Class 11 : Poltical Science (In English) – Lesson 2. Rights in the Indian Constitution
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔴 Introduction
This chapter, “Rights in Indian Constitution”, explains the meaning, importance, and protection of rights in a democratic society. Rights are essential for ensuring justice, liberty, equality, and dignity of individuals. They are legal guarantees that prevent misuse of power by the government and empower citizens to live freely and with respect.
🟢 What are Rights?
➡️ Rights are justified claims that individuals can make on society and the state.
🌿 Rights allow individuals to live with dignity, freedom, and security.
🧠 Importance of Rights:
✔️ Rights protect people from unjust government actions.
✔️ Rights enable individuals to express themselves freely and participate in governance.
✔️ Rights ensure equality and prevent discrimination or exploitation.
✏️ Note: Rights are essential in a democracy where citizens hold the government accountable.
🔵 Why Do We Need Rights?
✔️ Protection Against Exploitation:
Rights prevent the misuse of power by government officials or the powerful sections of society.
✔️ Ensuring Justice and Fairness:
Rights guarantee fair treatment for everyone regardless of caste, religion, or gender.
✔️ Participation in Democratic Processes:
Rights allow citizens to vote, express opinions, and participate in forming the government.
💡 Concept: Rights are the foundation of democracy and ensure peaceful and just society.
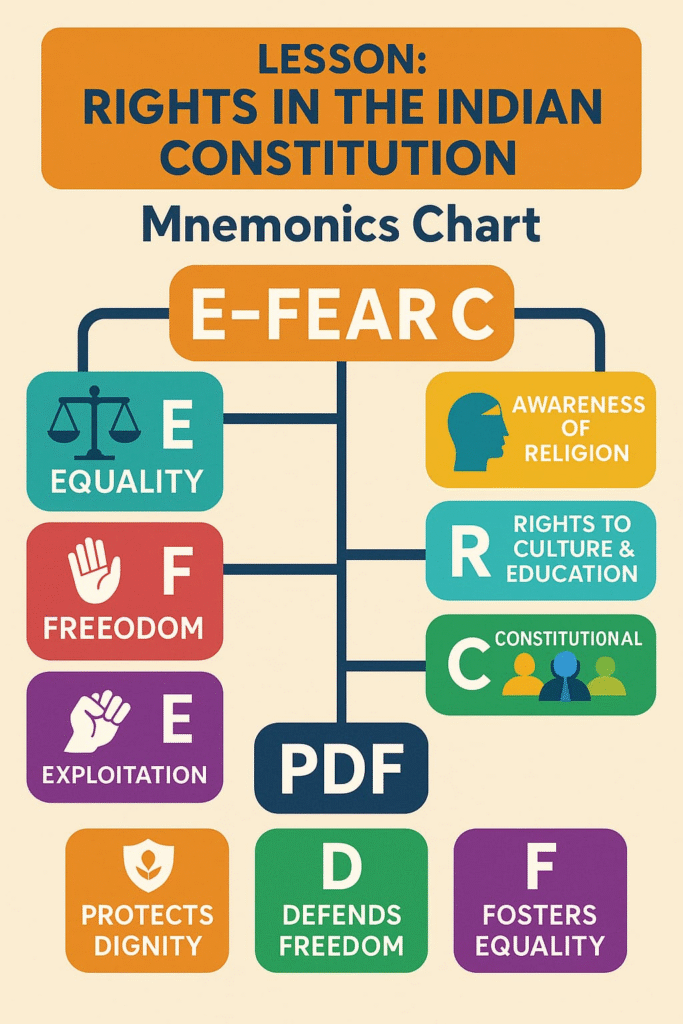
🟡 Fundamental Rights in Indian Constitution
The Indian Constitution provides six types of Fundamental Rights under Part III. These rights are enforceable by law through courts.
🔵 1. Right to Equality (Articles 14-18)
✔️ Equality before law
✔️ Prohibition of discrimination
✔️ Equality of opportunity in public employment
✔️ Abolition of untouchability
✔️ Abolition of titles
🧠 Purpose: To ensure every citizen is treated equally without bias.
🔴 2. Right to Freedom (Articles 19-22)
✔️ Freedom of speech and expression
✔️ Freedom to assemble peacefully
✔️ Freedom to form associations
✔️ Freedom to move freely
✔️ Freedom to reside and settle anywhere
✔️ Freedom to practice any profession
✏️ Note: These freedoms are subject to reasonable restrictions in the interest of sovereignty, public order, and morality.
