Class 10 : Science (In English) – Lesson 7. How do Organisms Reproduce?
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 Detailed Explanation
Introduction: The Need for Reproduction
All living organisms have a limited lifespan. To ensure continuity of life, they reproduce.
Reproduction: The biological process by which organisms produce new individuals of their own kind.
It ensures survival of species, transfer of genetic information, and variation for evolution.
💡 Concept: Reproduction is not essential for the survival of an individual, but essential for the survival of the species.
🟢 Types of Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction ✨
Involves a single parent, no gamete formation, offspring genetically identical (clones).
Faster, simpler, common in unicellular and lower organisms.
⚡ Methods:
Binary Fission (e.g. Amoeba, Paramecium) → Cell splits into two.
Multiple Fission (e.g. Plasmodium) → Splits into many cells at once.
Budding (e.g. Hydra, Yeast) → Small bud grows, detaches to form new organism.
Fragmentation (e.g. Spirogyra) → Body breaks into pieces, each grows into new one.
Regeneration (e.g. Planaria, Hydra) → Organism regenerates lost body parts into new individuals.
Vegetative Propagation (plants): New plants from vegetative parts.
🔵 Stem (potato, ginger)
🟢 Leaf (Bryophyllum)
🟡 Root (sweet potato)
✔️ Advantages: Quick, requires no special structures.
✏️ Note: No variation, so less adaptability.
Sexual Reproduction 🌍
Involves two parents, male and female gametes fuse → zygote → offspring.
Ensures variation, adaptability, and evolution.
Steps:
🔵 Gametogenesis (formation of gametes).
🟢 Fertilisation (fusion of gametes).
🟡 Zygote formation.
🔴 Development into new organism.
✔️ Advantages: Variations, survival in changing environment.
🟡 Sexual Reproduction in Plants 🌿
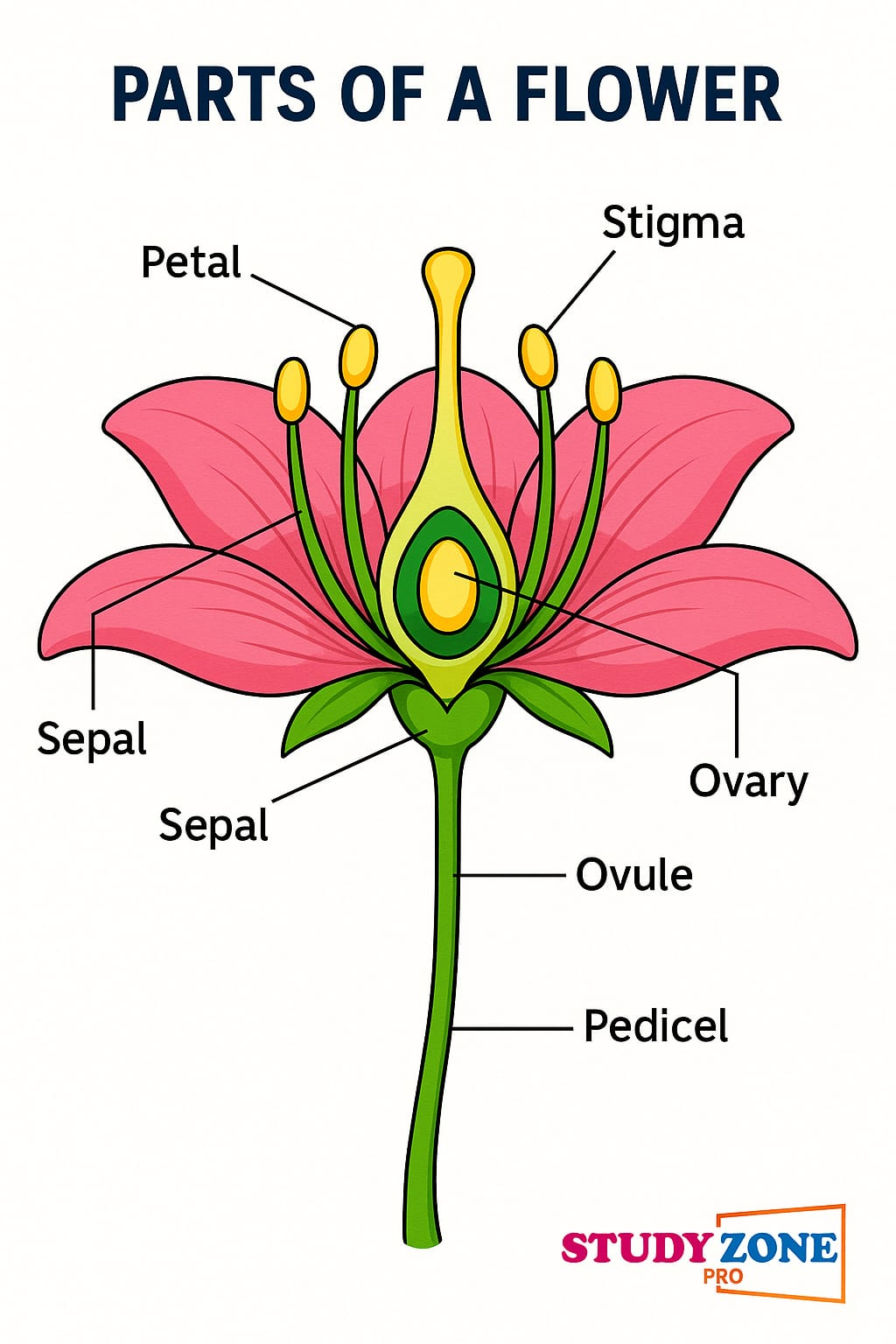
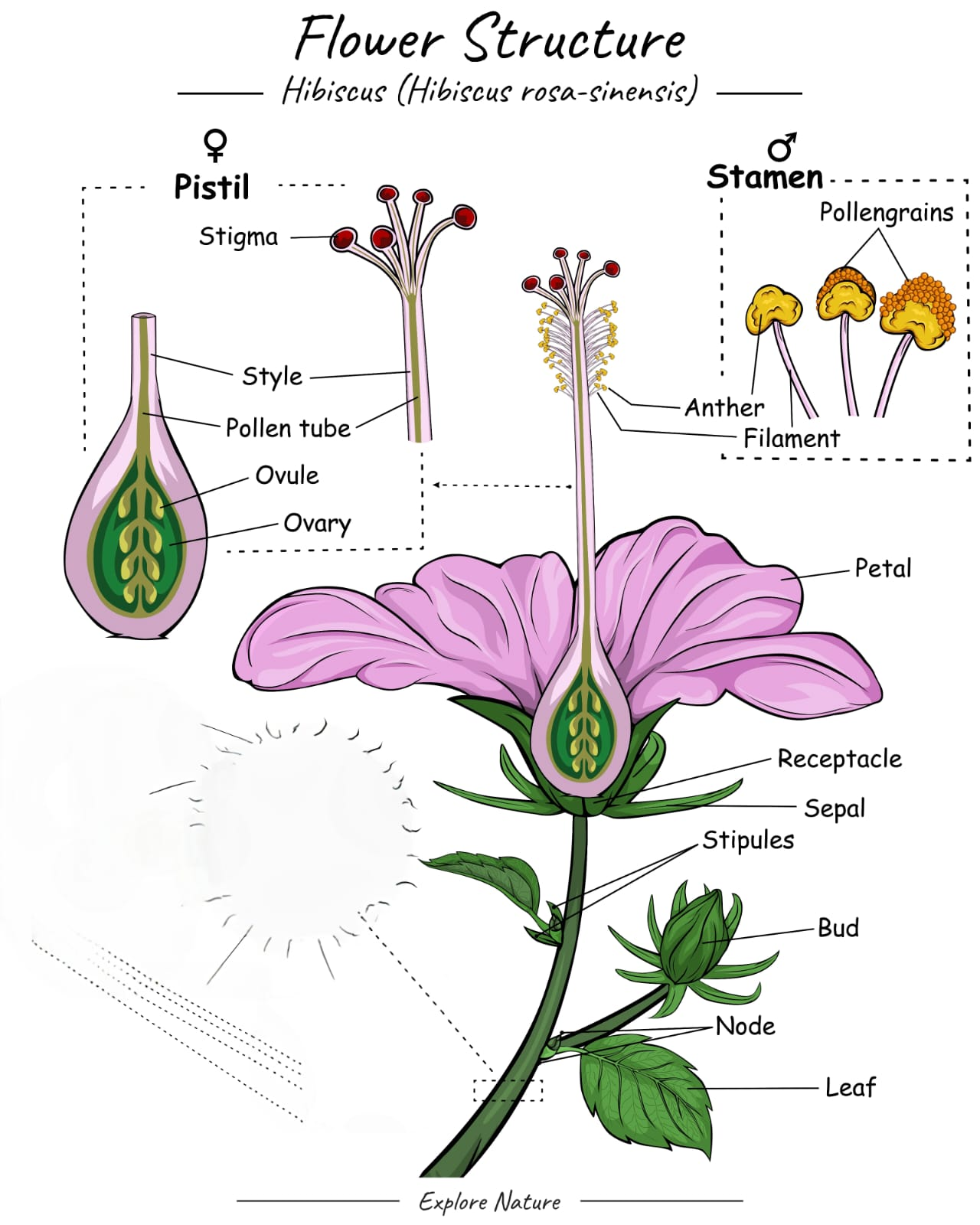
Male part: Stamen (anther + filament) → produces pollen (male gamete).
