2️⃣ Mitochondria
🟡 3️⃣ Nucleus
🔵 4️⃣ Golgi body
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Mitochondria
🔵 Question 8:
Which cell organelle is involved in photosynthesis?
🔴 1️⃣ Mitochondria
🟢 2️⃣ Chloroplast
🟡 3️⃣ Lysosome
🔵 4️⃣ Ribosome
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Chloroplast
🔵 Question 9:
The plasma membrane is made up of:
🔴 1️⃣ Carbohydrates and proteins
🟢 2️⃣ Lipids and proteins
🟡 3️⃣ Proteins only
🔵 4️⃣ Lipids only
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Lipids and proteins
🔵 Question 10:
Which model explains plasma membrane structure?
🔴 1️⃣ Sandwich model
🟢 2️⃣ Fluid mosaic model
🟡 3️⃣ Lamellar model
🔵 4️⃣ Unit membrane model
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Fluid mosaic model
🔵 Question 11:
Ribosomes are the site of:
🔴 1️⃣ DNA synthesis
🟢 2️⃣ Protein synthesis
🟡 3️⃣ Lipid synthesis
🔵 4️⃣ Respiration
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Protein synthesis
🔵 Question 12:
The function of lysosomes is:
🔴 1️⃣ Protein synthesis
🟢 2️⃣ Intracellular digestion
🟡 3️⃣ Respiration
🔵 4️⃣ Photosynthesis
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Intracellular digestion
🔵 Question 13:
The nucleolus is mainly composed of:
🔴 1️⃣ DNA and lipid
🟢 2️⃣ RNA and protein
🟡 3️⃣ DNA and protein
🔵 4️⃣ Carbohydrate and protein
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ RNA and protein
🔵 Question 14:
Centrioles are found in:
🔴 1️⃣ Plant cells
🟢 2️⃣ Animal cells
🟡 3️⃣ Both plant and animal
🔵 4️⃣ None
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Animal cells
🔵 Question 15:
The main function of Golgi apparatus is:
🔴 1️⃣ ATP production
🟢 2️⃣ Packaging and secretion
🟡 3️⃣ Protein synthesis
🔵 4️⃣ Digestion
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Packaging and secretion
🔵 Question 16:
Which of the following is a double membrane-bound organelle?
🔴 1️⃣ Lysosome
🟢 2️⃣ Mitochondria
🟡 3️⃣ Ribosome
🔵 4️⃣ Centrosome
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Mitochondria
🔵 Question 17:
Peroxisomes are involved in:
🔴 1️⃣ Photosynthesis
🟢 2️⃣ Fat metabolism
🟡 3️⃣ Respiration
🔵 4️⃣ Digestion
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Fat metabolism
🔵 Question 18:
Cell wall of plants is mainly composed of:
🔴 1️⃣ Pectin
🟢 2️⃣ Cellulose
🟡 3️⃣ Lignin
🔵 4️⃣ Hemicellulose
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Cellulose
🔵 Question 19:
The plasma membrane allows certain molecules to pass through — this property is called:
🔴 1️⃣ Impermeability
🟢 2️⃣ Selective permeability
🟡 3️⃣ Osmosis
🔵 4️⃣ Diffusion
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Selective permeability
🔵 Question 20:
Cristae are found in:
🔴 1️⃣ Nucleus
🟢 2️⃣ Mitochondria
🟡 3️⃣ Golgi
🔵 4️⃣ ER
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Mitochondria
🔵 Question 21:
The functional unit of the cell is:
🔴 1️⃣ Nucleus
🟢 2️⃣ Protoplasm
🟡 3️⃣ Organelle
🔵 4️⃣ Cell itself
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ Cell itself
🔵 Question 22:
The 70S ribosomes are found in:
🔴 1️⃣ Eukaryotic cytoplasm
🟢 2️⃣ Mitochondria and prokaryotes
🟡 3️⃣ Only nucleus
🔵 4️⃣ ER
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Mitochondria and prokaryotes
🔵 Question 23:
Which organelle forms the spindle during cell division?