🟢 3. Right Against Exploitation (Articles 23-24)
✔️ Prohibition of human trafficking and forced labour
✔️ Prohibition of child labour under 14 years of age
💡 Concept: These rights protect vulnerable sections from exploitation.
🔵 4. Right to Freedom of Religion (Articles 25-28)
✔️ Freedom of conscience
✔️ Right to profess, practice, and propagate religion
✔️ Freedom to manage religious affairs
✔️ No compulsion to pay taxes for promotion of any religion
✔️ Freedom to attend religious worship
🧠 Purpose: India being a secular state, these rights ensure religious freedom to all.
🔴 5. Cultural and Educational Rights (Articles 29-30)
✔️ Protection of interests of minorities
✔️ Right to conserve language, script, or culture
✔️ Right of minorities to establish educational institutions
🌿 Importance: These rights promote cultural diversity and protect minority identities.
🟢 6. Right to Constitutional Remedies (Article 32)
✔️ Right to approach Supreme Court or High Court to enforce Fundamental Rights.
✔️ Called the “heart and soul of the Constitution” by Dr. B.R. Ambedkar.
✏️ Note: Courts can issue writs like Habeas Corpus, Mandamus, Prohibition, Quo Warranto, and Certiorari.
🔵 Directive Principles and Rights
➡️ Directive Principles of State Policy guide the government to promote welfare, justice, and equality.
➡️ Though not enforceable by courts, they complement Fundamental Rights.
💡 Concept: Together, they aim to achieve social and economic justice.
🟡 Relationship Between Fundamental Rights and Duties
✔️ Rights empower citizens; Duties remind them of their responsibilities.
✔️ Fundamental Duties were added to ensure citizens contribute positively to the nation.
🔴 Rights for Non-Citizens
Some rights apply only to Indian citizens, like Article 19. Others, like protection of life and liberty (Article 21), apply to all persons within India.
🟢 Amendment and Evolution of Rights
✔️ Over time, rights have evolved through judicial interpretations.
✔️ Right to Education (Article 21A) was added as Fundamental Right by 86th Amendment.
✔️ Right to Privacy declared part of Article 21 by Supreme Court (2017).
🔵 How Courts Protect Rights
✔️ Judiciary ensures laws comply with Fundamental Rights.
✔️ Courts strike down any law violating these rights.
✔️ Judiciary strengthens democracy by upholding rights.
🟡 Significance of Fundamental Rights
✔️ Safeguard dignity and freedom of individuals.
✔️ Strengthen democracy by limiting state power.
✔️ Provide legal protection and remedy.
🔴 Challenges to Rights
➡️ Emergency situations may suspend rights like freedom.
➡️ Restrictions can lead to debates over balancing security and freedom.
🔵 Examples of Landmark Cases
✔️ Kesavananda Bharati Case (1973): Protected Basic Structure of Constitution.
✔️ Maneka Gandhi Case (1978): Expanded interpretation of Article 21.
✔️ Puttaswamy Case (2017): Declared Right to Privacy fundamental.
🟢 Why This Lesson Matters
💡 Importance in Real Life:
✔️ Helps individuals understand their rights and how to safeguard them.
✔️ Educates citizens about the legal framework protecting freedoms.
✔️ Encourages responsible participation in democracy.
⚡ In Exams:
A strong foundation for understanding Indian polity, law, and governance questions.
📝 QUICK RECAP:
🔵 Fundamental Rights = Core of democracy
🟢 Equality, Freedom, Protection, Religious Rights
🔴 Rights protect dignity, freedom, justice
🟡 Judiciary ensures enforcement
🔵 Rights + Duties = Balanced citizenship
🔵 SUMMARY (300 WORDS)
The chapter “Rights in Indian Constitution” explains the necessity, meaning, and protection of rights in a democratic society. Rights are essential claims citizens make on the state to lead a life of dignity, freedom, and equality. They protect individuals from arbitrary government actions and uphold democracy.
The Constitution provides six types of Fundamental Rights: Right to Equality, Right to Freedom, Right Against Exploitation, Right to Freedom of Religion, Cultural and Educational Rights, and Right to Constitutional Remedies. These rights empower citizens, promote justice, and uphold individual dignity. Some rights are available only to Indian citizens, while others apply universally.
