Class 11 : Geography (In English) – Lesson 16. Structure and Physiography
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
✨ Introduction
This chapter explains the physical structure and physiographic divisions of भारत (India). It highlights the geological history of the Indian landmass, its evolution through tectonic movements, and how these factors have shaped the current physiographic features of the country.
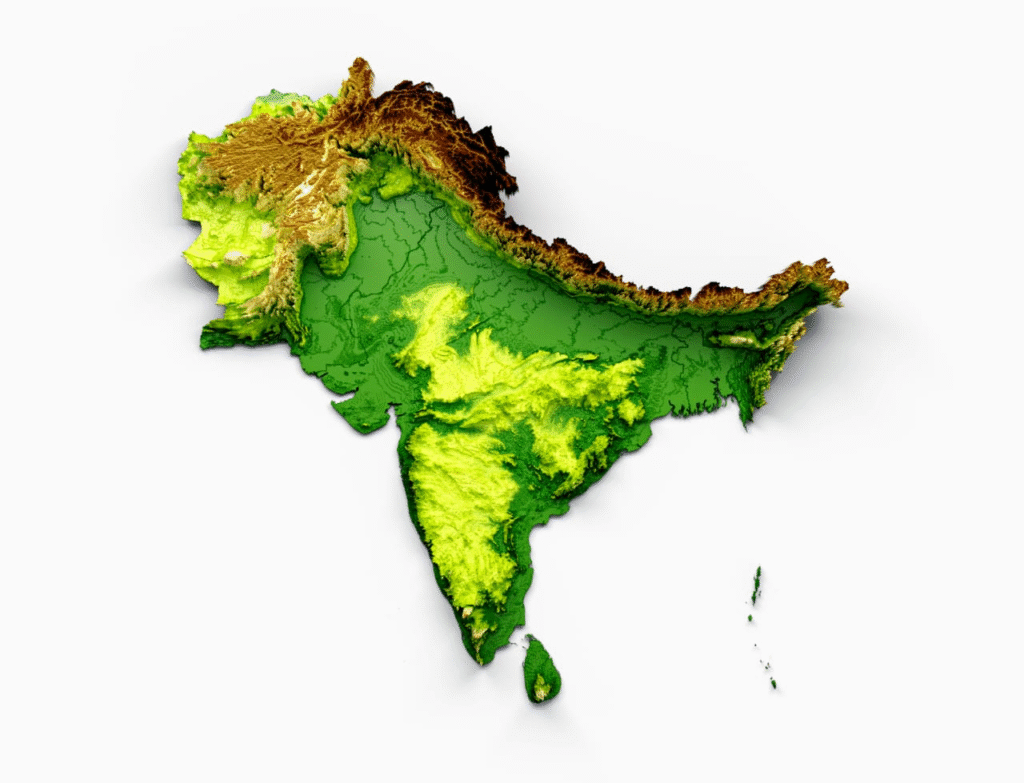
🔵 Geological Structure of India
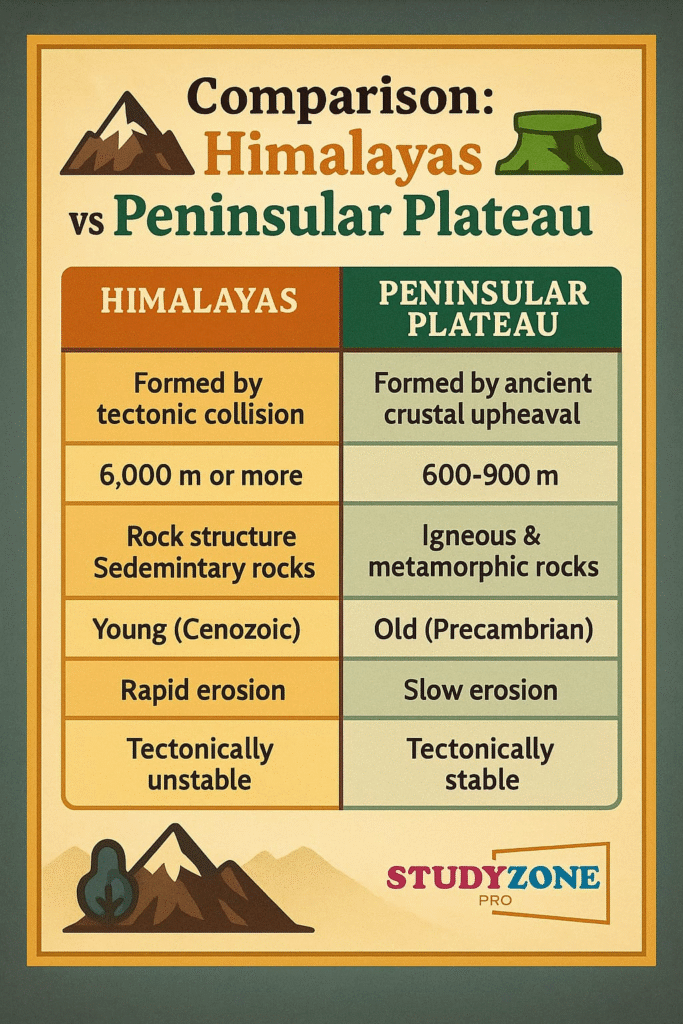
➡️ The geological structure of India) reveals how the Earth’s interior forces shaped its surface. The Peninsular India) is considered the most ancient part, while the Himalayan mountains are geologically young.
