Class 10 : Science (In English) – Lesson 1. Chemical Reactions and Equations
EXPLANATION AND SUMMARY
Chemical reactions are the foundation of chemistry. Every change that takes place around us – from the rusting of iron to the digestion of food – involves chemical reactions. The NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 1, “Chemical Reactions and Equations,” introduces students to the basics of these chemical changes and the way they are represented through chemical equations.
What is a Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process in which one or more substances (called reactants) are converted into new substances (called products) with different chemical properties. These changes are usually accompanied by observable features such as:
Change in state (solid, liquid, gas)
Change in color
Evolution of gas
Change in temperature
Formation of a precipitate
Example:
When magnesium ribbon is burnt in air, it reacts with oxygen to form magnesium oxide:
Magnesium (Mg) + Oxygen (O₂) → Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
This reaction is accompanied by a bright white flame and the formation of white powder (MgO).
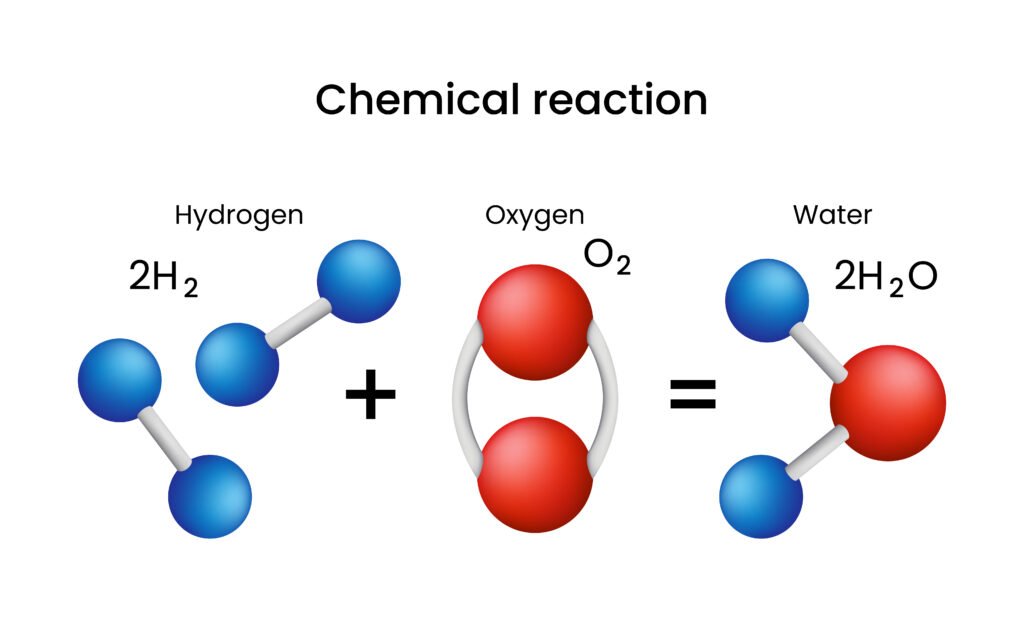
Chemical Equations
A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction using symbols and formulae of the substances involved.
Word Equation Example:
Hydrogen + Oxygen → Water
Chemical Equation:
H₂ + O₂ → H₂O
But this is not balanced – which brings us to a key concept:
Balancing Chemical Equations
A chemical equation must obey the Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This means that the number of atoms of each element must be equal on both sides of the equation.
Unbalanced Equation:
H₂ + O₂ → H₂O
(On LHS: 2 hydrogen atoms, 2 oxygen atoms; On RHS: 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 oxygen atom)
Balanced Equation:
2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
Now, both sides have:
4 hydrogen atoms
2 oxygen atoms
Steps to Balance a Chemical Equation:
Write the unbalanced equation.
Count the atoms of each element.
Adjust the coefficients (numbers in front of the formulae) to balance each atom.
Do not change subscripts in formulas.
Double-check all atoms and coefficients.
