Class 11 : Poltical Science (In English) – Lesson 1. Constitution: Why and How?
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY

🔴 Introduction
The chapter “Constitution – Why and How” explains the meaning, need, and importance of the Constitution for any country. It highlights how a Constitution provides a fundamental legal framework within which the government operates. It protects citizens’ rights, limits the powers of the state, and expresses the collective aspirations of society.
🟢 What is a Constitution?
➡️ A Constitution is the fundamental legal document that lays down the principles, structure, powers, and duties of the government.
🌿 It determines how power is exercised and how laws are framed.
🧠 Key purposes of the Constitution:
✔️ It provides stability to the political system.
✔️ It sets limits on governmental powers.
✔️ It protects individual rights and freedoms.
✔️ It guides the functioning of institutions.
✏️ Note: Without a Constitution, governance can become arbitrary and unjust.
🔵 Why Do We Need a Constitution?
✔️ Defines the Structure of Government:
It establishes institutions such as the legislature, executive, and judiciary.
✔️ Limits the Power of the State:
It prevents the misuse of authority and power by establishing checks and balances.
✔️ Protects Rights and Liberties:
It guarantees civil, political, and economic rights necessary for human dignity.
✔️ Establishes Rule of Law:
It ensures that no one is above the law.
💡 Concept: The Constitution reflects the will of the people and acts as the supreme law.
🟡 Functions of a Constitution
✔️ Expression of Ideals:
It expresses the shared values of justice, equality, liberty, and fraternity.
✔️ Establishes Institutions:
It creates and defines the roles of political institutions.
✔️ Regulates Power:
It divides power among various organs of the government to ensure balance.
✔️ Guarantees Rights:
It protects civil liberties and provides mechanisms for their enforcement.
🔴 How is a Constitution Made?
🧠 Factors influencing Constitution-making:
✔️ Historical background
✔️ Freedom struggle experiences
✔️ Social, political, and economic needs
✔️ Ideals of justice and equality
🌿 Process of Constitution-making in India:
➡️ The Constituent Assembly was formed in 1946.
➡️ Representation was ensured from all communities.
➡️ Dr. B.R. Ambedkar chaired the Drafting Committee.
➡️ The Constitution was adopted on 26th November 1949 and came into force on 26th January 1950.
✏️ Note: Constitution-making reflects the aspirations and compromises of a society at a specific time.
🔵 How Does the Constitution Ensure Justice and Rights?
✔️ Fundamental Rights:
Rights such as equality, freedom, right to life, and education ensure justice.
✔️ Directive Principles of State Policy:
They guide the state to promote welfare and reduce inequalities.
✔️ Independent Judiciary:
Courts safeguard the Constitution and ensure rights are upheld.
💡 Concept: The Constitution balances freedom with law and order.
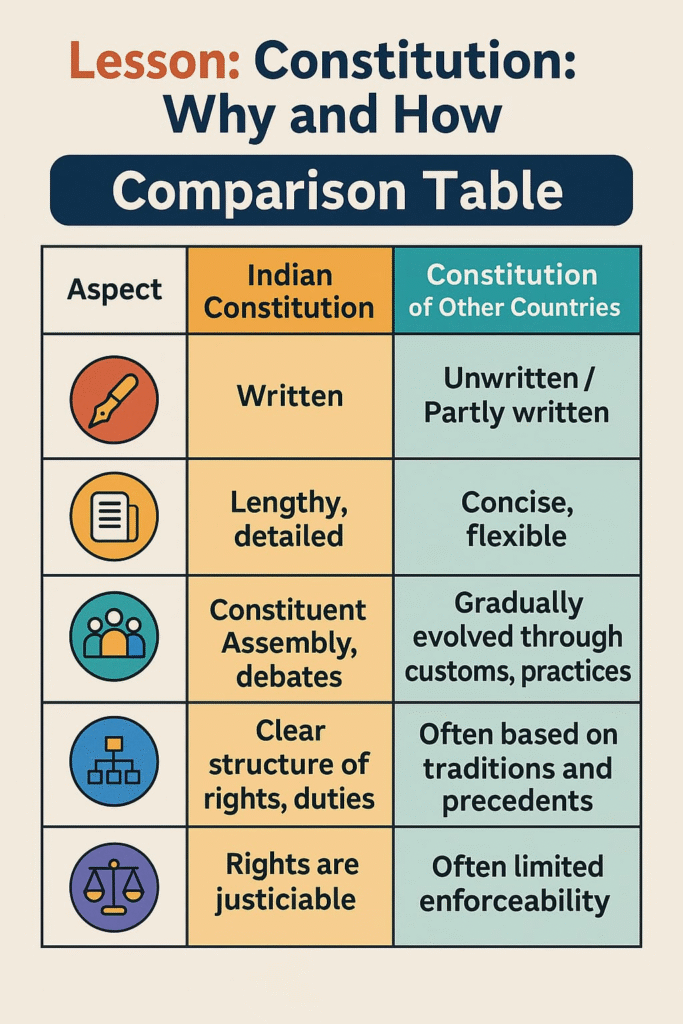
🟢 How is the Constitution Different from Ordinary Law?
