Class 10 : Science (In English) – Lesson 6. Control and Coordination
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
🔵 Detailed Explanation
Introduction: The Need for Control and Coordination
Living organisms continuously respond to changes around them—light, sound, touch, smell, taste, and internal stimuli like hunger or pain. To survive, they require systems that control activities and coordinate responses efficiently.
In plants, coordination is mainly chemical, through hormones.
In animals, it is through the nervous system and endocrine system.
💡 Concept: Control ensures order, coordination ensures integration—together they make responses accurate.
🔵 Nervous System in Animals
The nervous system is the fastest way of control in animals. It works via specialised cells called neurons.
Structure of Neuron
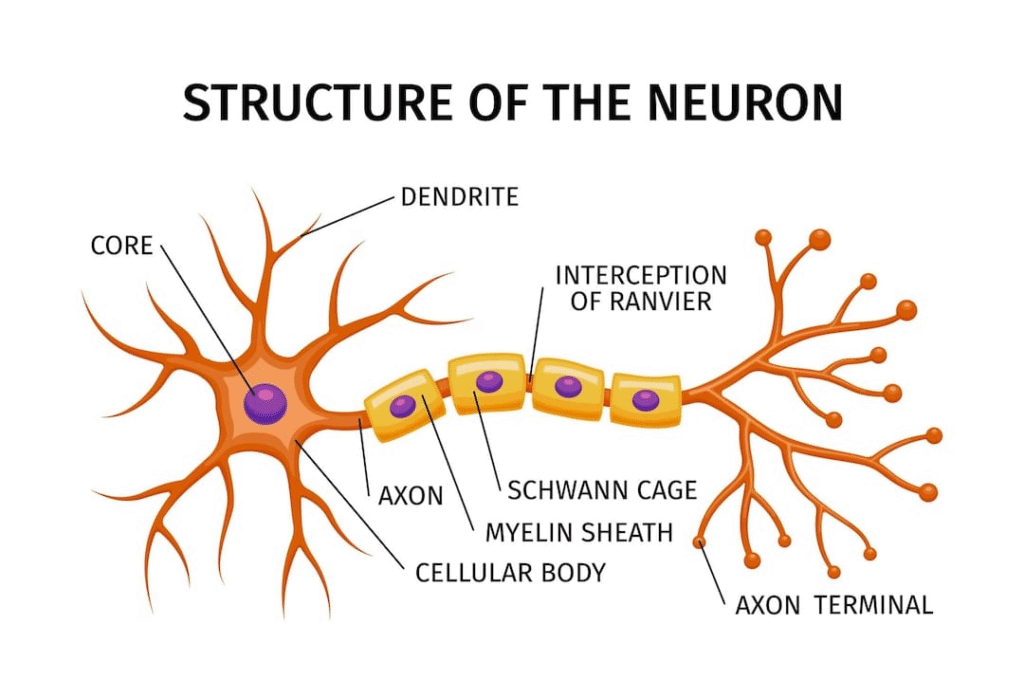
Cell body: Contains nucleus and cytoplasm.
Dendrites: Receive impulses from surroundings.
Axon: Transmits impulses away from cell body.
Synapse: Junction between two neurons; impulses travel chemically here.
➡️ Function: Neurons transmit impulses as electrochemical signals, measured in milliseconds.
🟢 Transmission of Nerve Impulse
Stimulus received by dendrites.
Electrical signal generated in cell body.
Travels through axon → synapse.
Chemical neurotransmitters carry impulse to next neuron or effector organ.
✔️ Effector: A muscle (contracts) or a gland (secretes).
🟡 Human Nervous System
Divided into:
Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Nerves branching from CNS.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Involuntary activities (heartbeat, digestion).
