Class 10 : Social Science (In English) – Lesson 11. Manufacturing Industries
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY

🌍 1. Importance of Manufacturing Industries
🏭 Industries convert raw materials → finished products (cotton → cloth, iron → steel).
🌾 Supports agriculture (machines, fertilizers, tools).
💰 Contributes ~27% of GDP (industry + manufacturing combined).
👥 Provides large-scale employment.
📦 Boosts trade & exports (textiles, steel, engineering goods).
🌍 Indicator of economic strength & development.
⚙️ 2. Types of Manufacturing Industries
Agro-based Industries 🌾
Raw material: agriculture.
Examples: cotton textiles, jute, sugar, edible oils.
Mineral-based Industries ⛏️
Raw material: minerals.
Examples: iron & steel, cement, aluminium, machine tools.
Chemical-based Industries 🧪
Examples: fertilizers, paints, synthetic fibres, plastics.
Forest-based Industries 🌲
Raw material: forest products.
Examples: paper, plywood, furniture.
Basic & Heavy Industries ⚙️
Produce machinery, steel → base for other industries.
Consumer Industries 🛍️
Direct goods for consumers.
Examples: textiles, sugar, food processing.
🧵 3. Textile Industry (Agro-based)
🌾 Oldest & largest industry in India.
Types:
Cotton → Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu.
Jute → West Bengal, Bihar, Assam.
Silk → Karnataka, West Bengal, Assam.
Wool → Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan.
💰 Major exporter → earns foreign exchange.
👥 Provides maximum employment after agriculture.
⛓️ 4. Iron and Steel Industry (Mineral-based)
⚙️ Backbone of modern industry (“feeding industry”).
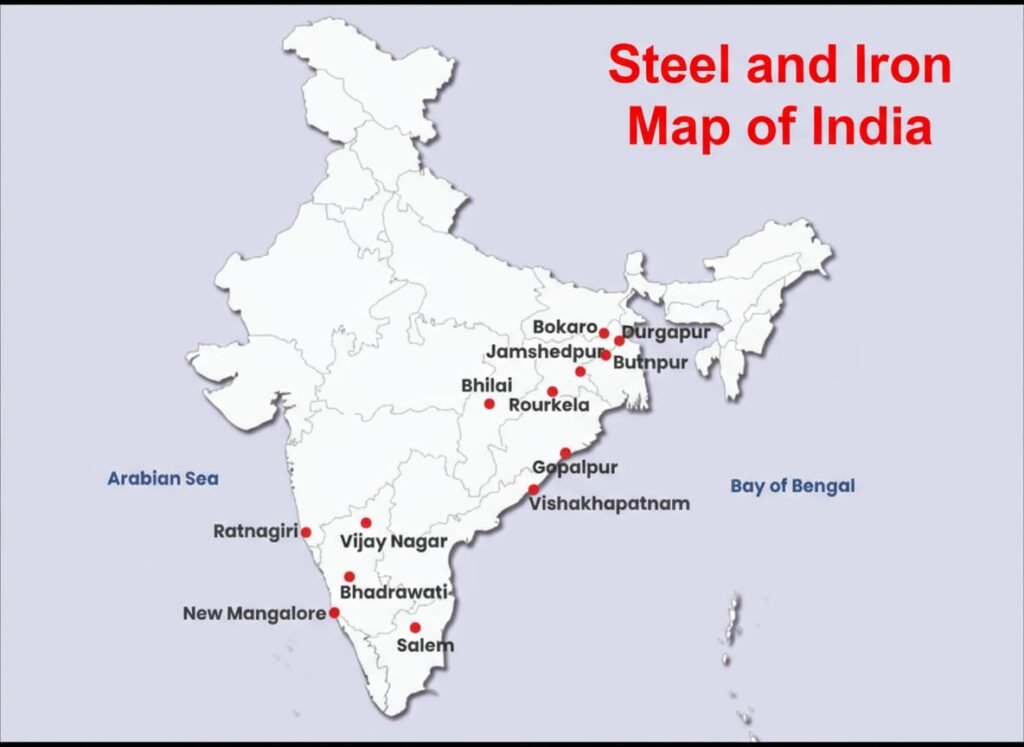
📍 Major centres: Jamshedpur, Bhilai, Rourkela, Bokaro, Durgapur.
Inputs: iron ore, coal, limestone, manganese, water, labour.
Products: steel, rods, plates, machinery.
Challenges: high cost, outdated technology, global competition.
🏗️ 5. Cement Industry
Raw materials: limestone, silica, gypsum, coal.
📍 States: Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu.