Constitution Ordinary Law
Supreme law of the country Passed by the legislature
Difficult to amend Easier to amend
Lays basic principles Deals with specific issues
✏️ Note: The Constitution stands above all other laws.
🟡 Features of the Indian Constitution
✔️ Written and Lengthy:
It contains detailed provisions covering every aspect of governance.
✔️ Federal Structure:
It divides powers between the Centre and the States.
✔️ Parliamentary System:
The executive is accountable to the legislature.
✔️ Independent Judiciary:
The judiciary protects the Constitution and rights.
✔️ Secularism:
The state maintains neutrality towards all religions.
✔️ Fundamental Rights and Duties:
These ensure citizen protection and responsibilities.
🔴 Flexibility and Rigidity of the Constitution
➡️ Some provisions can be amended easily, others require a more complex procedure.
✔️ This ensures flexibility while protecting core values.
🧠 Examples of Amendments:
42nd Amendment: Known as the ‘Mini-Constitution’
44th Amendment: Restored civil liberties post-Emergency
🔵 Importance of the Preamble
✔️ Declares India as Sovereign, Socialist, Secular, Democratic, Republic
✔️ Guarantees Justice, Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity
✔️ Reflects the spirit and objectives of the Constitution
💡 Concept: The Preamble acts as the guiding light for interpretation.
🟢 Role of the Judiciary in Protecting the Constitution
✔️ Judiciary acts as the guardian of the Constitution.
✔️ It ensures laws are in harmony with constitutional values.
✔️ It protects citizens’ rights through judicial review.
🟡 Significance of Fundamental Rights
✔️ Protect individuals from state excesses.
✔️ Ensure dignity, freedom, and equality.
✔️ Fundamental for democracy and personal growth.
🔴 Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSPs)
✔️ Provide guidelines to the government for promoting social and economic justice.
✔️ Although non-justiciable, they shape laws and policies.
🔵 Relationship Between Rights and Duties
✔️ Rights ensure individual freedom.
✔️ Duties remind citizens of their responsibilities to uphold freedom and law.
✔️ Both together maintain balance in society.
🟢 Amending the Constitution
✔️ Amendments allow adaptation to changing times.
✔️ Process outlined in Article 368.
✔️ Balances flexibility with stability.
🔴 How the Constitution Reflects People’s Aspirations
✔️ Constitution embodies the will of the people.
✔️ Provides mechanisms for peaceful change.
✔️ Reflects historical struggles and future vision.
🔵 Why This Lesson Matters
💡 Connection to Society:
✔️ Teaches importance of laws, rights, and governance structures.
✔️ Helps understand duties as responsible citizens.
✔️ Empowers individuals to protect democracy and justice.
⚡ In Exams:
Understanding this lesson is essential for polity, law, and governance questions in competitive exams.
📝 QUICK RECAP:
🔵 Constitution = Framework of governance
🟢 Functions = Rights, duties, limits, powers
🔴 Indian Constitution = Written, flexible, detailed
🟡 Preamble = Spirit of the Constitution
🔵 Rights + Duties = Balanced society
🔵 SUMMARY (300 WORDS)
The chapter “Constitution – Why and How” explains the significance of a Constitution as the supreme legal document guiding the governance of a country. A Constitution is necessary to define the powers and functions of institutions, limit the authority of the state, protect individual rights, and ensure justice, equality, and liberty.
It outlines the purpose of the Constitution: establishing democratic institutions, regulating power distribution, and safeguarding civil liberties. The Indian Constitution is written, detailed, and flexible, allowing adaptation through amendments. It embodies features like federalism, parliamentary system, secularism, and independence of judiciary.
The Preamble captures India’s core ideals: Sovereignty, Socialism, Secularism, Democracy, and Republic. It guarantees Justice, Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity to all citizens. Fundamental Rights ensure freedom and dignity, while Directive Principles aim to achieve social and economic justice.
The Constitution is not static. Amendments under Article 368 allow it to evolve. Rights and duties go hand-in-hand to create a responsible and lawful society.