Brain
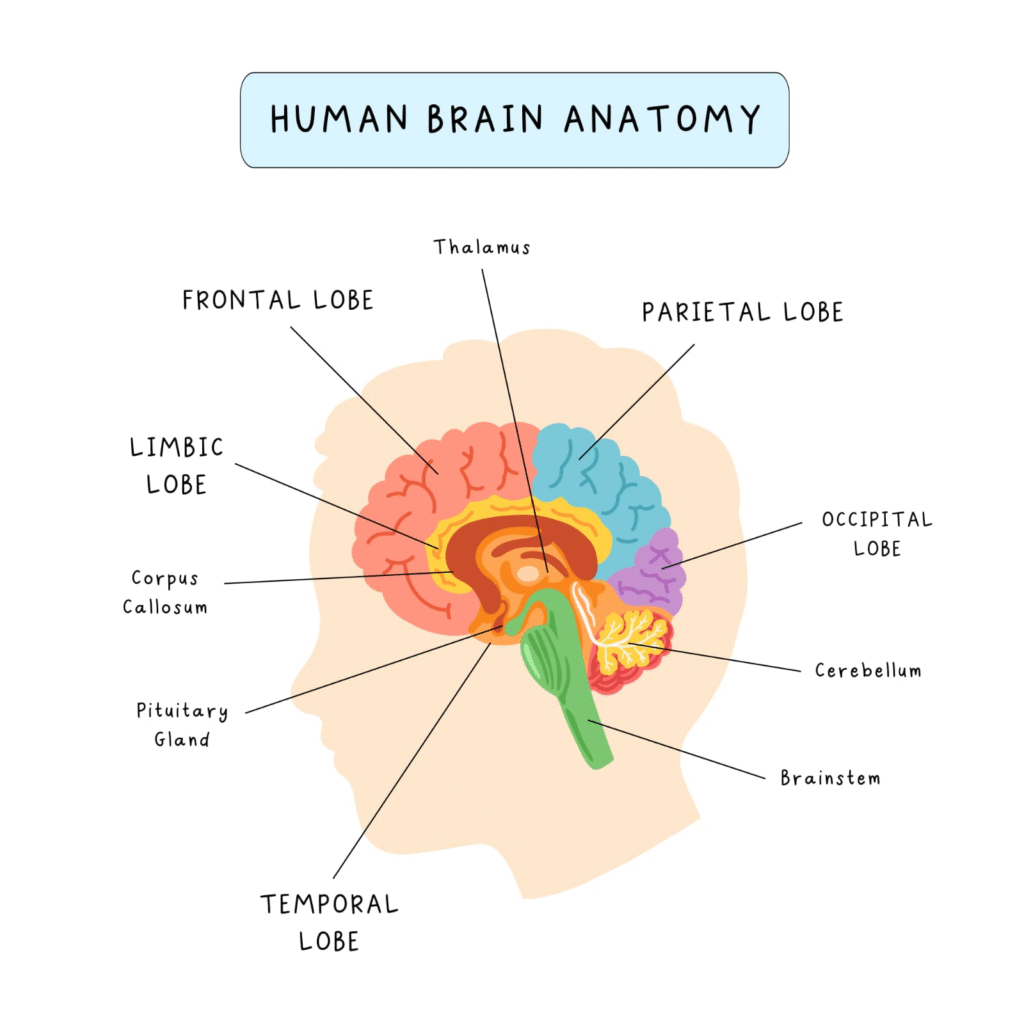
Forebrain: Controls thinking, reasoning, memory, voluntary actions, sensory interpretation.
Midbrain: Controls reflexes related to vision and hearing.
Hindbrain:
🔵 Cerebellum – balance and posture.
🟢 Medulla oblongata – involuntary functions (breathing, heartbeat).
🟡 Pons – relay centre.
✏️ Note: Brain is protected by skull, cushioned by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
🔴 Reflex Action
Reflex: Quick, automatic response to a stimulus without conscious thought.
Pathway: Stimulus → receptor → sensory neuron → spinal cord → motor neuron → effector.
Example: Withdrawing hand from hot object.
💡 Concept: Reflexes protect the body from sudden danger.
🟢 Coordination by Hormones in Animals
Hormones are chemical messengers secreted by endocrine glands, released into blood, and act on target organs.