Uses: construction of houses, roads, bridges, dams.
🌍 Export to Middle East, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh.
Challenges: environmental pollution from dust.
🚗 6. Automobile & Engineering Industries
🚗 Produce trucks, cars, scooters, motorcycles, engines, railway coaches.
📍 Centres: Delhi, Gurugram, Chennai, Pune, Mumbai, Jamshedpur.
🏭 Engineering industries manufacture machine tools, heavy equipment.
🧪 7. Chemical Industry
Includes organic & inorganic chemicals.
Products: fertilizers, plastics, drugs, dyes, paints, cosmetics.
📍 Gujarat, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, UP.
India → 3rd largest in Asia in chemicals.
💡 8. Information Technology and Electronics
🖥️ Produces software, hardware, chips, mobile phones, digital goods.
📍 Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Chennai, Noida, Mumbai.
🌍 India → global IT hub; large export potential.
🌱 9. Environmental Impact of Industries
🌫️ Air pollution: smoke, SO₂, particulate matter.
💧 Water pollution: chemicals, dyes, fertilizers.
🌳 Land degradation: dumping waste.
🔊 Noise pollution: heavy machines.
🌡️ Industrial pollution → climate change, health hazards.
🌍 10. Measures for Sustainable Industrial Growth
♻️ Adopt clean & green technology.
🚰 Treat industrial effluents before disposal.
🌳 Afforestation around industrial areas.
🌞 Promote eco-friendly industries (renewables, recycling).
📜 Strict laws to check industrial pollution.
📝 Summary
Manufacturing industries convert raw materials into finished products, strengthening the economy. They provide jobs, exports, and support agriculture. India’s industries include agro-based (textiles, sugar, jute), mineral-based (iron, steel, cement), chemical, forest-based, and engineering industries.
Textiles remain the largest industry, while iron & steel form the backbone of modern development. Other industries like automobiles, cement, chemicals, and IT contribute to GDP and global trade. However, industries cause air, water, and land pollution, threatening sustainability.
Sustainable growth requires clean technologies, waste treatment, afforestation, and strict regulation.
⚡ Quick Recap
🏭 Industries = backbone of economy.
🌾 Agro-based → cotton, jute, sugar.
⛏️ Mineral-based → iron & steel, cement, aluminium.
🧪 Chemical, 🌲 Forest-based, ⚙️ Engineering.
👥 Provide jobs + boost exports.
🌫️ Pollution = major challenge.
♻️ Green technology = need of the hour.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
Question 1. Multiple choice questions
(i) Which one of the following industries uses bauxite as a raw material?
(a) Aluminium Smelting
(b) Cement
(c) Paper
(d) Steel
Answer:
🟢 (a) Aluminium Smelting
(ii) Which one of the following industries manufactures telephones, computers, etc.?
(a) Steel
(b) Electronic
(c) Aluminium Smelting
(d) Information Technology
Answer:
🟢 (b) Electronic
Question 2. Answer the following briefly in not more than 30 words.
(i) What is manufacturing?
Answer:
🏭 Manufacturing is the production of goods in large quantities after processing raw materials into more valuable products.
🌾 Example: Cotton → Cloth, Iron ore → Steel.
(ii) What are basic industries? Give an example.
Answer:
⚙️ Basic industries supply raw materials to other industries.
Example: Iron and Steel industry → provides steel to engineering, construction, automobile sectors.
Question 3. Write the answers of the following questions in about 120 words.
(i) How do industries pollute the environment?
Answer:
🌫️ Air Pollution: Smoke from chimneys, SO₂, CO₂, dust particles cause respiratory problems.
💧 Water Pollution: Effluents, dyes, chemicals discharged into rivers kill aquatic life.
🌱 Land Degradation: Dumping of solid wastes, toxic residues, and deforestation.
🔊 Noise Pollution: Loud machinery, drilling, and construction disturb humans and wildlife.
👉 Thus, industries affect air, water, land, and sound environment, leading to ecological imbalance.
(ii) Discuss the steps to be taken to minimise environmental degradation by industry.
Answer:
♻️ Adopt cleaner technologies and recycle industrial waste.
🚰 Treat effluents before releasing into rivers and lakes.
🌳 Afforestation around industrial zones to absorb pollutants.
🌍 Shift to renewable energy (solar, wind, hydropower) instead of coal and diesel.
📜 Enforce strict pollution-control laws and penalties for violators.
👉 With sustainable practices, industries can grow while protecting the environment.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
🔵 Q1. Which industry uses bauxite as raw material?