🟢 Geological History:
1️⃣ Precambrian rocks of Peninsular India) are among the oldest in the world.
2️⃣ The Himalayas formed later due to the collision of the Indian Plate with the Eurasian Plate).
🔴 Formation of Himalayas
➡️ The Himalayas are a result of tectonic collision between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate) about 40-50 million years ago.
🌿 Stages of Formation:
✔️ Tethys Sea existed between these plates.
✔️ Sediments accumulated in Tethys got compressed.
✔️ Collision caused uplift forming Himalayas.
✏️ Note: Himalayas are still rising due to ongoing tectonic activities.
🟡 The Northern Plains
➡️ The Northern Plains are formed by the alluvial deposits from major rivers – Indus, Ganga,and Brahmaputra.
🧠 Features:
✔️ Flat and fertile land.
✔️ Created through deposition processes over millions of years.
✔️ Supports dense population due to agriculture.
🔵 Peninsular Plateau
➡️ The Peninsular Plateau is the oldest landmass of India. It is part of the Gondwana landmass which broke from Pangaea).
🌿 Features:
✔️ Irregular terrain with hills and valleys.
✔️ Composed mainly of igneous and metamorphic rocks.
✔️ Rich in mineral resources.
🧠 Important Subdivisions:
1️⃣ Central Highlands
2️⃣ Deccan Plateau
🟢 Coastal Plains
➡️ India has two coastal plains – Eastern Coastal Plain and Western Coastal Plain.
🌿 Western Coastal Plain:
✔️ Narrow, between Western Ghats and Arabian Sea.
✔️ Contains estuaries.
🌿 Eastern Coastal Plain:
✔️ Wider, between Eastern Ghats and Bay of Bengal.
✔️ Contains deltas of Ganga, Godavari), Kaveri) rivers.
🔴 Islands of India)
➡️ India) has two major island groups:
1️⃣ Lakshadweep Islands (Arabian Sea)
2️⃣ Andaman and Nicobar Islands (Bay of Bengal)
🌿 Lakshadweep:
✔️ Coral origin
✔️ Flat and small
🌿 Andaman and Nicobar:
✔️ Volcanic origin
✔️ Mountainous and forested
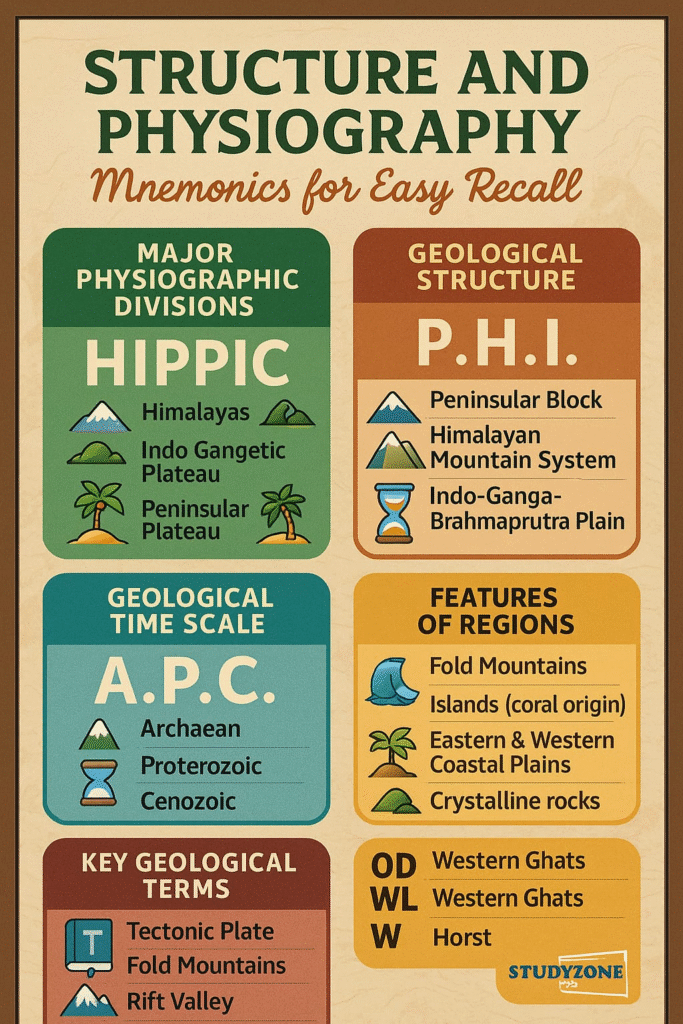
🟡 Physiographic Divisions of India.