Female part: Carpel (ovary + style + stigma) → ovule contains egg cell.
➡️ Process:
Pollination – Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma.
Self-pollination (same flower/plant).
Cross-pollination (different plant, by wind, water, insects, etc.).
Fertilisation – Pollen tube carries male gamete → fuses with egg in ovule → zygote formed.
Post-fertilisation changes – Ovule → seed; Ovary → fruit.
💡 Concept: Pollination is a prerequisite for fertilisation in plants.
🔴 Reproduction in Human Beings 🧠
Humans reproduce sexually with high complexity and control.
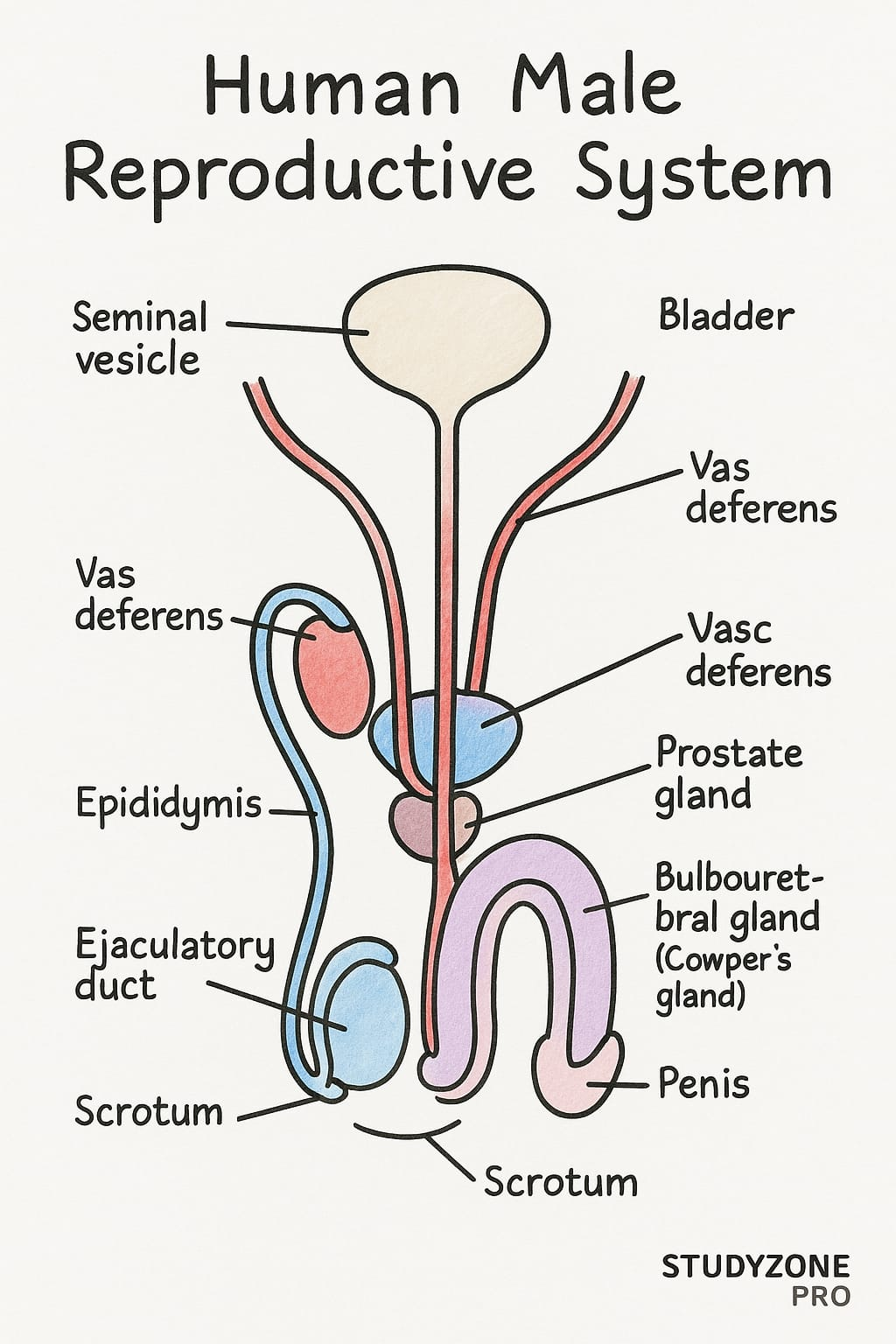
Male Reproductive System
Testes: Produce sperms + male hormone testosterone.