🔴 1️⃣ Lysosome
🟢 2️⃣ Centriole
🟡 3️⃣ Golgi
🔵 4️⃣ Ribosome
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Centriole
🔵 Question 24:
The outermost layer in an animal cell is:
🔴 1️⃣ Cell wall
🟢 2️⃣ Plasma membrane
🟡 3️⃣ Cytoplasm
🔵 4️⃣ Glycocalyx
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Plasma membrane
🔵 Question 25:
The unit of inheritance is:
🔴 1️⃣ Chromosome
🟢 2️⃣ Gene
🟡 3️⃣ Nucleolus
🔵 4️⃣ Ribosome
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Gene
🔵 Question 26:
Which of the following lacks membrane-bound organelles?
🔴 1️⃣ Plant cell
🟢 2️⃣ Animal cell
🟡 3️⃣ Bacterial cell
🔵 4️⃣ Fungal cell
✔️ Answer: 3️⃣ Bacterial cell
🔵 Question 27:
The site of lipid synthesis is:
🔴 1️⃣ Rough endoplasmic reticulum
🟢 2️⃣ Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
🟡 3️⃣ Ribosomes
🔵 4️⃣ Golgi apparatus
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
🔵 Question 28:
Polysomes are:
🔴 1️⃣ Cluster of ribosomes on a single mRNA
🟢 2️⃣ Ribosomes without mRNA
🟡 3️⃣ Ribosomes in mitochondria
🔵 4️⃣ Ribosomes in chloroplast
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Cluster of ribosomes on a single mRNA
🔵 Question 29:
The fluidity of plasma membrane is mainly due to:
🔴 1️⃣ Proteins
🟢 2️⃣ Phospholipids
🟡 3️⃣ Carbohydrates
🔵 4️⃣ Cholesterol
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Phospholipids
🔵 Question 30:
Cristae increase surface area in:
🔴 1️⃣ Golgi apparatus
🟢 2️⃣ Mitochondria
🟡 3️⃣ ER
🔵 4️⃣ Nucleus
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Mitochondria
🔵 Question 31:
The main function of rough ER is:
🔴 1️⃣ Lipid synthesis
🟢 2️⃣ Protein synthesis
🟡 3️⃣ Detoxification
🔵 4️⃣ ATP synthesis
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Protein synthesis
🔵 Question 32:
Which organelle is called “suicidal bag”?
🔴 1️⃣ Ribosome
🟢 2️⃣ Lysosome
🟡 3️⃣ Golgi
🔵 4️⃣ Mitochondria
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Lysosome
🔵 Question 33:
In plant cells, plasmodesmata connect:
🔴 1️⃣ Vacuoles
🟢 2️⃣ Cytoplasm of adjacent cells
🟡 3️⃣ Nuclei
🔵 4️⃣ Cell walls
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Cytoplasm of adjacent cells
🔵 Question 34:
Ribosomes are composed of:
🔴 1️⃣ DNA and protein
🟢 2️⃣ RNA and protein
🟡 3️⃣ RNA and lipid
🔵 4️⃣ DNA and lipid
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ RNA and protein
🔵 Question 35:
Prokaryotic DNA is:
🔴 1️⃣ Linear and with histones
🟢 2️⃣ Circular and without histones
🟡 3️⃣ Circular with histones
🔵 4️⃣ Linear without histones
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Circular and without histones
🔵 Question 36:
The primary function of vacuole in plant cells is:
🔴 1️⃣ Photosynthesis
🟢 2️⃣ Storage and turgor maintenance
🟡 3️⃣ Respiration
🔵 4️⃣ Transport
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Storage and turgor maintenance
🔵 Question 37:
Middle lamella is made up of:
🔴 1️⃣ Pectin
🟢 2️⃣ Cellulose
🟡 3️⃣ Lignin
🔵 4️⃣ Hemicellulose
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Pectin
🔵 Question 38:
Which of the following is not a component of endomembrane system?
🔴 1️⃣ ER
🟢 2️⃣ Golgi
🟡 3️⃣ Lysosome
🔵 4️⃣ Mitochondria
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ Mitochondria
🔵 Question 39:
In which phase of cell cycle are chromosomes not visible?