The judiciary protects these rights through mechanisms like judicial review and writs. Rights evolve through amendments and court decisions, such as the inclusion of Right to Education and Right to Privacy.
Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles together aim to achieve social and economic justice. Rights and Duties complement each other; citizens enjoy freedoms but must also respect the rights of others and contribute to the nation’s welfare.
This chapter reinforces the importance of rights in securing a just, free, and equal society where citizens can live without fear or discrimination. Understanding rights is crucial for active, informed participation in democracy and safeguarding the Constitution’s spirit.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1:
Write true or false against each of these statements:
(a) A Bill of Rights lays down the rights enjoyed by the people of a country.
(b) A Bill of Rights protects the liberties of an individual.
(c) Every country of the world has a Bill of Rights.
(d) The Constitution guarantees remedy against violation of Rights.
🟢 Answer 1:
(a) ✅ True
(b) ✅ True
(c) ❌ False
(d) ✅ True
🌿 Explanation:
Not every country has a Bill of Rights. The Indian Constitution guarantees remedy through the Right to Constitutional Remedies (Article 32).
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Question 2:
Which of the following is the best description of Fundamental Rights?
(a) All the rights an individual should have.
(b) All the rights given to citizens by law.
(c) The rights given and protected by the Constitution.
(d) The rights given by the Constitution that cannot ever be restricted.
🟢 Answer 2:
✅ (c) The rights given and protected by the Constitution.
🌿 Explanation:
Fundamental Rights are guaranteed by the Constitution and can be enforced through courts.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Question 3:
Read the following situations. Which Fundamental Right is being used or violated in each case and how?
(a) Overweight male cabin crew are allowed to get promotion in the national airlines but their women colleagues who gain weight are penalised.
(b) A director makes a documentary film that criticises the policies of the government.
(c) People displaced by a big dam take out a rally demanding rehabilitation.
(d) Andhra society runs Telugu medium schools outside Andhra Pradesh.
🟢 Answer 3:
(a) Right to Equality (Article 14–15) violated due to discrimination.
(b) Right to Freedom of Speech and Expression (Article 19) exercised.
(c) Right to Freedom of Assembly and Protest (Article 19) exercised.
(d) Cultural and Educational Rights (Article 29–30) exercised.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Question 4:
Which of the following is a correct interpretation of the Cultural and Educational Rights?
(a) Only children belonging to the minority group that has opened educational institution can study there.
(b) Government schools must ensure that children of the minority group will be introduced to their belief and culture.
(c) Linguistic and religious minorities can open schools for their children and keep it reserved for them.
(d) Linguistic and religious minorities can demand that their children must not study in any educational institution except those managed by their own community.
🟢 Answer 4:
✅ (c) Linguistic and religious minorities can open schools for their children and keep it reserved for them.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Question 5:
Which of the following is a violation of Fundamental Rights and why?
(a) Not paying minimum wages
(b) Banning of a book
(c) Banning of loudspeakers after 9 p.m.
(d) Making a speech
🟢 Answer 5:
✅ (a) Not paying minimum wages
🌿 Explanation:
It violates the Right Against Exploitation (Article 23–24) and Right to Equality (Article 14).
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Question 6:
An activist working among the poor says that the poor don’t need Fundamental Rights. What they need are Directive Principles to be made legally binding. Do you agree with this? Give your reasons.
🟢 Answer 6:
✅ No, Fundamental Rights are necessary for protecting individual freedoms and dignity.
Directive Principles guide policy but cannot replace enforceable rights like freedom of speech, equality, and protection from exploitation.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Question 7:
Several reports show that caste groups previously associated with scavenging are forced to continue in this job. Those in positions of authority refuse to give them any other job. Their children are discouraged from pursuing education. Which of their Fundamental Rights are being violated in this instance?
🟢 Answer 7:
✅ Right to Equality (Article 14–15), Right Against Exploitation (Article 23), and Right to Education (Article 21A) are violated.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Question 8:
A petition by a human rights group drew attention of the court to the condition of starvation and hunger in the country. Over five crore tonnes of food grains was stored in the godowns of the Food Corporation of India. Research shows that a large number of ration cardholders do not know about the quantity of food grains they can purchase from fair price shops. It requested the court to order the government to improve its public distribution system.