India’s vast land can be divided into six physiographic divisions:
🔵 1. The Northern and North-Eastern Mountains
➡️ Includes Himalayas and Purvanchal hills.
➡️ Young, fold mountains.
➡️ Acts as natural barrier and climatic divider.
🔵 2. The Northern Plains
➡️ Extensive, flat, alluvial plains.
➡️ Rich in agriculture and dense settlements.
🔵 3. The Peninsular Plateau
➡️ Oldest and most stable part.
➡️ Source of many rivers.
🔵 4. The Indian Desert, Thar desert
➡️ Located in Rajasthan .
➡️ Sandy terrain, arid climate.
🔵 5. The Coastal Plains
➡️ Eastern and Western coastal stretches.
➡️ Important for trade, ports, and agriculture.
🔵 6. The Islands
➡️ Strategically and ecologically significant.
➡️ Supports biodiversity and tourism.
🟢 Real-life Connection and Application
➡️ Agriculture: The fertile plains and plateaus support varied crops.
➡️ Minerals: Plateau regions are mineral-rich aiding industries.
➡️ Climate Impact: Mountains protect from cold winds, influence monsoon.
➡️ Transport and Trade: Coastal plains enable port activities and trade.
🔴 Why This Lesson Matters:
✔️ Helps understand India’s physical geography.
✔️ Explains the formation of landforms through natural forces.
✔️ Highlights India’s diverse physical features influencing lifestyle, economy, and environment.
📝 Quick Recap:
🔵 Himalayas – Young fold mountains, still rising
🟢 Northern Plains – Formed by alluvium, highly fertile
🔴 Peninsular Plateau – Oldest, mineral-rich, stable
🟡 Desert – Rajasthan, arid zone
🌿 Coastal Plains – Eastern, Western divisions
✔️ Islands – Lakshadweep (coral), Andaman-Nicobar (volcanic)
✨ Summary (300 Words)
🔵 Structure and Physiography of India explains the geological history and physical divisions of the country.
🟢 Himalayas formed through tectonic collision uplift the north. They act as a climatic barrier and a source of perennial rivers.
🔴 The Northern Plains are fertile alluvial deposits from the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra rivers, supporting dense population and agriculture.
🟡 The Peninsular Plateau is the oldest, rich in minerals, with highlands and river basins. Divided into Central Highlands and Deccan Plateau, it shapes the country’s geology.
🌿 The Indian Desert in Rajasthan is arid with sand dunes and scarce water.
➡️ Coastal Plains are divided into Eastern (delta-rich, broad) and Western (narrow, estuarine) regions supporting agriculture, fishing, and trade.
🏝️ Islands: Lakshadweep (coral, flat) and Andaman-Nicobar (volcanic, hilly) are significant for biodiversity and security.
✔️ India’s physical structure defines its agriculture, economy, climate, and biodiversity. Mountains, plains, plateaus, deserts, coasts, and islands together form the rich physical heritage shaping life in India.
➡️ Understanding this geography enhances awareness of resource management, disaster mitigation, and sustainable development.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Q 1. Multiple Choice Questions
(i) Which one of the water bodies separates the Andaman from the Nicobar?
(A) 11° Channel
(B) Gulf of Mannar
(C) 10° Channel
(D) Andaman Sea
✅ Answer: (C) 10° Channel
(ii) On which of the following hill ranges is the ‘Dodabetta’ peak situated?