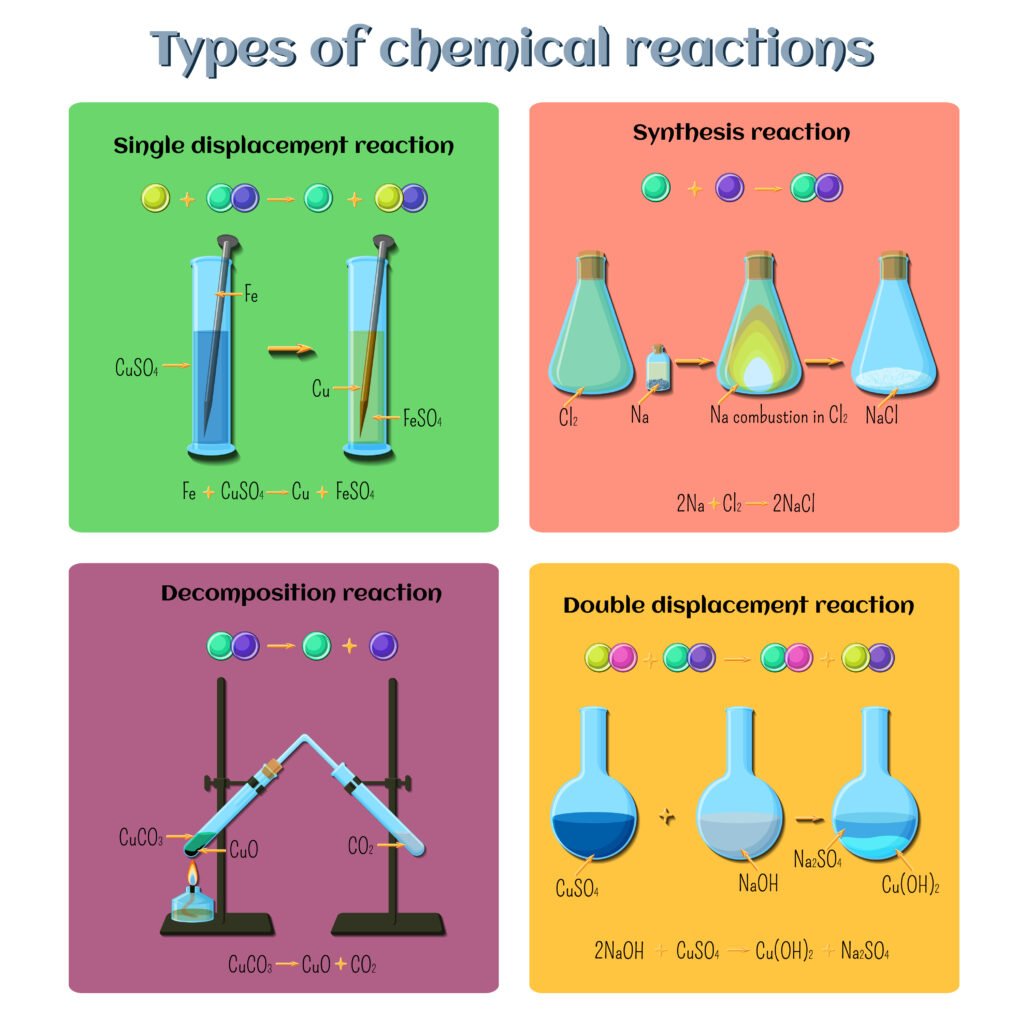
Types of Chemical Reactions
The chapter categorizes chemical reactions into five major types:
Combination Reaction
Two or more reactants combine to form a single product.
Example:
CaO (quick lime) + H₂O → Ca(OH)₂ (slaked lime)
This is an exothermic reaction, as heat is released.
Decomposition Reaction
A single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
Example:
2H₂O → 2H₂ + O₂ (electrolysis of water)
Types of decomposition:
Thermal decomposition (using heat)
Photolytic decomposition (using light)
Electrolytic decomposition (using electricity)
Displacement Reaction
A more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound.
Example:
Zn + CuSO₄ → ZnSO₄ + Cu
(Zinc displaces copper from copper sulfate solution)
Double Displacement Reaction
Two compounds exchange ions to form new compounds.