The chapter emphasizes the role of the judiciary in safeguarding the Constitution, ensuring laws align with democratic principles. Overall, the Constitution reflects the aspirations of the people and is central to governance, rights protection, and democratic functioning.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1:
Which of these is not a function of the constitution?
(a) It gives a guarantee of the rights of the citizen.
(b) It marks out different spheres of power for different branches of government.
(c) It ensures that good people come to power.
(d) It gives expression to some shared values.
🟢 Answer 1:
The correct answer is (c) It ensures that good people come to power.
✔️ The Constitution guarantees rights, distributes power among government organs, and reflects shared values like justice and liberty.
❌ It cannot guarantee that only good people will come to power; that depends on democratic processes like elections.
🔴 Question 2:
Which of the following is a good reason to conclude that the authority of the constitution is higher than that of the parliament?
(a) The constitution was framed before the parliament came into being.
(b) The constitution makers were more eminent leaders than the members of the parliament.
(c) The constitution specifies how parliament is to be formed and what are its powers.
(d) The constitution cannot be amended by the parliament.
🟡 Answer 2:
The correct answer is (c) The constitution specifies how parliament is to be formed and what are its powers.
✔️ Parliament derives its power from the Constitution, not the other way round.
✔️ The Constitution sets the framework within which the Parliament operates, making it superior.
🔵 Question 3:
State whether the following statements about a constitution are True or False.
(a) Constitutions are written documents about formation and power of the government.
(b) Constitutions exist and are required only in democratic countries.
(c) Constitution is a legal document that does not deal with ideals and values.
(d) A constitution gives its citizens a new identity.
🟢 Answer 3:
(a) ✅ True. Constitutions outline the structure and power of government.
(b) ❌ False. Constitutions exist in all countries, democratic or not.
(c) ❌ False. Constitutions do reflect ideals and values such as justice, liberty, equality.
(d) ✅ True. Constitutions give citizens a sense of legal and political identity.
🔴 Question 4:
State whether the following inferences about the making of the Indian Constitution are Correct or Incorrect. Give reasons to support your answer.
(a) The Constituent Assembly did not represent the Indian people since it was not elected by all citizens.
(b) Constitution making did not involve any major decision since there was a general consensus among the leaders at that time about its basic framework.
(c) There was little originality in the Constitution, for much of it was borrowed from other countries.
🟡 Answer 4:
(a) Incorrect. Though not directly elected by universal franchise, it was broadly representative of the Indian people’s interests through provincial assemblies.
(b) Incorrect. The making of the Constitution involved intense debate and critical decisions; consensus was achieved through discussion, not absence of decisions.
(c) Incorrect. While borrowing ideas, India’s Constitution integrated and adapted these to suit its unique social, cultural, and political conditions, which makes it original.
🔵 Question 5:
Give two examples each to support the following conclusions about the Indian Constitution:
(a) The Constitution was made by credible leaders who commanded people’s respect.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Dr. भीमराव आम्बेडकर as Drafting Committee Chairman
✔️ पंडित जवाहरलाल नेहरू as first Prime Minister and Constitution supporter
(b) The Constitution has distributed power in such a way as to make it difficult to subvert it.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ Division of powers between केंद्र and राज्य
✔️ Independent Judiciary to keep checks on executive and legislature
(c) The Constitution is the locus of people’s hopes and aspirations.
🟢 Answer:
✔️ It promises Justice, Liberty, Equality, Fraternity in the Preamble
✔️ Provides Fundamental Rights guaranteeing dignity and freedom
🔴 Question 6:
Why is it necessary for a country to have a clear demarcation of powers and responsibilities in the constitution? What would happen in the absence of such a demarcation?
🟡 Answer 6:
✔️ A clear demarcation prevents conflicts between different branches of government and ensures smooth functioning.
✔️ It helps avoid misuse of power, protects citizens’ rights, and ensures accountability.
❌ Without this, there would be confusion, overlap of powers, and likely clashes leading to inefficiency and injustice.
🔵 Question 7:
Why is it necessary for a constitution to place limitations on the rulers? Can there be a constitution that gives no power at all to the citizens?
🟢 Answer 7:
✔️ Limitations prevent rulers from becoming authoritarian and ensure respect for rights.
✔️ A constitution without any power to citizens is meaningless; citizens must have rights and opportunities to participate in governance.
✔️ Democracies thrive on checks and balances.
🔴 Question 8:
The Japanese Constitution was made when the US occupation army was still in control of Japan after its defeat in the Second World War. The Japanese constitution could not have had any provision that the US government did not like. Do you see any problem in this way of making the constitution? In which way was the Indian experience different from this?
🟡 Answer 8:
✔️ Such a constitution lacks complete sovereignty as it reflects external influence, not the people’s will.