Major Human Hormones
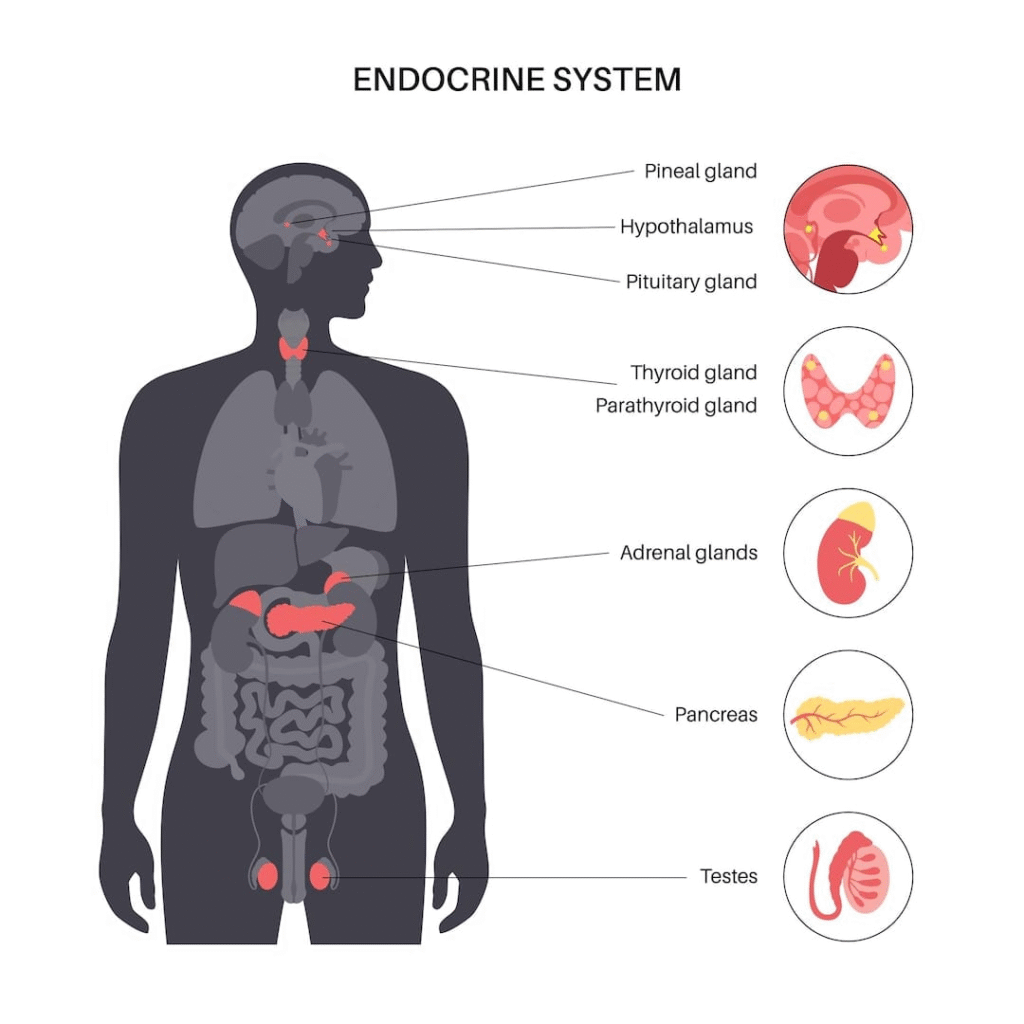
Pituitary gland: Master gland; growth hormone; controls other glands.
Thyroid: Produces thyroxine; regulates metabolism.
Adrenal glands: Adrenaline; increases heartbeat, blood pressure in emergencies.
Pancreas: Insulin regulates blood sugar.
Testes/Ovaries: Sex hormones (testosterone, estrogen, progesterone).
✔️ Endocrine system provides slower but longer-lasting control compared to nervous system.
🟡 Coordination in Plants
Plants lack nervous system but show responses using chemical messengers and growth regulators.
Tropic Movements 🌿
Directional responses of plants to stimuli:
Phototropism: Stem bends towards light.
Geotropism: Roots grow downward due to gravity.
Hydrotropism: Roots grow towards water.
Thigmotropism: Tendrils coil around support.
✔️ Controlled by plant hormones (auxins).
Nastic Movements
Non-directional responses:
Example: Folding of leaves in Mimosa pudica when touched.
Caused by changes in turgor pressure in specialized cells.
🔴 Plant Hormones
Auxins: Promote cell elongation, root initiation, phototropism.
Gibberellins: Stimulate stem elongation, seed germination.
Cytokinins: Promote cell division, delay aging of leaves.
Abscisic Acid (ABA): Inhibits growth, induces dormancy, closes stomata during stress.
✏️ Note: Hormones work in coordination to maintain plant growth and responses.
Importance of Control and Coordination
Maintains internal balance (homeostasis).