Scrotum: Maintains temperature for sperm production.
Vas deferens: Transports sperms.
Seminal vesicles & prostate gland: Add fluids → semen.
Penis: Organ for sperm transfer.
Female Reproductive System
Ovaries: Produce ova (eggs) + female hormones (estrogen, progesterone).
Fallopian tubes (oviducts): Site of fertilisation.
Uterus: Site of implantation and development of embryo.
Vagina: Birth canal, receives sperms.
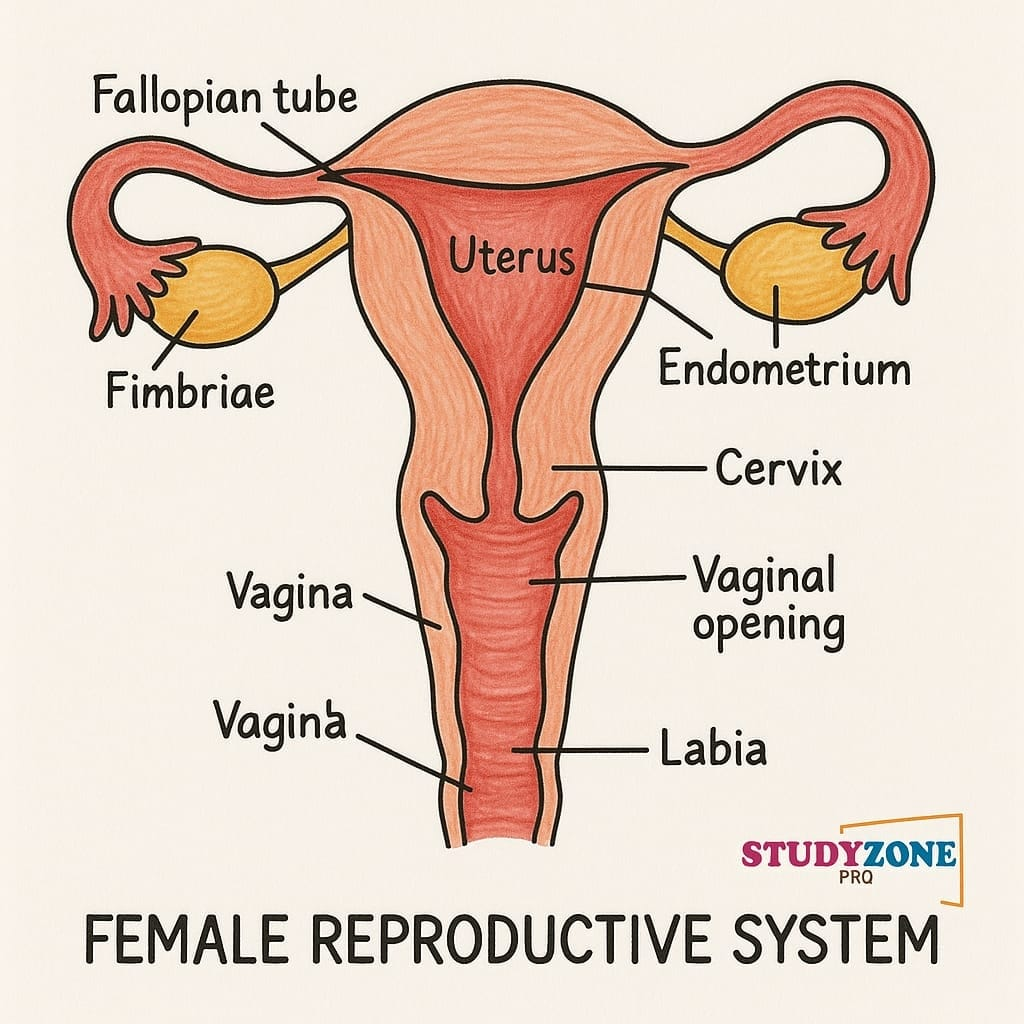
➡️ Fertilisation: Occurs in fallopian tube → zygote → embryo → foetus → baby develops in uterus.
✔️ Menstruation: If fertilisation does not occur, uterus lining sheds every ~28 days.
🟣 Contraception & Birth Control
✔️ Methods to prevent unwanted pregnancies and regulate population.
Barrier methods: Condoms, diaphragms.
Chemical methods: Oral pills (hormonal control).
Intrauterine devices (IUDs): Copper-T.
Surgical methods: Vasectomy (male), Tubectomy (female).
💡 Concept: Contraceptives help in family planning and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
🟠 Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) ⚠️
Spread by sexual contact with infected person.
Examples: AIDS (HIV), Gonorrhoea, Syphilis.
Prevention: Safe sex practices, awareness, use of protection.