(a) Which different rights does this case involve? How are these rights interlinked?
(b) Should these rights form part of the right to life?
🟢 Answer 8:
(a) Right to Life (Article 21) and Right to Equality (Article 14) are involved. These rights are linked because lack of access to food affects life and dignity.
(b) Yes, the Right to Life includes the right to live with dignity, which requires access to basic necessities like food.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Question 9:
Read the statement by Somnath Lahiri in the Constituent Assembly quoted in this chapter. Do you agree with him? If yes, give instances to prove it. If not, give arguments against his position.
🟢 Answer 9:
✅ Yes, Somnath Lahiri argued for stronger protection of rights against possible misuse by the government. Instances like the Emergency (1975) show the importance of robust rights protections.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Question 10:
Which of the Fundamental Rights is in your opinion the most important right? Summarise its provisions and give arguments to show why it is most important.
🟢 Answer 10:
✅ Right to Equality is the most important as it ensures all citizens are treated equally before law, without discrimination. This right forms the foundation for other rights and supports justice, fairness, and dignity.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🌸 CODE 3 | 30 QUESTIONS
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 1️⃣ Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
🔵 Q1. Which Article of the Indian Constitution is known as the ‘Heart and Soul of the Constitution’?
(A) Article 21
(B) Article 32
(C) Article 14
(D) Article 19
✅ Answer: (B) Article 32
🔵 Q2. Which Fundamental Right ensures equality before the law?
(A) Right to Freedom
(B) Right to Equality
(C) Right against Exploitation
(D) Right to Constitutional Remedies
✅ Answer: (B) Right to Equality
🔵 Q3. Right to Freedom includes which of the following?
(A) Right to property
(B) Right to free and compulsory education
(C) Freedom of speech and expression
(D) Freedom to exploit others
✅ Answer: (C) Freedom of speech and expression
🔵 Q4. The right against exploitation prohibits:
(A) Child labour under the age of 14
(B) Women working at night
(C) Migration of labourers
(D) Strikes by workers
✅ Answer: (A) Child labour under the age of 14
🔵 Q5. Which of these rights is available to both citizens and non-citizens?
(A) Article 19
(B) Article 21
(C) Article 15
(D) Article 30
✅ Answer: (B) Article 21
🔵 Q6. Which Right was added through the 86th Amendment?
(A) Right to Privacy
(B) Right to Constitutional Remedies
(C) Right to Education
(D) Right to Property
✅ Answer: (C) Right to Education
🔵 Q7. Fundamental Rights are primarily enforced through:
(A) Parliament
(B) Executive
(C) Judiciary
(D) President
✅ Answer: (C) Judiciary
🔵 Q8. Which of the following is NOT a Fundamental Right in India?
(A) Right to Equality
(B) Right to Vote
(C) Right to Freedom
(D) Cultural and Educational Rights
✅ Answer: (B) Right to Vote
🔵 Q9. Which writ is issued to produce a person detained unlawfully?
(A) Habeas Corpus
(B) Mandamus
(C) Certiorari
(D) Prohibition
✅ Answer: (A) Habeas Corpus
🔵 Q10. Article 19 guarantees how many freedoms?
(A) 4
(B) 5
(C) 6
(D) 7
✅ Answer: (C) 6
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 2️⃣ Fill in the Blanks (3 Questions)
🔴 Q11. __ is the Right to move the Supreme Court directly in case of violation of Fundamental Rights.
✅ Answer: Right to Constitutional Remedies
🔴 Q12. Fundamental Rights are included in Part _ of the Indian Constitution.
✅ Answer: Part III
🔴 Q13. Article _ provides protection of life and personal liberty.
✅ Answer: Article 21
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟢 3️⃣ True / False (2 Questions)
🟢 Q14. Fundamental Rights in India can never be suspended under any circumstances.
✅ Answer: False
🟢 Q15. Cultural and Educational Rights protect the interests of minorities.
✅ Answer: True
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟡 4️⃣ Assertion-Reason Type (2 Questions)
🟡 Q16.
Assertion (A): Right to Education is a Fundamental Right under Article 21A.
Reason (R): Every child between the ages of 6 to 14 must receive free and compulsory education.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
✅ Answer: (A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
🟡 Q17.
Assertion (A): Freedom of Religion is guaranteed to all citizens in India.