🔴 1️⃣ Prophase
🟢 2️⃣ Interphase
🟡 3️⃣ Metaphase
🔵 4️⃣ Anaphase
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Interphase
🔵 Question 40:
The genetic material of a cell is present in:
🔴 1️⃣ Ribosome
🟢 2️⃣ Nucleus
🟡 3️⃣ Cytoplasm
🔵 4️⃣ Golgi
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Nucleus
🔵 Question 41:
Lysosomes originate from:
🔴 1️⃣ ER
🟢 2️⃣ Golgi apparatus
🟡 3️⃣ Nucleus
🔵 4️⃣ Ribosomes
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Golgi apparatus
🔵 Question 42:
The basic structural and functional unit of life is:
🔴 1️⃣ Nucleus
🟢 2️⃣ Cell
🟡 3️⃣ Organelle
🔵 4️⃣ Cytoplasm
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Cell
🔵 Question 43:
Cell wall is absent in:
🔴 1️⃣ Fungi
🟢 2️⃣ Animal cells
🟡 3️⃣ Bacteria
🔵 4️⃣ Algae
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Animal cells
🔵 Question 44:
The nuclear membrane is continuous with:
🔴 1️⃣ Plasma membrane
🟢 2️⃣ Endoplasmic reticulum
🟡 3️⃣ Golgi
🔵 4️⃣ Lysosome
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Endoplasmic reticulum
🔵 Question 45:
Which of the following is absent in mature RBCs?
🔴 1️⃣ Nucleus
🟢 2️⃣ Mitochondria
🟡 3️⃣ ER
🔵 4️⃣ All of these
✔️ Answer: 4️⃣ All of these
🔵 Question 46:
Which structure is responsible for maintaining cell shape?
🔴 1️⃣ Cytoskeleton
🟢 2️⃣ Nucleus
🟡 3️⃣ Lysosome
🔵 4️⃣ Ribosome
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Cytoskeleton
🔵 Question 47:
The functional association of ER, Golgi and vesicles forms the:
🔴 1️⃣ Endomembrane system
🟢 2️⃣ Cytoskeleton
🟡 3️⃣ Endosome
🔵 4️⃣ Peroxisome
✔️ Answer: 1️⃣ Endomembrane system
🔵 Question 48:
The process of engulfing solid particles by cell is:
🔴 1️⃣ Exocytosis
🟢 2️⃣ Phagocytosis
🟡 3️⃣ Pinocytosis
🔵 4️⃣ Diffusion
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Phagocytosis
🔵 Question 49:
The ribosomes attached to ER form:
🔴 1️⃣ Smooth ER
🟢 2️⃣ Rough ER
🟡 3️⃣ Golgi complex
🔵 4️⃣ None
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Rough ER
🔵 Question 50:
Which of the following controls all cellular activities?
🔴 1️⃣ Cytoplasm
🟢 2️⃣ Nucleus
🟡 3️⃣ Plasma membrane
🔵 4️⃣ Golgi body
✔️ Answer: 2️⃣ Nucleus
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
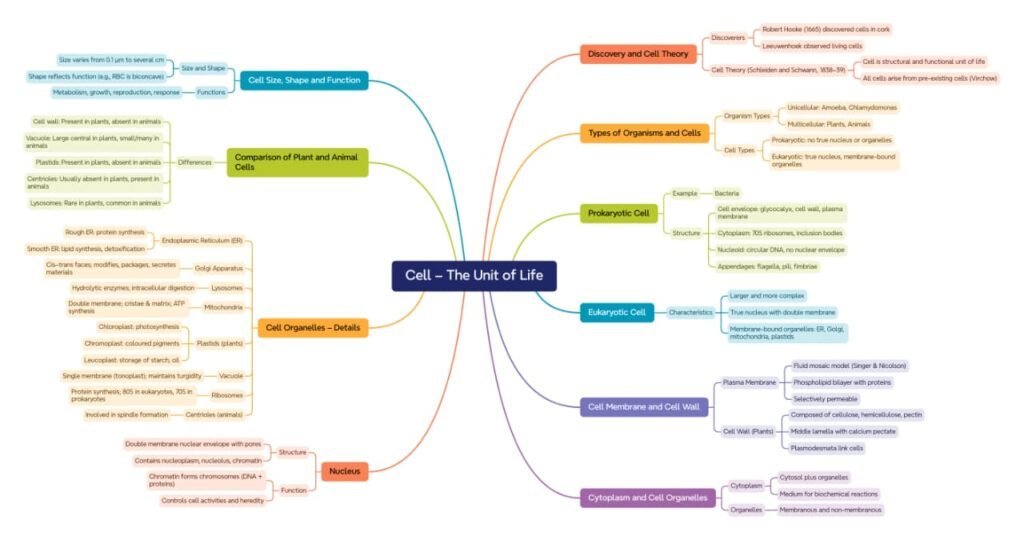
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