🟤 Importance of Variation
Variations occur due to sexual reproduction and DNA replication errors.
Some variations are beneficial and help species survive changing environment.
Basis of evolution and natural selection.
✔️ Example: Bacteria developing resistance to antibiotics.
🟢 Summary
Asexual Reproduction: Single parent, no gametes, clones, includes binary fission, budding, fragmentation, regeneration, vegetative propagation.
Sexual Reproduction in Plants: Stamen and carpel, pollination → fertilisation → seed & fruit formation.
Human Reproduction: Male system (testes, vas deferens, glands, penis); Female system (ovaries, fallopian tube, uterus, vagina). Fertilisation in fallopian tube, embryo develops in uterus. Menstruation cycle ~28 days.
Contraception: Barrier, chemical, surgical, IUDs.
STDs: AIDS, syphilis, gonorrhoea.
Variation: Key to survival, adaptability, and evolution.
📝 Quick Recap
🌿 Asexual reproduction = simple, fast, no variation.
🌍 Sexual reproduction = gametes fuse, variation introduced.
🌸 Plants: Pollination + fertilisation → seeds & fruits.
🧠 Humans: Fertilisation in fallopian tube, embryo in uterus.
⚡ Contraception methods prevent pregnancy & STDs.
✔️ Variation ensures survival and evolution.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1:
Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in
(a) Amoeba
(b) Yeast
(c) Plasmodium
(d) Leishmania
✔️ Answer: (b) Yeast
💡 Yeast reproduces asexually by budding. A small outgrowth or bud forms on the parent cell, grows, and eventually detaches to become a new yeast cell.
🔵 Question 2:
Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
(a) Ovary
(b) Uterus
(c) Vas deferens
(d) Fallopian tube
✔️ Answer: (c) Vas deferens
💡 Vas deferens is part of the male reproductive system that transports sperms from the testes to the urethra.
🔵 Question 3:
The anther contains
(a) sepals
(b) ovules
(c) pistil
(d) pollen grains
✔️ Answer: (d) Pollen grains
💡 Anthers are part of the stamen, the male reproductive organ of a flower. They contain pollen sacs where pollen grains (male gametes) are produced.
🔵 Question 4:
What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
✔️ Answer:
➡️ Sexual reproduction introduces variation in the offspring.
➡️ Variations increase the adaptability and survival chances of species in changing environments.
➡️ It leads to evolution through natural selection, ensuring long-term species stability.
🔵 Question 5:
What are the functions performed by the testis in human beings?
✔️ Answer:
➡️ Testes produce male gametes called sperms.
➡️ They also secrete the male hormone testosterone, which controls secondary sexual characters like facial hair and voice deepening.
🔵 Question 6:
Why does menstruation occur?
✔️ Answer:
💡 In females, if fertilization does not occur, the thickened lining of the uterus and its blood vessels break down and are released through the vagina as blood and tissue flow. This process is called menstruation.
🔵 Question 7:
Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
✔️ Answer:
Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
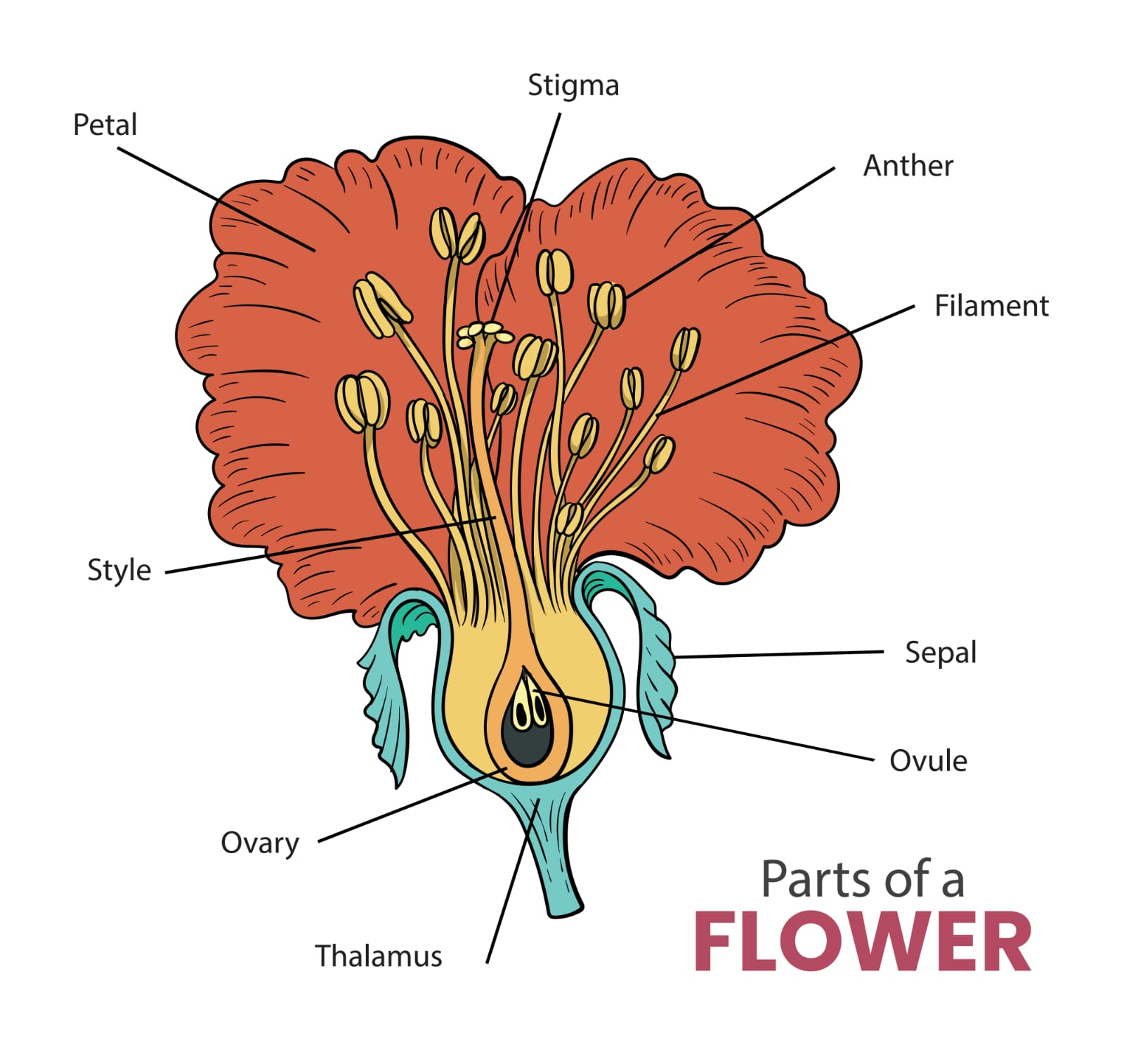
💡 The diagram should include:
Ovule inside Ovary
Sepal
Petal
Stamen (Anther + Filament)
Pistil (Stigma, Style, Ovary)
🔵 Question 8:
What are the different methods of contraception?
✔️ Answer:
➡️ Barrier methods: Condoms, diaphragms, which prevent sperm from reaching the ovum.
➡️ Chemical methods: Oral contraceptive pills that alter hormone levels and prevent ovulation.
➡️ Surgical methods: Vasectomy (males) and tubectomy (females), which block gamete transport.
🔵 Question 9:
How are the modes for reproduction different in unicellular and multicellular organisms?
✔️ Answer:
➡️ Unicellular organisms (e.g., Amoeba) reproduce by asexual methods like binary fission or budding.
➡️ Multicellular organisms (e.g., humans, plants) use sexual reproduction involving the fusion of male and female gametes, leading to genetic variation.
🔵 Question 10:
How does reproduction help in providing stability to populations of species?
✔️ Answer:
💡 Reproduction ensures the continuation of species by replacing older individuals with new ones. It maintains population size and genetic diversity, providing stability to the ecosystem.
🔵 Question 11:
What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods?
✔️ Answer:
➡️ To control population growth.
➡️ To avoid unwanted pregnancies.
➡️ To maintain health and spacing between children.
➡️ To prevent sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
⚙️ Section A: Q1–6 (1 Mark Each – MCQ Type)
🔵 Question 1: Which of the following is a method of asexual reproduction in Amoeba?
🔵 (A) Budding
🟢 (B) Fragmentation
🔴 (C) Binary fission
🟡 (D) Spore formation
✔️ Answer: (C) Binary fission
💡 Amoeba divides into two daughter cells by binary fission, where the nucleus splits first followed by cytoplasm.
🔵 Question 2: Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
🔵 (A) Ovary
🟢 (B) Oviduct
🔴 (C) Uterus
🟡 (D) Vas deferens
✔️ Answer: (D) Vas deferens
💡 Vas deferens is part of the male reproductive system.
🔵 Question 3: In humans, fertilization takes place in —
🔵 (A) Ovary
🟢 (B) Uterus
🔴 (C) Oviduct (Fallopian tube)
🟡 (D) Cervix
✔️ Answer: (C) Oviduct (Fallopian tube)
💡 Fertilization occurs in the oviduct where sperm and ovum fuse to form a zygote.
🔵 Question 4: Which structure protects the developing embryo in human females?
🔵 (A) Ovary
🟢 (B) Uterus
🔴 (C) Oviduct
🟡 (D) Cervix
✔️ Answer: (B) Uterus
💡 The embryo implants in the uterine wall where it develops safely.