Example:
Na₂SO₄ + BaCl₂ → BaSO₄ (↓) + 2NaCl
(BaSO₄ is an insoluble precipitate)
Redox Reactions
A reaction where both oxidation (loss of electrons) and reduction (gain of electrons) take place simultaneously.
Example:
Zn + CuSO₄ → ZnSO₄ + Cu
Zinc is oxidized, and copper is reduced.
Oxidation and Reduction
These two processes are central to many reactions.
Oxidation: Addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen.
Reduction: Removal of oxygen or addition of hydrogen.
Example:
C + O₂ → CO₂ (Carbon is oxidized)
CuO + H₂ → Cu + H₂O (Copper oxide is reduced; hydrogen is oxidized)
Effects of Oxidation in Everyday Life
Corrosion:
The slow destruction of metals due to reaction with atmospheric moisture, oxygen, or acids.
Example:
Rusting of iron –
4Fe + 3O₂ + xH₂O → 2Fe₂O₃·xH₂O (Hydrated iron oxide)
Prevention:
Painting
Galvanization
Oiling/greasing
Coating with non-reactive metal
Rancidity:
The oxidation of fats and oils in food, which leads to a foul smell and taste.
Prevention:
Storing food in airtight containers
Using antioxidants
Refrigeration
Packing in nitrogen gas
Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
Exothermic Reaction: Releases heat
e.g., combustion of fuels
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O + heat
Endothermic Reaction: Absorbs heat
e.g., decomposition of calcium carbonate
CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂ (requires heating)
Representation of Physical States
Chemical equations often include physical states:
(s) – solid
(l) – liquid
(g) – gas
(aq) – aqueous (dissolved in water)
Example:
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H₂O(l)
Catalysts
Some reactions require the presence of a catalyst – a substance that speeds up the reaction without itself undergoing any permanent change.
Example:
Decomposition of KClO₃:
2KClO₃ → 2KCl + 3O₂ (in presence of MnO₂ catalyst).
Conclusion
The chapter “Chemical Reactions and Equations” forms a fundamental base for understanding all chemical changes. It not only teaches how to write and balance equations but also provides insight into various types of reactions that occur in our daily lives. It connects theory to real-world examples such as rusting, food spoilage, and combustion. Through clear classification and demonstration of reactions, the lesson lays a strong foundation for more complex chemical concepts in future studies.
A deep understanding of this lesson helps students appreciate the importance of chemical reactions not just in laboratories but in all natural and industrial processes around us.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK:-
1. Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect?
2PbO(s) + C(s) → 2Pb(s) + CO2(g)
(a) Lead is getting reduced
(b) Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised
(c) Carbon is getting oxidised
(d) Lead oxide is getting reduced
(i) (a) and (b)
(ii) (a) and (c)
(iii) (a), (b) and (c)
(iv) all
Answer: (i) (a) and (b)
Explanation: In this reaction, lead oxide (PbO) is losing oxygen to form lead metal, which means lead is getting reduced . Carbon is gaining oxygen to form carbon dioxide, which means carbon is getting oxidised . Statement (a) is incorrect because lead is actually getting reduced, not oxidised. Statement (b) is incorrect because carbon dioxide is the product formed when carbon gets oxidised, not the substance getting oxidised .
2. Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
. The above reaction is an example of a
(a) combination reaction
(b) double displacement reaction
(c) decomposition reaction
(d) displacement reaction
Answer: (d) displacement reaction
Explanation: This is a displacement reaction because aluminum, being more reactive than iron, displaces iron from its oxide (Fe2O3) to form aluminum oxide (Al2O3) . In displacement reactions, a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound . This is also known as the thermite reaction and is used in welding railway tracks .
3. What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron fillings? Tick the correct answer.
(a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced
(b) Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced
(c) No reaction takes place
(d) Iron salt and water are produced
Answer: (a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced
Explanation: When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron fillings, iron displaces hydrogen from the acid to form iron chloride and hydrogen gas . The balanced chemical equation is: Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2 . This is a displacement reaction where iron, being more reactive than hydrogen, displaces it from the acid .