✔️ Indian Constitution was made by its own elected representatives, reflecting Indian aspirations without foreign interference.
✔️ Thus, India’s Constitution is more democratic and legitimate.
🔵 Question 9:
Rajat asked his teacher this question: “The constitution is a fifty-year-old and therefore outdated book. No one took my consent for implementing it. It is written in such tough language that I cannot understand it. Tell me why should I obey this document?” If you were the teacher, how would you answer Rajat?
🟢 Answer 9:
✔️ The Constitution represents collective consent given through elected leaders and not individual consent.
✔️ It protects his rights and ensures his freedom and safety.
✔️ Its language may be legal, but its principles ensure justice, equality, and dignity for him and all citizens.
🔴 Question 10:
In a discussion on the experience of the working of our Constitution, three speakers took three different positions:
(a) Harbans: The Indian Constitution has succeeded in giving us a framework of democratic government.
(b) Neha: The Constitution made solemn promises of ensuring liberty, equality and fraternity. Since this has not happened, the Constitution has failed.
(c) Nazima: The Constitution has not failed us. We have failed the Constitution.
Do you agree with any of these positions? If yes, why? If not, what is your own position?
🟡 Answer 10:
✔️ Nazima’s view is closest to truth. The Constitution provides a strong framework, but its success depends on people’s actions and governments’ sincerity.
✔️ Citizens and leaders must uphold its values for true democracy to thrive.
✔️ Therefore, the Constitution has not failed; we must improve our conduct.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
🔵 1️⃣ 10 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs):
🔴 Q1. Which of the following is NOT a feature of a constitution?
(A) It defines powers of government
(B) It gives rights to citizens
(C) It prescribes religious practices
(D) It limits state power
✅ Answer: (C) It prescribes religious practices
🟢 Q2. Who was the Chairman of the Drafting Committee of the Indian Constitution?
(A) Jawaharlal Nehru
(B) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
(C) Mahatma Gandhi
(D) Rajendra Prasad
✅ Answer: (B) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
🔴 Q3. Which of the following statements about the Constitution is correct?
(A) It is a flexible document
(B) It is superior to Parliament
(C) It cannot be changed
(D) It only benefits the rulers
✅ Answer: (B) It is superior to Parliament
🟢 Q4. Which part of the Constitution expresses its spirit?
(A) Fundamental Duties
(B) Fundamental Rights
(C) Directive Principles
(D) Preamble
✅ Answer: (D) Preamble
🔴 Q5. Constitution came into force on:
(A) 15 August 1947
(B) 26 January 1950
(C) 2 October 1948
(D) 26 November 1949
✅ Answer: (B) 26 January 1950
🟢 Q6. Constitution provides:
(A) Structure of Government
(B) Laws for all festivals
(C) Religious rules
(D) Rules of foreign trade
✅ Answer: (A) Structure of Government
🔴 Q7. What does the Constitution safeguard?
(A) Wealth of the state
(B) Rights and liberties of citizens
(C) Interests of only political parties
(D) Power of army
✅ Answer: (B) Rights and liberties of citizens
🟢 Q8. Which Article deals with amendments to the Constitution?
(A) 368
(B) 370
(C) 356
(D) 35
✅ Answer: (A) 368
🔴 Q9. The Constitution is necessary to prevent:
(A) Abuse of power
(B) Celebration of festivals
(C) Economic losses
(D) Construction of buildings
✅ Answer: (A) Abuse of power
🟢 Q10. Which of the following is NOT derived from any foreign Constitution?
(A) Federalism
(B) Parliamentary System
(C) Secularism
(D) India’s cultural heritage
✅ Answer: (D) India’s cultural heritage
🔵 2️⃣ 3 Fill in the Blanks Questions:
🔴 Q11. The Indian Constitution was adopted on __.
✅ Answer: 26 November 1949
🟢 Q12. The Preamble declares India to be Sovereign, Socialist, Secular, _ Republic.
✅ Answer: Democratic
🔴 Q13. The Constitution is the __ law of the land.
✅ Answer: supreme
🔵 3️⃣ 2 True / False Questions:
🔴 Q14. The Constitution provides guidelines for the working of the government.
✅ Answer: True
🟢 Q15. Citizens have no role in the functioning of democracy as per Constitution.
✅ Answer: False
🔵 4️⃣ 2 Assertion-Reason Type MCQs:
🔴 Q16.
Assertion (A): The Constitution ensures protection of rights and freedoms.
Reason (R): Without a Constitution, rulers may misuse power.
Options:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
✅ Answer: (A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
🟢 Q17.