🔵 Question 5: Vegetative propagation by leaves is seen in —
🔵 (A) Bryophyllum
🟢 (B) Yeast
🔴 (C) Spirogyra
🟡 (D) Rhizopus
✔️ Answer: (A) Bryophyllum
💡 In Bryophyllum, buds present on leaf margins grow into new plants.
🔵 Question 6: Which one of the following diseases is not sexually transmitted?
🔵 (A) HIV-AIDS
🟢 (B) Hepatitis B
🔴 (C) Gonorrhea
🟡 (D) Diabetes
✔️ Answer: (D) Diabetes
💡 Diabetes is a metabolic disorder, not an STD.
⚡ Section B: Q7–12 (2 Marks Each – Short Answers)
🔵 Question 7: What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction?
✔️ Answer:
DNA copying ensures that genetic information is transferred from parent to offspring. This maintains the body design and characteristics of a species. Minor variations during copying lead to evolution over generations.
🟢 Question 8: Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction.
✔️ Answer:
➡️ Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces identical offspring (e.g., fission in Amoeba).
➡️ Sexual reproduction involves two parents, male and female gametes, and leads to variations in offspring.
🔴 Question 9: What is fragmentation? Give one example.
✔️ Answer:
Fragmentation is a method of asexual reproduction where the body of an organism breaks into smaller fragments, each capable of growing into a new individual.
💡 Example: Spirogyra.
🟡 Question 10: What are the functions of the human ovary?
✔️ Answer:
Ovaries produce female gametes (ova) and secrete female sex hormones — estrogen and progesterone — which regulate menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
🔵 Question 11: What is pollination? Mention its two types.
✔️ Answer:
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of a flower.
Types:
1️⃣ Self-pollination – within the same flower or same plant.
2️⃣ Cross-pollination – between flowers of different plants.
🟢 Question 12: What is the function of the placenta during pregnancy?
✔️ Answer:
Placenta connects the embryo with the mother’s body. It provides oxygen and nutrients to the fetus and removes waste products.
⚙️ Section C: Q13–22 (3 Marks Each – Mid-Length Answers)
🔵 Question 13: Explain the process of fertilization in human beings.
✔️ Answer:
During reproduction, sperm from the male enters the female reproductive tract and meets the ovum in the oviduct. The nucleus of the sperm fuses with that of the ovum to form a zygote. The zygote divides to form an embryo, which implants in the uterus.
🟢 Question 14: Describe the process of binary fission with an example.
✔️ Answer:
Binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction where an organism divides into two identical daughter cells.
Example: In Amoeba, the nucleus divides first followed by the cytoplasm, forming two new individuals.
🔴 Question 15: What is regeneration? How does it help an organism?
✔️ Answer:
Regeneration is the ability of an organism to regrow its lost body parts.
Example: Planaria can regenerate a complete body from small fragments.
💡 It helps organisms survive injury and reproduce asexually.
🟡 Question 16: Explain the structure and function of the human male reproductive system.
✔️ Answer:
It includes testes, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and penis.
Testes produce sperms and testosterone. Sperms travel through the vas deferens, mix with fluids from glands to form semen, and are released through the penis during ejaculation.
🔵 Question 17: Explain the menstrual cycle in human females.
✔️ Answer:
The menstrual cycle is a 28-day cycle in which an ovum is released from the ovary.
If fertilization does not occur, the thickened uterine wall breaks down and blood along with tissue is discharged (menstruation).
If fertilization occurs, menstruation stops and pregnancy begins.
🟢 Question 18: What are sexually transmitted diseases? Give two examples.
✔️ Answer:
Diseases transmitted through sexual contact are called sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
Examples — HIV-AIDS and Gonorrhea.
💡 These can be prevented by using protection and maintaining hygiene.
🔴 Question 19: Describe the process of vegetative propagation.
✔️ Answer:
In vegetative propagation, new plants are formed from vegetative parts like stem, root, or leaf.
Examples:
• Stem cutting – Rose
• Tubers – Potato
• Leaves – Bryophyllum
💡 It allows rapid reproduction and identical offspring.
🟡 Question 20: State the main functions of the human female reproductive system.
✔️ Answer:
Ovaries produce ova and female hormones.
Oviducts provide a site for fertilization.
The uterus nourishes and protects the developing embryo.
🔵 Question 21: Explain the role of hormones in human reproduction.
✔️ Answer:
Hormones control the development of reproductive organs and secondary sexual characters.
Testosterone in males and estrogen-progesterone in females regulate gamete formation and reproductive cycles.
🟢 Question 22: What is the significance of variation in reproduction?