4. What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced?
Answer: A balanced chemical equation is one in which the number of atoms of each element is equal on both the reactant and product sides of the equation . Chemical equations should be balanced to obey the Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction . This means the total mass of reactants must equal the total mass of products . Balancing ensures that the same number of each type of atom appears on both sides of the equation .
5. Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them.
(a) Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia
(b) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide
(c) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate
(d) Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas
Answer:
(a) Unbalanced: H2 + N2 → NH3
Balanced: 3H2 + N2 → 2NH3
(b) Unbalanced: H2S + O2 → H2O + SO2
Balanced: 2H2S + 3O2 → 2H2O + 2SO2
(c) Unbalanced: BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 → AlCl3 + BaSO4
Balanced: 3BaCl2 + Al2(SO4)3 → 2AlCl3 + 3BaSO4
(d) Unbalanced: K + H2O → KOH + H2
Balanced: 2K + 2H2O → 2KOH + H2
6.Balance the following chemical equations.
(a) HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
(b) NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + HCl
Answer:
(a) 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
(b) 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3 (already balanced)
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
7. Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
(a) Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide → Calcium carbonate + Water
(b) Zinc + Silver nitrate → Zinc nitrate + Silver
(c) Aluminium + Copper chloride → Aluminium chloride + Copper
(d) Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride
Answer:
(a) Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
(b) Zn + 2AgNO3 → Zn(NO3)2 + 2Ag
(c) 2Al + 3CuCl2 → 2AlCl3 + 3Cu
(d) BaCl2 + K2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2KCl
8. Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case.
(a) Potassium bromide(aq) + Barium iodide(aq) → Potassium iodide(aq) + Barium bromide(s)
(b) Zinc carbonate(s) → Zinc oxide(s) + Carbon dioxide(g)
(c) Hydrogen(g) + Chlorine(g) → Hydrogen chloride(g)
(d) Magnesium(s) + Hydrochloric acid(aq) → Magnesium chloride(aq) + Hydrogen(g)
Answer:
(a) 2KBr(aq) + BaI2(aq) → 2KI(aq) + BaBr2(s) – Double displacement reaction
(b) ZnCO3(s) → ZnO(s) + CO2(g) – Decomposition reaction
(c) H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g) – Combination reaction
(d) Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) – Displacement reaction
9. What does one mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Answer: Exothermic reactions are those in which energy is released in the form of heat along with the formation of products . The reaction mixture becomes warm during these reactions . Examples include:
Burning of natural gas: CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) + heat
Respiration: C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(aq) → 6CO2(aq) + 6H2O(l) + energy
Endothermic reactions are those in which energy is absorbed from the surroundings . These reactions require energy input to proceed . Examples include:
Photosynthesis: 6CO2(aq) + 6H2O(l) + sunlight → C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(aq)
Decomposition of calcium carbonate: CaCO3(s) + heat → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
10. Why is respiration considered an exothermic reaction? Explain.
Answer: Respiration is considered an exothermic reaction because it releases energy in the form of heat . During respiration, glucose combines with oxygen in our body cells to form carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy that maintains our body temperature . The chemical equation is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy . This energy is essential for all life processes and is released as heat, making respiration an exothermic process .
11. Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer: Decomposition reactions are called the opposite of combination reactions because in combination reactions, two or more substances combine to form a single product, while in decomposition reactions, a single substance breaks down into two or more simpler substances .
Examples:
Combination reaction: 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l)
Decomposition reaction: 2H2O(l) → 2H2(g) + O2(g)
Other decomposition examples:
ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2
CaCO3 + heat → CaO + CO2
2HgO → 2Hg + O2
12. Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
Answer:
(a) Thermal decomposition (heat):
2KClO3 + heat → 2KCl + 3O2
(Decomposition of potassium chlorate)
(b) Photolysis (light):
2H2O2 + light → 2H2O + O2
(Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide)
(c) Electrolysis (electricity):
2NaCl + electricity → 2Na + Cl2
(Decomposition of sodium chloride)
13. What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer:
Displacement reaction: A more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound . Only one displacement occurs .