Enables organisms to respond and adapt to environment.
Helps in growth, reproduction, defense, and survival.
🟢 Summary
Nervous System: Neurons transmit impulses; CNS (brain, spinal cord), PNS, ANS; brain functions in forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain. Reflex action provides quick response.
Hormonal Control in Animals: Endocrine glands secrete hormones—pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, testes/ovaries. Provide slow but lasting regulation.
Coordination in Plants: Tropic movements (photo, geo, hydro, thigmo), nastic movements. Plant hormones—auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid.
Significance: Ensures survival, adaptation, and smooth functioning of organisms.
📝 Quick Recap
🧠 Nervous system: Neurons, brain parts, reflex action.
🌿 Plant coordination: Tropic and nastic movements.
⚡ Hormones: Chemical messengers in animals and plants.
✔️ Control + coordination = balance, adaptation, survival.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
🔵 Question 1:
Which of the following is a plant hormone?
(a) Insulin
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Oestrogen
(d) Cytokinin
✔️ Answer: (d) Cytokinin
💡 Cytokinin is a plant hormone that promotes cell division and growth. The others (Insulin, Thyroxin, Oestrogen) are animal hormones.
🟢 Question 2:
The gap between two neurons is called a —
(a) dendrite
(b) synapse
(c) axon
(d) impulse
✔️ Answer: (b) synapse
💡 A synapse is the junction between two neurons where nerve impulses are transmitted through chemical messengers called neurotransmitters.
🔴 Question 3:
The brain is responsible for —
(a) thinking
(b) regulating the heartbeat
(c) balancing the body
(d) all of the above
✔️ Answer: (d) all of the above
💡 The brain performs multiple functions: the cerebrum handles thinking, the medulla controls involuntary actions like heartbeat, and the cerebellum maintains balance.
🟡 Question 4:
What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
✔️ Answer:
Receptors detect information from the environment and send signals to the brain and spinal cord for response.
If receptors fail, the body cannot sense stimuli such as pain, heat, or light, leading to injuries or inability to respond to environmental changes.
💡 Example: Damage to eye receptors causes blindness; ear receptor failure leads to deafness.
🔵 Question 5:
Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
✔️ Answer:
✔️ Structure of neuron:
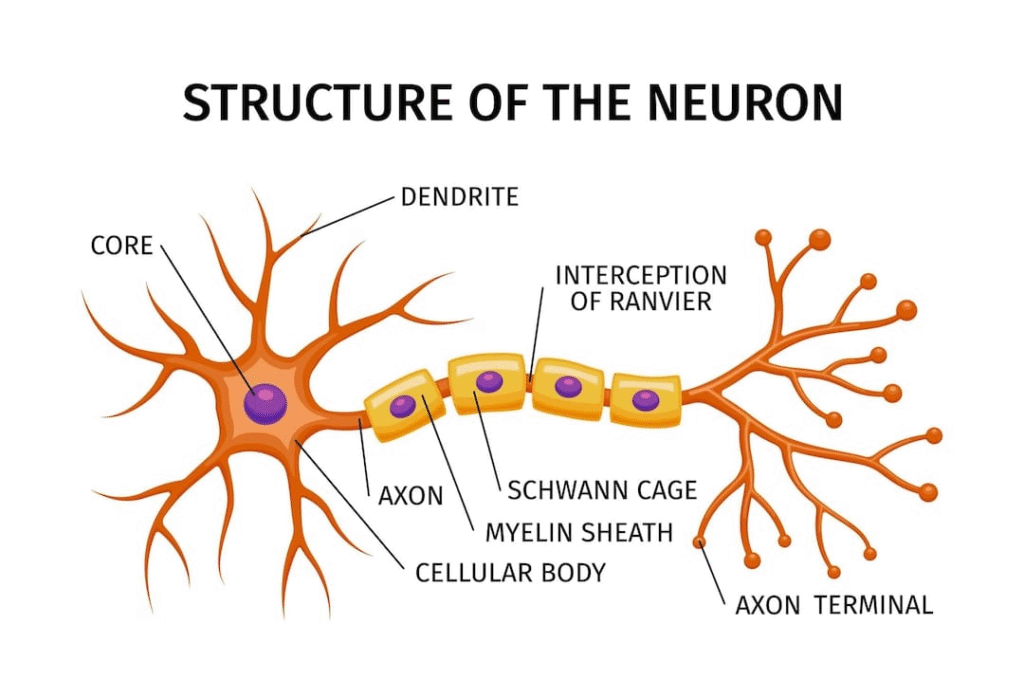
A neuron consists of three parts —
1️⃣ Cell body (cyton): Contains the nucleus and cytoplasm.