✔️ Answer:
Variation ensures survival of species in changing environments. It provides adaptability and evolutionary advantages to organisms.
🧠 Section D: Q23–30 (4 Marks Each – Long and Case-Based Answers)
🔵 Question 23: Explain the process of sexual reproduction in flowering plants.
✔️ Answer:
Flowering plants reproduce sexually through pollination, fertilization, and seed formation.
After pollination, pollen reaches the stigma and grows a pollen tube toward the ovule.
The male gamete fuses with the female gamete (egg) to form a zygote. The ovule develops into a seed, and the ovary becomes the fruit.
🟢 Question 24: Describe the human female reproductive system and explain its functions.
✔️ Answer:
It consists of ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix, and vagina.
Ovaries produce ova; the oviduct transports them and is the site of fertilization.
The uterus provides protection and nourishment to the embryo, and the cervix acts as a passage during childbirth.
🔴 Question 25: Describe three methods of asexual reproduction in organisms.
✔️ Answer:
1️⃣ Fission: The parent splits into two or more individuals (Amoeba, Paramecium).
2️⃣ Budding: A small outgrowth develops into a new organism (Yeast, Hydra).
3️⃣ Spore formation: Spores are produced that grow into new organisms (Rhizopus).
🟡 Question 26: Explain with a diagrammatic description the process of fertilization and embryo development in humans.
✔️ Answer:
Fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube when sperm and ovum fuse to form a zygote.
The zygote divides repeatedly and becomes an embryo.
The embryo moves to the uterus and gets implanted in its wall, where it develops into a fetus.
🔵 Question 27: What are contraceptive methods? Explain any three types.
✔️ Answer:
Contraceptive methods prevent pregnancy.
1️⃣ Barrier methods: Use of condoms prevents sperm from reaching egg.
2️⃣ Chemical methods: Oral pills alter hormone levels to stop ovulation.
3️⃣ Surgical methods: Vasectomy (in males) and Tubectomy (in females) block gamete transport.
🟢 Question 28: Case-based question:
A couple wishes to prevent pregnancy. The doctor explains three methods — barrier, chemical, and surgical.
✔️ Answer:
Barrier methods (like condoms) stop sperm-egg contact.
Chemical methods (like oral pills) prevent ovulation.
Surgical methods (like vasectomy or tubectomy) permanently block gamete passage.
💡 Contraception helps in family planning and prevents sexually transmitted diseases.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
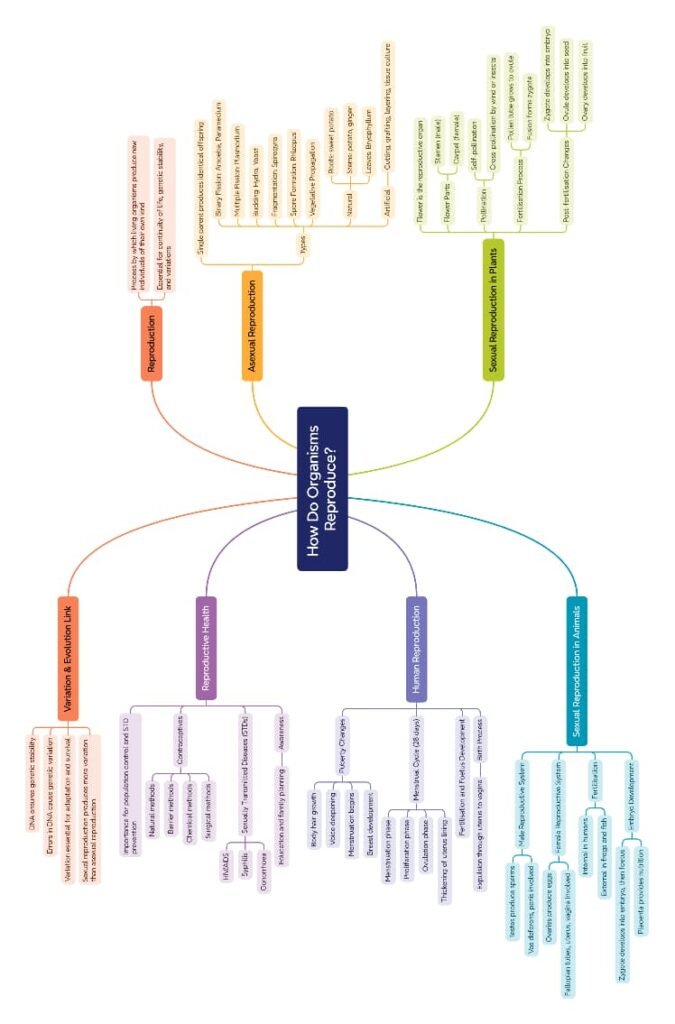
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