Example: Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
Double displacement reaction: Two compounds exchange their ions to form two new compounds . Mutual exchange of ions occurs between two compounds .
Example: 2KBr + BaI2 → 2KI + BaBr2
The key difference is that displacement involves one element replacing another, while double displacement involves exchange of ions between two compounds .
14. In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involves displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Answer: Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
In this reaction, copper displaces silver from silver nitrate solution because copper is more reactive than silver . This is a displacement reaction used in the refining process of silver .
15. What do you mean by a precipitation reaction? Explain by giving examples.
Answer: A precipitation reaction occurs when two solutions containing soluble salts are mixed, resulting in the formation of an insoluble solid called a precipitate . The precipitate settles at the bottom of the container . These are special cases of double displacement reactions where one of the products formed is insoluble in water .
Examples:
CdSO4(aq) + K2S(aq) → CdS(s) + K2SO4(aq)
2NaOH(aq) + MgCl2(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + Mg(OH)2(s)
Na2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
16.Explain the following in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples each.
(a) Oxidation (b) Reduction
Answer:
(a) Oxidation: Addition of oxygen to an element or compound .
Examples:
4Na(s) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s) (sodium gains oxygen)
2H2S + 3O2 → 2H2O + 2SO2 (sulfur gains oxygen)
(b) Reduction: Removal of oxygen from a compound .
Examples:
CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(l) (copper oxide loses oxygen)
2HgO → 2Hg + O2 (mercury oxide loses oxygen)
17. A shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element ‘X’ and the black coloured compound formed.
Answer: The shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ is copper (Cu) . When copper is heated in air, it reacts with atmospheric oxygen to form copper oxide (CuO), which is the black coloured compound .
Chemical equation: 2Cu(s) + O2(g) → 2CuO(s)
18. Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Answer: Paint is applied on iron articles to prevent rusting . When iron is left unpainted, it comes in contact with atmospheric oxygen and moisture, leading to the formation of iron(III) oxide (rust) . Paint creates a protective barrier that prevents the metal surface from coming in contact with air and moisture, thus preventing the oxidation process that causes rusting . This saves millions of dollars annually in maintenance of bridges and monuments .
19. Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Answer: Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen to prevent rancidity . Rancidity occurs when oils and fats react with atmospheric oxygen, producing unpleasant smell and taste . Nitrogen is an inert gas that creates an unreactive environment around the food, preventing oxidation and thus preventing rancidity . This extends the shelf life of the food products .
20. Explain the following terms with one example each.
(a) Corrosion (b) Rancidity
Answer:
(a) Corrosion: A process where refined metals are gradually oxidized by atmospheric oxygen to form more stable compounds like oxides . The metal gradually degrades during this process .
Example: Rusting of iron – Iron reacts with oxygen and moisture to form iron oxide (rust) . This causes enormous economic loss as millions of dollars are spent annually in preventing rusting of bridges and monuments .
(b) Rancidity: The condition produced by aerial oxidation of oils and fats present in food materials, resulting in unpleasant taste and smell .
Example: When butter or cooking oil is left exposed to air for a long time, it develops a bad smell and taste due to oxidation . Rancidity can be prevented by storing food in refrigerators at low temperatures or by adding antioxidants .
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
[CBSE MODEL QUESTION PAPER]
🔹 1. Multiple Choice Questions (10 Marks)
Q1. Which of the following changes is definitely a chemical change?
A. Melting of ice
B. Dissolution of salt in water
C. Evaporation of alcohol
D. Formation of curd from milk
Answer: D
Q2. The chemical equation:
Fe + CuSO₄ → FeSO₄ + Cu is an example of:
A. Double displacement reaction
B. Combination reaction
C. Decomposition reaction
D. Displacement reaction
Answer: D
Q3. Which reaction is endothermic in nature?
A. Burning of coal
B. Decomposition of CaCO₃
C. Neutralization reaction
D. Reaction of water with quick lime
Answer: B
Q4. What is the correct balanced form of this reaction?