2️⃣ Dendrites: Receive impulses from other neurons.
3️⃣ Axon: Transmits impulses to other neurons or muscles.
💡 Function: The neuron carries messages in the form of electrical impulses throughout the body, forming the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
🟢 Question 6:
How does phototropism occur in plants?
✔️ Answer:
Phototropism is the movement or growth of plant parts in response to light.
When light falls on one side of the plant, auxin (a plant hormone) moves to the shaded side, causing cells there to elongate more. This results in the bending of the shoot toward light.
💡 Shoots show positive phototropism; roots show negative phototropism.
🔴 Question 7:
Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
✔️ Answer:
In spinal cord injury, reflex actions and communication between the brain and body parts get affected.
Impulses cannot travel to or from the brain, leading to paralysis or loss of control in body movements below the injury site.
🟡 Question 8:
How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
✔️ Answer:
Chemical coordination in plants is controlled by hormones called phytohormones.
Auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene regulate various processes like growth, seed germination, ripening, and dormancy.
💡 These hormones coordinate activities in the absence of a nervous system.
🔵 Question 9:
What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
✔️ Answer:
Organisms need control and coordination to respond to stimuli and maintain internal stability.
The nervous and endocrine systems help in sending, receiving, and processing information so that all organs work together efficiently.
💡 Without coordination, different parts of the body would act independently and disrupt normal functioning.
🟢 Question 10:
How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
✔️ Answer:
➡️ Involuntary actions: These are automatic functions like heartbeat and breathing controlled by the medulla.
➡️ Reflex actions: These are sudden, quick responses to external stimuli, like pulling your hand away from a flame, controlled by the spinal cord.
💡 Reflexes are protective; involuntary actions maintain body functions.
🔴 Question 11:
Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
✔️ Answer:
The nervous system works through electrical impulses transmitted by neurons. It is fast and gives immediate responses, like muscle movement.
The hormonal system works through chemical messengers (hormones) secreted into the blood. It is slower but produces long-lasting effects, such as growth or metabolism.
💡 Both systems coordinate to maintain body balance and internal stability.
🟡 Question 12:
What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs?
✔️ Answer:
Movement in sensitive plants like Mimosa pudica occurs due to changes in water pressure within cells and does not involve nerves or muscles. It is a chemical and turgor-based response.
Movement in human legs involves muscle contraction controlled by the nervous system through electrical impulses.
💡 Plant movement is slow and chemical; human movement is fast and controlled by neurons.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
(CBSE MODEL QUESTIONS PAPER)
ESPECIALLY MADE FROM THIS LESSON ONLY
⚙️ Section A: Q1–6 (1 Mark Each – MCQ Type)
🔵 Question 1: Which part of the human brain controls posture and balance?
🔵 (A) Cerebrum
🟢 (B) Cerebellum
🔴 (C) Medulla oblongata
🟡 (D) Pons
✔️ Answer: (B) Cerebellum
💡 The cerebellum helps maintain balance, posture, and coordination of voluntary movements.
🔵 Question 2: Which of the following is not a part of the human nervous system?
🔵 (A) Spinal cord
🟢 (B) Brain
🔴 (C) Heart
🟡 (D) Nerves
✔️ Answer: (C) Heart
💡 The heart is controlled by the nervous system but it is not a part of it.
🔵 Question 3: The main function of the plant hormone auxin is to —
🔵 (A) Promote cell division in roots
🟢 (B) Inhibit seed germination
🔴 (C) Promote cell elongation in shoots
🟡 (D) Promote leaf fall
✔️ Answer: (C) Promote cell elongation in shoots
💡 Auxin helps in the bending of shoots toward light by elongating cells on the shaded side.
🔵 Question 4: Which part of the brain controls involuntary actions like breathing and heartbeat?