Assertion (A): Constitution can never be changed.
Reason (R): Amendment is not allowed in Indian Constitution.
Options:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, but R is false.
(D) A is false, but R is true.
✅ Answer: (D) A is false, but R is true.
🔵 5️⃣ 3 Short Answer Questions (30 words limit):
🔴 Q18. Why is a Constitution necessary?
✅ Answer: It defines powers, limits misuse of authority, protects rights, and provides a stable framework for governance.
🟢 Q19. What is the role of the Preamble?
✅ Answer: It reflects the aims, spirit, and ideals of the Constitution like justice, equality, liberty, and fraternity.
🔴 Q20. Why does the Constitution separate powers?
✅ Answer: To ensure no organ of government misuses power and democracy functions effectively.
🔵 6️⃣ 3 Mid-Length Answer Questions (60 words limit):
🔴 Q21. Explain two functions of the Constitution.
✅ Answer: The Constitution defines government structure and protects fundamental rights. It limits power misuse and establishes legal procedures for fair governance.
🟢 Q22. Why is the Constitution superior to Parliament?
✅ Answer: Parliament’s powers come from the Constitution. It cannot make laws beyond constitutional limits. Constitution is the supreme law guiding all institutions.
🔴 Q23. Why did India need a written Constitution?
✅ Answer: India’s diversity, colonial history, and the need to establish democratic rights made it essential to have a detailed, written Constitution to ensure unity and justice.
🔵 7️⃣ 2 Long Answer Questions (120 words limit):
🔴 Q24. How does the Constitution protect citizens’ rights?
✅ Answer: The Constitution provides Fundamental Rights ensuring equality, freedom, and protection from arbitrary state actions. Judiciary safeguards these rights through judicial review. Citizens can approach courts if rights are violated. Directive Principles guide governments to create a just society. Thus, the Constitution balances individual liberty with state authority.
🟢 Q25. How is the Indian experience of constitution-making different from Japan?
✅ Answer: India’s Constitution was created by its elected Constituent Assembly after thorough debate, reflecting people’s aspirations. In contrast, Japan’s Constitution post-WWII was influenced by US occupation, limiting its autonomy. India’s process was democratic, free from external pressure, making its Constitution legitimate and accepted by its people.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
KNOWLEDGE WITH FUN

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
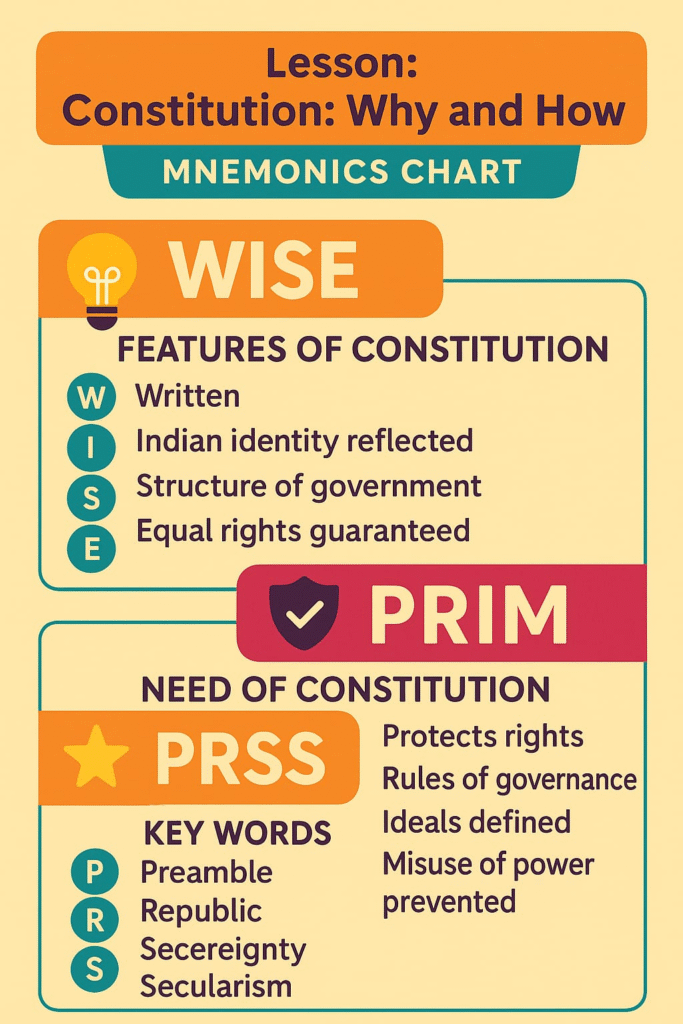
MNEMONICS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