🟡 Options:
(A) Cement
(B) Aluminium Smelting
(C) Steel
(D) Paper
🟢 Answer: (B) Aluminium Smelting
🔵 Q2. Which industry manufactures telephones and computers?
🟡 Options:
(A) Steel
(B) Electronic
(C) Aluminium Smelting
(D) Textile
🟢 Answer: (B) Electronic
🔵 Q3. Which is called a basic industry?
🟡 Options:
(A) Steel
(B) Textile
(C) Sugar
(D) Paper
🟢 Answer: (A) Steel
🔵 Q4. Which industry is the largest organised sector in India?
🟡 Options:
(A) Jute
(B) Sugar
(C) Textile
(D) Paper
🟢 Answer: (C) Textile
🔵 Q5. Which state is the largest producer of cotton textiles?
🟡 Options:
(A) West Bengal
(B) Gujarat
(C) Tamil Nadu
(D) Punjab
🟢 Answer: (B) Gujarat
🔵 Q6. Which city is called the “Manchester of India”?
🟡 Options:
(A) Mumbai
(B) Kolkata
(C) Ahmedabad
(D) Chennai
🟢 Answer: (C) Ahmedabad
🔵 Q7. Which state is the largest producer of jute textiles?
🟡 Options:
(A) Assam
(B) Bihar
(C) West Bengal
(D) Odisha
🟢 Answer: (C) West Bengal
🔵 Q8. Which industry is known as the backbone of modern industry?
🟡 Options:
(A) Iron and Steel
(B) Cotton
(C) Cement
(D) Chemical
🟢 Answer: (A) Iron and Steel
🔵 Q9. Which is the second most important metallurgical industry after iron and steel?
🟡 Options:
(A) Aluminium
(B) Copper
(C) Zinc
(D) Manganese
🟢 Answer: (A) Aluminium
🔵 Q10. Which state is the largest producer of cement?
🟡 Options:
(A) Rajasthan
(B) Gujarat
(C) Tamil Nadu
(D) Maharashtra
🟢 Answer: (A) Rajasthan
🔵 Q11. Which industry is a bulk consumer of coal?
🟡 Options:
(A) Textile
(B) Cement
(C) Iron and Steel
(D) Sugar
🟢 Answer: (C) Iron and Steel
🔵 Q12. Which chemical industry is the largest in India?
🟡 Options:
(A) Plastics
(B) Fertilizers
(C) Drugs
(D) Dyes
🟢 Answer: (B) Fertilizers
🔵 Q13. Which city is called the “Electronic Capital of India”?
🟡 Options:
(A) Mumbai
(B) Bengaluru
(C) Delhi
(D) Hyderabad
🟢 Answer: (B) Bengaluru
🔵 Q14. Which industry provides the maximum employment after agriculture?
🟡 Options:
(A) IT
(B) Textile
(C) Iron and Steel
(D) Jute
🟢 Answer: (B) Textile
🔵 Q15. Which region is famous for silk textile industry?
🟡 Options:
(A) West Bengal
(B) Assam
(C) Karnataka
(D) Gujarat
🟢 Answer: (C) Karnataka
🔵 Q16. Which industry is the main consumer of limestone?
🟡 Options:
(A) Sugar
(B) Cement
(C) Steel
(D) Paper
🟢 Answer: (B) Cement
🔵 Q17. Which is the oldest industry in India?
🟡 Options:
(A) Jute
(B) Cotton textile
(C) Cement
(D) Iron and Steel
🟢 Answer: (B) Cotton textile
🔵 Q18. Which industry is not polluting but clean and eco-friendly?
🟡 Options:
(A) Fertilizers
(B) Paper
(C) IT & Software
(D) Cement
🟢 Answer: (C) IT & Software
🔵 Q19. Which of these is a consumer industry?
🟡 Options:
(A) Cement
(B) Machine tools
(C) Cotton textile
(D) Iron and Steel
🟢 Answer: (C) Cotton textile
🔵 Q20. What is manufacturing?
🟢 Answer:
🏭 Manufacturing is the process of producing goods in large quantities after processing raw materials into more valuable products.
Example: Cotton → Cloth, Iron ore → Steel.
🔵 Q21. What are basic industries? Give an example.
🟢 Answer:
⚙️ Industries whose products serve as raw materials for other industries.
Example: Iron and Steel industry.
🔵 Q22. Name two agro-based industries.
🟢 Answer:
🧵 Cotton textiles.
🌾 Sugar industry.
🔵 Q23. Mention two mineral-based industries.
🟢 Answer:
⛏️ Iron and Steel.