🔵 (A) Cerebrum
🟢 (B) Cerebellum
🔴 (C) Medulla oblongata
🟡 (D) Midbrain
✔️ Answer: (C) Medulla oblongata
💡 Medulla controls involuntary activities such as breathing and heartbeat.
🔵 Question 5: Which plant hormone promotes ripening of fruits?
🔵 (A) Cytokinin
🟢 (B) Ethylene
🔴 (C) Auxin
🟡 (D) Gibberellin
✔️ Answer: (B) Ethylene
💡 Ethylene promotes ripening of fruits and aging in plants.
🔵 Question 6: Which of the following is a reflex action?
🔵 (A) Reading a book
🟢 (B) Pulling hand away from hot object
🔴 (C) Talking to a friend
🟡 (D) Writing an answer
✔️ Answer: (B) Pulling hand away from hot object
💡 Reflex actions are quick automatic responses controlled by the spinal cord.
⚡ Section B: Q7–12 (2 Marks Each – Short Answers)
🔵 Question 7: What is a synapse?
✔️ Answer:
A synapse is a junction between two neurons or between a neuron and a muscle cell. The transmission of nerve impulses across a synapse occurs through chemicals called neurotransmitters.
🟢 Question 8: Distinguish between voluntary and involuntary actions.
✔️ Answer:
Voluntary actions are performed consciously under the control of the cerebrum, like walking or writing.
Involuntary actions are automatic and controlled by the medulla or spinal cord, like breathing or heartbeat.
🔴 Question 9: What are hormones? Name any two plant hormones.
✔️ Answer:
Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate functions in animals and plants.
Examples of plant hormones — Auxin and Gibberellin.
🟡 Question 10: Why is the reflex arc important?
✔️ Answer:
The reflex arc allows quick and automatic responses to harmful stimuli without the involvement of the brain, thus protecting the body from injury.
🔵 Question 11: Write two differences between nervous control and hormonal control.
✔️ Answer:
Nervous control is fast and transmitted through neurons, whereas hormonal control is slow and carried through the bloodstream. Nervous responses are short-lived, while hormonal responses last longer.
🟢 Question 12: What are tropic movements? Name any two types.
✔️ Answer:
Tropic movements are directional growth responses of plants toward or away from external stimuli.
Examples — Phototropism (light) and Geotropism (gravity).
⚙️ Section C: Q13–22 (3 Marks Each – Mid-Length Answers)
🔵 Question 13: Explain the structure and function of a neuron.
✔️ Answer:
A neuron has three main parts — the cell body, dendrites, and axon.
The cell body contains the nucleus and cytoplasm. Dendrites receive impulses, while the axon transmits them to other neurons or muscles. The neuron carries messages as electrical and chemical signals throughout the body.
🟢 Question 14: Describe the pathway of a reflex action with an example.
✔️ Answer:
The reflex action pathway is: stimulus → receptor → sensory neuron → spinal cord → motor neuron → effector → response.
Example — When a person touches a hot object, the sensory neuron sends impulses to the spinal cord, which sends signals through the motor neuron to withdraw the hand.
🔴 Question 15: What is phototropism? Describe an experiment to demonstrate it.
✔️ Answer:
Phototropism is the bending of plant parts in response to light.
Experiment — Place a potted plant near a window. The shoot bends toward light because auxin accumulates on the shaded side, causing cells there to elongate more.
🟡 Question 16: Explain how the human brain is protected.
✔️ Answer:
The brain is protected by the skull (cranium), three protective membranes called meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid which cushions it from shocks and injuries.
🔵 Question 17: Describe the role of the spinal cord in coordination.
✔️ Answer:
The spinal cord transmits nerve impulses to and from the brain and also coordinates reflex actions by forming a reflex arc.
🟢 Question 18: Explain how plant hormones control growth and movement.
✔️ Answer:
Auxins promote shoot growth and phototropism.
Gibberellins promote stem elongation and seed germination.
Cytokinins promote cell division.
Abscisic acid inhibits growth and causes wilting.
Ethylene promotes fruit ripening.
🔴 Question 19: What is the function of the cerebrum?
✔️ Answer:
The cerebrum controls voluntary actions, thinking, learning, reasoning, and memory. It also receives sensory information and sends motor responses to body parts.
🟡 Question 20: Differentiate between phototropism and geotropism.
✔️ Answer:
Phototropism is the response of plant parts toward or away from light. Shoots show positive phototropism while roots show negative phototropism.