Reason (R): India is a secular country where the State has no religion.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
✅ Answer: (A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔷 5️⃣ Short Answer (30 words limit, 3 Questions)
🔷 Q18. What is the significance of Fundamental Rights?
✅ Answer: They protect citizens from arbitrary actions of the state and ensure equality, freedom, and dignity necessary for a democratic society.
🔷 Q19. Mention two safeguards of Fundamental Rights in India.
✅ Answer: Courts can issue writs; citizens can directly approach the Supreme Court under Article 32.
🔷 Q20. Name two rights available to minorities under Cultural and Educational Rights.
✅ Answer: Right to preserve language and culture, Right to establish educational institutions.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔶 6️⃣ Mid-Length Answers (60 words limit, 3 Questions)
🔶 Q21. How does Right to Equality promote democracy?
✅ Answer: It ensures equal treatment before the law, prevents discrimination based on religion, caste, gender, or race, and promotes equal opportunity in public employment, strengthening democratic principles of fairness and justice.
🔶 Q22. Why is the Right against Exploitation important in India?
✅ Answer: It prohibits human trafficking, forced labour, and child labour, safeguarding vulnerable groups and ensuring dignity, which is vital in a country with historical social inequalities.
🔶 Q23. How do Fundamental Rights relate to the Directive Principles of State Policy?
✅ Answer: Fundamental Rights are legally enforceable, while Directive Principles guide governance. Together, they aim to establish social, economic, and political justice, ensuring citizens’ overall welfare.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟣 7️⃣ Long Answer (120 words limit, 2 Questions)
🟣 Q24. Explain the importance of the Right to Freedom in detail.
✅ Answer: The Right to Freedom under Articles 19–22 guarantees essential liberties such as speech, assembly, movement, and association. It empowers citizens to express opinions, form organizations, and engage in lawful activities. However, these freedoms are subject to reasonable restrictions for maintaining public order, security, and morality. This right forms the bedrock of democracy, allowing individuals to lead dignified lives without fear or oppression and participate fully in the nation’s political and social life.
🟣 Q25. Discuss the relationship between Rights and Duties of citizens.
✅ Answer: Rights and Duties are complementary. While Rights allow individuals to live freely and claim protection from the State, Duties ensure that people respect others’ rights and contribute to the nation’s welfare. Performing duties like respecting the Constitution, promoting harmony, and protecting the environment strengthens democratic values and maintains societal balance, reinforcing the spirit of citizenship.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM COMPETITION EXAMS
🔵 Q1. Which of the following are envisaged by the Right against Exploitation in the Constitution of India?
(A) Prohibition of traffic in human beings and forced labour
(B) Abolition of untouchability
(C) Protection of the interests of minorities
(D) Prohibition of employment of children in factories and mines
✅ Answer: (A) and (D)
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2017
📝 Explanation: Articles 23 and 24 prohibit human trafficking, forced labour, and child labour.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟢 Q2. Rights are claims of the citizens against the State. This is known as:
(A) Duties
(B) Privileges
(C) Rights
(D) Immunities
✅ Answer: (C) Rights
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2017
📝 Explanation: Rights allow citizens to make claims on the State for protection, welfare, and freedoms.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Q3. In the context of India, which one of the following is the correct relationship between Rights and Duties?
(A) Rights are correlative with Duties
(B) Rights are independent of Duties
(C) Duties are more important than Rights
(D) Rights exist without Duties
✅ Answer: (A) Rights are correlative with Duties
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2017
📝 Explanation: Indian Constitution links Fundamental Rights and Duties as complementary.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟡 Q4. “To uphold and protect the Sovereignty, Unity and Integrity of India” is a provision under:
(A) Preamble of the Constitution
(B) Directive Principles of State Policy
(C) Fundamental Rights
(D) Fundamental Duties
✅ Answer: (D) Fundamental Duties
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2015
📝 Explanation: This is explicitly listed under Fundamental Duties (Article 51A).
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟣 Q5. Which of the following rights was described by B.R. Ambedkar as the heart and soul of the Constitution?
(A) Right to Freedom of Religion
(B) Right to Property
(C) Right to Equality
(D) Right to Constitutional Remedies
✅ Answer: (D) Right to Constitutional Remedies
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2002
📝 Explanation: B.R. Ambedkar emphasized Article 32 as the core guarantee of all rights.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟠 Q6. Right to Equality is guaranteed under which Articles of the Indian Constitution?