⚙️ Cement.
🌟 SECTION C — Short Answer (3 marks each)
🔵 Q24. State three features of the textile industry in India.
🟢 Answer:
🧵 Oldest industry; vast market demand.
👥 Provides maximum employment after agriculture.
📦 Contributes significantly to exports.
🔵 Q25. Distinguish between public sector and private sector industries.
🟢 Answer:
🏛️ Public sector: Owned by government (e.g., SAIL).
🏢 Private sector: Owned by individuals/firms (e.g., TISCO).
⚖️ Public = welfare + infrastructure; Private = profit-oriented.
🔵 Q26. Give three reasons why the iron and steel industry is located near coal and iron ore mines.
🟢 Answer:
⛏️ Iron ore is the basic raw material.
🔥 Coal needed as energy source.
🚚 Reduces transport cost by locating close to raw materials.
🔵 Q27. Why is cement industry strategically located in India?
🟢 Answer:
🧱 Needs bulky raw materials → limestone, gypsum.
📍 Availability in states like Rajasthan, MP, Gujarat.
🚉 Near markets and transport for easy distribution.
🔵 Q28. Mention three problems of jute industry in India.
🟢 Answer:
🪢 Stiff competition from synthetic substitutes.
🌍 Competition from Bangladesh.
📉 Fluctuating demand in international markets.
🌟 SECTION D — Long Answer (5 marks each)
🔵 Q29. Describe the distribution and importance of cotton textile industry in India.
🟢 Answer:
📍 Centres: Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Coimbatore, Kanpur, Kolkata.
🌾 Uses cotton as raw material; labour-intensive.
👥 Provides jobs to millions.
📦 Major export earner.
🧵 Supports other industries (garments, fashion).
🔵 Q30. Explain the role of manufacturing industries in the development of a country.
🟢 Answer:
🏭 Adds value to raw materials.
💰 Contributes to GDP & export earnings.
👥 Generates large-scale employment.
⚙️ Supplies tools & machines for agriculture.
🌍 Boosts trade and strengthens economy.
🔵 Q31. “Industrial pollution is a serious problem in India.” Explain.
🟢 Answer:
🌫️ Air: smoke, SO₂, dust from factories.
💧 Water: effluents from tanneries, paper, dyes.
🌱 Land: dumping solid waste, toxic sludge.
🔊 Noise: heavy machines, construction sites.
👉 Pollution damages health, crops, aquatic life, and soil fertility.
🔵 Q32. Suggest five measures to reduce environmental degradation by industries.
🟢 Answer:
♻️ Recycle & reuse waste.
🚰 Treat effluents before release.
🌳 Plant trees around industrial areas.
🌞 Use renewable energy (solar, wind).
📜 Strict enforcement of pollution control laws.
🌟 SECTION E — Case/Source-Based (4 marks each)
🔵 Q33. Case: A factory in Odisha uses bauxite as raw material.
(i) Which industry is this? (1)
(ii) Which metal is produced? (1)
(iii) Give two uses of this metal. (2)
🟢 Answer:
(i) 🏭 Aluminium smelting.
(ii) Aluminium.
(iii) ✈️ Aircraft, ⚡ electrical wires.
🔵 Q34. Case: A farmer’s son works in a textile mill in Ahmedabad.
(i) Which industry is this? (1)
(ii) Why is Ahmedabad suitable for this industry? (1)
(iii) Mention two challenges faced by this industry. (2)
🟢 Answer:
(i) 🧵 Cotton textile industry.
(ii) 🌾 Availability of cotton, cheap labour, transport.
(iii) 👕 Competition from synthetics; outdated machinery.
🔵 Q35. Source: “India is the second largest producer of cement.”
(i) Which raw material is mainly used? (1)
(ii) Name two cement-producing states. (1)
(iii) Mention two uses of cement. (2)
🟢 Answer:
(i) 🧱 Limestone.
(ii) 📍 Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh.
(iii) 🏠 Building houses; 🛣️ road & dam construction.
🌟 SECTION F — Map/Skill-Based (5 marks)
🔵 Q36. On an outline map of India, locate and label four major iron and steel plants.
🟢 Answer:
Jamshedpur (Jharkhand).
Bhilai (Chhattisgarh).
Rourkela (Odisha).
Durgapur (West Bengal).
🔵 Q37. For visually impaired candidates: Write names of any four centres of cotton textile industry.
🟢 Answer:
Mumbai (Maharashtra).
Ahmedabad (Gujarat).
Coimbatore (Tamil Nadu).
Kanpur (Uttar Pradesh).
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