(A) Nilgiri hills
(B) Anaimalai hills
(C) Cardamom hills
(D) Nallamala hills
✅ Answer: (A) Nilgiri hills
🔴 Q 2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) If a person is to travel to Lakshadweep, from which coastal plain does he prefer and why?
✅ Answer: A person travelling to Lakshadweep will prefer the western coastal plain because it lies adjacent to the Arabian Sea, from where the Lakshadweep islands are easily accessible through ports such as Kochi and Mangaluru.
(ii) Where in India will you find a cold desert? Name some important ranges of this region.
✅ Answer: A cold desert is found in Ladakh region of India. The important ranges found here include the Karakoram Range, Ladakh Range, Zanskar Range, and the Greater Himalayas. This region experiences extreme cold and arid climate.
(iii) Why is the western coastal plain devoid of any delta?
✅ Answer: The western coastal plain is devoid of any delta because the west-flowing rivers are short and fast-moving. They do not carry enough alluvium to form deltas and instead form estuaries as they meet the Arabian Sea.
🟢 Q 3. Answer the following questions in not more than 125 words.
(i) Make a comparison of the island groups of the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
✅ Answer: The Arabian Sea islands consist of the Lakshadweep Islands which are of coral origin, flat, and small in size. They are located near the Kerala coast and comprise tiny atolls and reefs. On the other hand, the Bay of Bengal islands include the Andaman and Nicobar Islands which are larger, hilly, and of volcanic origin. These islands are forested and possess significant biodiversity. While the Lakshadweep Islands have no volcanoes, the Andaman Islands even have an active volcano—Barren Island. The Bay of Bengal islands are strategically important for India’s defence and trade as they lie close to Southeast Asia.
(ii) What are the important geomorphological features found in the river valley plains?
✅ Answer: The river valley plains exhibit significant geomorphological features such as ox-bow lakes, meanders, floodplains, natural levees, point bars, and braided streams. These features develop through the depositional and erosional activities of rivers. These plains are composed of alluvial soil deposited over centuries, making them among the most fertile lands in India. Such features are highly beneficial for agriculture and settlement due to the presence of rich soil and availability of water.
(iii) If you move from Badrinath to Sundarbans delta along the course of the river Ganga, what major geomorphological features will you come across?
✅ Answer: Travelling from Badrinath to Sundarbans delta along the Ganga river, one will witness varied geomorphological features such as gorges, V-shaped valleys, rapids and waterfalls in the upper reaches of the Himalayas. As the river descends into the middle course, features like meanders, floodplains, ox-bow lakes, natural levees become prominent. In the lower course, especially in the delta region of Sundarbans, the river splits into distributaries, forming the largest delta with tidal creeks, mangrove forests, and marshes. This journey showcases the transformation of the landscape shaped by river processes from source to mouth.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔵 1️⃣ MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs) (Q1–Q10)
🌷 Q1. The oldest landmass of भारत (India) is:
(A) Northern Plains
(B) Peninsular Plateau
(C) Western Coastal Plains
(D) Himalayas
✅ Answer: (B) Peninsular Plateau
🌷 Q2. The youngest mountain range in भारत (India) is:
(A) Vindhyan Range
(B) Aravalli Range
(C) Himalayas
(D) Satpura Range
✅ Answer: (C) Himalayas
🌷 Q3. Which plain is formed by the deposition of alluvial soil?
(A) Northern Plains
(B) Deccan Plateau
(C) Western Ghats
(D) Coastal Plains
✅ Answer: (A) Northern Plains
🌷 Q4. Which one of the following rivers forms a delta before meeting the sea?
(A) Narmada
(B) Tapi
(C) Godavari
(D) Mahi
✅ Answer: (C) Godavari
🌷 Q5. The Thar Desert lies in which state?
(A) Rajasthan
(B) Gujarat
(C) Punjab
(D) Haryana
✅ Answer: (A) Rajasthan
🌷 Q6. The Himalayas are an example of:
(A) Block mountains
(B) Volcanic mountains
(C) Fold mountains
(D) Residual mountains
✅ Answer: (C) Fold mountains
🌷 Q7. Which part of भारत (India) contains coral islands?
(A) Lakshadweep
(B) Andaman
(C) Nicobar
(D) Sundarbans
✅ Answer: (A) Lakshadweep
🌷 Q8. Which rivers form estuaries on the western coast?