(A) Article 16 to Article 20
(B) Article 15 to Article 19
(C) Article 14 to Article 18
(D) Article 13 to Article 17
✅ Answer: (C) Article 14 to Article 18
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2002
📝 Explanation: Articles 14–18 guarantee Equality before Law, End of Titles, etc.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q7. Article 15 of the Indian Constitution is classified under which Fundamental Right?
(A) Right to Freedom of Religion
(B) Right against Exploitation
(C) Cultural and Educational Rights
(D) Right to Equality
✅ Answer: (D) Right to Equality
📅 Exam: SSC CGL 1995
📝 Explanation: Article 15 prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟢 Q8. No one can be compelled to sing the National Anthem because:
(A) Violates Freedom of Speech
(B) Violates Freedom of Conscience and Religion
(C) No legal provision obliging this
(D) All of the above
✅ Answer: (D) All of the above
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 1996
📝 Explanation: Courts upheld right to dissent under Article 19 and 25.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Q9. A British citizen staying in India cannot claim which right?
(A) Freedom of trade and profession
(B) Equality before Law
(C) Protection of life and liberty
(D) Freedom of religion
✅ Answer: (A) Freedom of trade and profession
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 1999
📝 Explanation: Some rights like freedom of trade/profession under Article 19 are only for citizens.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q1. Which one of the following Articles of the Constitution of India safeguards the rights of minorities to establish and run educational institutions of their choice?
(A) Article 19
(B) Article 26
(C) Article 29
(D) Article 30
✅ Answer: (D) Article 30
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2015
📝 Explanation: Article 30 specifically protects minorities’ rights to establish and administer educational institutions.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟢 Q2. Which of the following Articles deals with the Right to Equality before the law in India?
(A) Article 14
(B) Article 16
(C) Article 19
(D) Article 21
✅ Answer: (A) Article 14
📅 Exam: SSC CHSL 2017
📝 Explanation: Article 14 ensures equal protection of the laws and equality before the law for all citizens.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Q3. Under which Article of the Indian Constitution can a citizen directly approach the Supreme Court to enforce Fundamental Rights?
(A) Article 19
(B) Article 21
(C) Article 32
(D) Article 226
✅ Answer: (C) Article 32
📅 Exam: UPSC Prelims 2013
📝 Explanation: Article 32 is the ‘Right to Constitutional Remedies’ and allows direct approach to the Supreme Court.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟡 Q4. Right to Education was made a Fundamental Right by which Constitutional Amendment?
(A) 42nd Amendment
(B) 44th Amendment
(C) 86th Amendment
(D) 93rd Amendment
✅ Answer: (C) 86th Amendment
📅 Exam: BPSC Prelims 2018
📝 Explanation: The 86th Constitutional Amendment Act, 2002 inserted Article 21A making Right to Education a Fundamental Right.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔵 Q5. Which of the following is NOT a Fundamental Right under the Indian Constitution?
(A) Right to Equality
(B) Right to Freedom
(C) Right to Vote
(D) Right to Constitutional Remedies
✅ Answer: (C) Right to Vote
📅 Exam: SSC CGL 2018
📝 Explanation: Right to Vote is a legal right under the Representation of the People Act, not a Fundamental Right.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟢 Q6. Which of the following writs is issued to release a person who is unlawfully detained?
(A) Habeas Corpus
(B) Certiorari
(C) Mandamus
(D) Quo Warranto
✅ Answer: (A) Habeas Corpus
📅 Exam: CDS 2017
📝 Explanation: ‘Habeas Corpus’ means ‘to have the body’; it protects against illegal detention.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🔴 Q7. Fundamental Rights are mentioned in which Part of the Constitution?
(A) Part II
(B) Part III
(C) Part IV
(D) Part IVA
✅ Answer: (B) Part III
📅 Exam: SSC CHSL 2019
📝 Explanation: Fundamental Rights are included in Part III, Articles 12 to 35 of the Constitution.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
🟡 Q8. Which Fundamental Right prohibits trafficking and forced labour?
(A) Right to Equality
(B) Right to Freedom
(C) Right against Exploitation
(D) Right to Freedom of Religion
✅ Answer: (C) Right against Exploitation
📅 Exam: UPSC CDS 2015
📝 Explanation: Articles 23 and 24 of the Constitution prohibit human trafficking, forced labour, and child labour.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MNEMONICS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