Geotropism is the response to gravity. Roots show positive geotropism while shoots show negative geotropism.
🔵 Question 21: How does the endocrine system help in coordination?
✔️ Answer:
The endocrine glands secrete hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones act on specific target organs to regulate metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Example: Insulin regulates blood sugar level.
🟢 Question 22: Name the five main endocrine glands and their functions.
✔️ Answer:
Pituitary gland controls other glands, thyroid regulates metabolism, adrenal prepares the body for stress, pancreas controls sugar level, and gonads control reproductive functions.
🧠 Section D: Q23–30 (4 Marks Each – Long and Case-Based)
🔵 Question 23: Explain the coordination between the nervous and endocrine systems in humans.
✔️ Answer:
The nervous system controls immediate responses through electrical impulses, while the endocrine system regulates long-term changes through hormones.
The hypothalamus connects the brain with the endocrine system by controlling the pituitary gland. During stress, the brain signals adrenal glands to release adrenaline for “fight or flight” response.
🟢 Question 24: Describe the structure and function of the human brain.
✔️ Answer:
The human brain has three parts —
Forebrain (cerebrum) controls voluntary actions, memory, and intelligence.
Midbrain controls reflex movements of eyes and head.
Hindbrain includes the cerebellum (balance) and medulla (involuntary actions).
The brain coordinates all body activities and responses.
🔴 Question 25: How do plants respond to stimuli without a nervous system?
✔️ Answer:
Plants use chemical messengers called hormones to respond to stimuli.
Tropic movements like phototropism (light) and geotropism (gravity) occur due to differential growth caused by uneven distribution of hormones such as auxins.
🟡 Question 26: What is adrenaline? Explain its role in our body.
✔️ Answer:
Adrenaline is a hormone secreted by the adrenal glands during emergencies.
It increases heartbeat, breathing rate, and blood flow to muscles, preparing the body for “fight or flight.”
🔵 Question 27: Compare the roles of the nervous system and hormonal system in coordination.
✔️ Answer:
The nervous system uses electrical impulses for fast communication, while the endocrine system uses chemical messengers (hormones) for slower but long-lasting effects.
The nervous system acts through neurons, while the endocrine system acts through glands that release hormones into the bloodstream.
🟢 Question 28: Case-based question: A person accidentally touches a sharp pin and immediately withdraws his hand. Explain the pathway involved.
✔️ Answer:
The stimulus (pin prick) is received by receptors in the skin. The sensory neuron carries the message to the spinal cord. The spinal cord processes it and sends signals through a motor neuron to the effector muscle. The muscle contracts, and the hand is withdrawn instantly. This is a reflex action controlled by the spinal cord.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
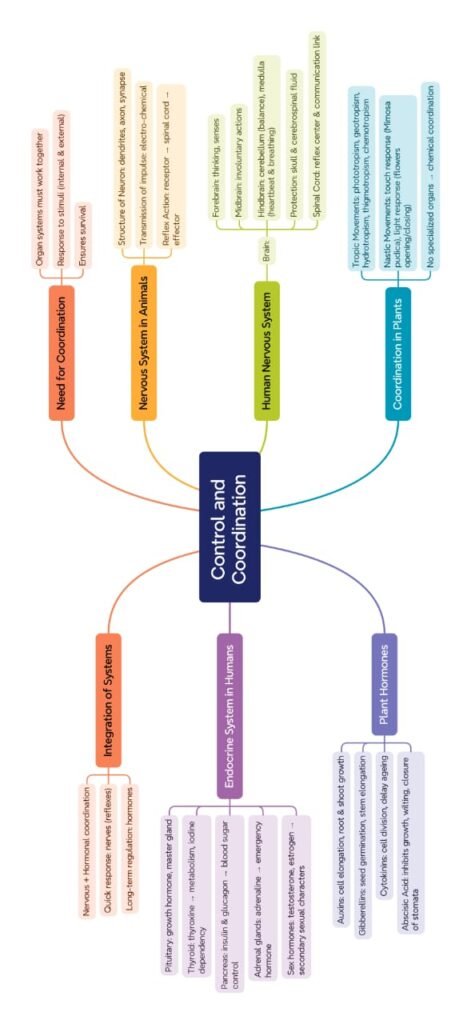
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