(A) Godavari and Krishna
(B) Mahanadi and Kaveri
(C) Narmada and Tapi
(D) Brahmaputra and Ganga
✅ Answer: (C) Narmada and Tapi
🌷 Q9. Which of the following hills are not part of the Purvanchal Hills?
(A) Patkai Hills
(B) Naga Hills
(C) Khasi Hills
(D) Mizo Hills
✅ Answer: (C) Khasi Hills
🌷 Q10. Which sea is located to the west of भारत (India)?
(A) Arabian Sea
(B) Bay of Bengal
(C) Red Sea
(D) Pacific Ocean
✅ Answer: (A) Arabian Sea
🟢 2️⃣ FILL IN THE BLANKS (Q11–Q13)
🌿 Q11. The Himalayas were formed due to the collision of plate and the plate.
✅ Answer: Indian) plate and Eurasian) plate
🌿 Q12. The __ Plateau is rich in minerals and resources.
✅ Answer: Deccan Plateau
🌿 Q13. The rivers of the western coastal plains form __ instead of deltas.
✅ Answer: estuaries
🔴 3️⃣ TRUE / FALSE (Q14–Q15)
🍀 Q14. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are volcanic in origin.
✅ Answer: True
🍀 Q15. The Western Coastal Plains are broader than the Eastern Coastal Plains.
✅ Answer: False
🟡 4️⃣ ASSERTION AND REASON (Q16–Q17)
🌼 Q16.
Assertion (A): The Northern Plains are densely populated.
Reason (R): They are fertile and suitable for agriculture.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
✅ Answer: (A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
🌼 Q17.
Assertion (A): The Peninsular Plateau is tectonically stable.
Reason (R): It consists of ancient crystalline rocks.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
✅ Answer: (A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
🔵 5️⃣ SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (30 words limit) (Q18–Q20)
💠 Q18. Why are Himalayas important for India?
✅ Answer: Himalayas protect India from cold winds, act as a climatic barrier, and are the source of perennial rivers and biodiversity.
💠 Q19. What is the significance of coastal plains?
✅ Answer: Coastal plains support agriculture, trade through ports, fishing, and tourism; Eastern plains are deltaic, Western plains have estuaries.
💠 Q20. Why is the Deccan Plateau important for India?
✅ Answer: The Deccan Plateau is rich in minerals, supports agriculture, and is the source of many rivers.
🟢 6️⃣ MID-LENGTH ANSWER QUESTIONS (60 words limit) (Q21–Q23)
🌟 Q21. Describe the features of the Northern Plains.
✅ Answer: Northern Plains are alluvial, flat, and fertile. They are formed by deposits from the Ganga, Yamuna, and Brahmaputra rivers. The plains support dense population due to agriculture and are subdivided into Bhabar, Terai, Bhangar, and Khadar regions.
🌟 Q22. What are the characteristics of Peninsular Plateau?
✅ Answer: The Peninsular Plateau is the oldest part of India, consisting of igneous and metamorphic rocks. It has uneven terrain, mineral-rich regions, and is divided into Central Highlands and Deccan Plateau, forming the source of rivers like Narmada and Godavari.
🌟 Q23. What are the major characteristics of the Indian Desert?
✅ Answer: The Indian Desert, also called the Thar Desert, is located in Rajasthan. It has sand dunes, extreme temperatures, scanty rainfall, and dry climate. Rivers are seasonal and vegetation is sparse.
🔴 7️⃣ LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS (120 words limit) (Q24–Q25)
🌻 Q24. Explain the significance of India’s physiographic divisions.
✅ Answer: India’s physiographic divisions reflect its diverse landforms – Himalayas, Northern Plains, Peninsular Plateau, Desert, Coastal Plains, and Islands. Himalayas influence climate, provide rivers and act as natural barriers. Plains are agriculturally rich. Plateau supports industries through minerals. Desert shapes lifestyle in Rajasthan. Coastal regions aid trade and agriculture. Islands enhance biodiversity and strategic security. These divisions impact climate, economy, resources, and population distribution.
🌻 Q25. Describe the characteristics and importance of the Coastal Plains of India.
✅ Answer: The Coastal Plains of India include the Eastern and Western coastal plains. Eastern Plains are broader with fertile deltas like Ganga and Godavari, supporting agriculture and fisheries. Western Plains are narrow with estuaries, supporting ports and trade. Coastal regions provide access to marine resources, enhance tourism, support dense population, and play a crucial role in India’s economy.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MNEMONICS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