Al + O₂ → Al₂O₃
A. Al + O₂ → Al₂O₃
B. 4Al + 3O₂ → 2Al₂O₃
C. 2Al + O₂ → Al₂O₃
D. Al + ½O₂ → Al₂O₃
Answer: B
Q5. A student added water to calcium oxide. The reaction can be classified as:
A. Endothermic and displacement
B. Exothermic and combination
C. Neutralization
D. Redox reaction
Answer: B
Q6. Which of the following is not an indicator of a chemical reaction?
A. Change in color
B. Change in temperature
C. Evolution of gas
D. Change in shape only
Answer: D
Q7. Which reaction shows both displacement and redox properties?
A. NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H₂O
B. AgNO₃ + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO₃
C. Zn + H₂SO₄ → ZnSO₄ + H₂
D. CaO + H₂O → Ca(OH)₂
Answer: C
Q8. What type of reaction is the rusting of iron?
A. Combination and redox
B. Displacement and redox
C. Double displacement and oxidation
D. Thermal decomposition
Answer: A
Q9. Which of the following helps in preventing rancidity in packaged food?
A. Exposure to sunlight
B. Mixing with water
C. Keeping in open air
D. Flushing with nitrogen gas
Answer: D
Q10. Which one is a photolytic decomposition reaction?
A. 2KClO₃ → 2KCl + 3O₂
B. 2Pb(NO₃)₂ → 2PbO + 4NO₂ + O₂
C. 2AgCl → 2Ag + Cl₂
D. CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂
Answer: C
🔹 2. Fill in the Blanks (3 Marks)
Q11. The slow process in which fats and oils get oxidized in air is called _.
Answer: Rancidity
Q12. The compound used as a catalyst in the decomposition of potassium chlorate is _.
Answer: Manganese dioxide (MnO₂)
Q13. A balanced chemical equation must follow the _ of mass.
Answer: Law of Conservation
🔹 3. Assertion and Reason (3 Marks)
Choose: (A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true, R is false.
(D) A is false, R is true.
Q14.
Assertion (A): Burning of magnesium ribbon in air is a redox reaction.
Reason (R): In this reaction, magnesium is reduced and oxygen is oxidized.
Answer: C
Q15.
Assertion (A): Reaction between sodium sulphate and barium chloride forms a white precipitate.
Reason (R): Barium sulphate formed is insoluble in water.
Answer: A
Q16.
Assertion (A): Rusting of iron occurs in dry air.
Reason (R): Presence of moisture is necessary for rusting.
Answer: D
🔹 4. Select Right or Wrong (2 Marks)
Write “Right” or “Wrong” with reason.
Q17. A balanced equation allows unequal number of atoms on both sides as long as mass is conserved.
Answer: Wrong. The number of atoms must be equal on both sides to satisfy the Law of Conservation of Mass.
Q18. The reaction between hydrogen and chlorine to form hydrochloric acid is an example of a combination reaction.
Answer: Right. Two elements combine to form one compound.
🔹 5. Short Answer Questions (5 × 3 = 15 Marks)
(Write answers in about 50–70 words each)
Q19. Why is it essential to balance a chemical equation?
Answer: Balancing a chemical equation ensures the Law of Conservation of Mass is followed, which states that mass cannot be created or destroyed. An unbalanced equation suggests atoms are either lost or gained, which is physically impossible. Therefore, to accurately represent a chemical reaction and maintain stoichiometric correctness, balancing is necessary.
Q20. How can you test whether a chemical reaction is endothermic or exothermic? Give one example.
Answer: A reaction is exothermic if it releases heat (temperature increases) and endothermic if it absorbs heat (temperature decreases). For example, the reaction of quicklime (CaO) with water is exothermic, as it produces a significant amount of heat, warming the container. Measuring temperature change helps identify the nature.
Q21. What is a precipitation reaction? Give an example.
Answer: A precipitation reaction is a type of double displacement reaction where two aqueous solutions react to form an insoluble solid, called a precipitate. For instance, mixing solutions of BaCl₂ and Na₂SO₄ forms BaSO₄ as a white precipitate:
BaCl₂ + Na₂SO₄ → BaSO₄↓ + 2NaCl
Q22. Why is food packed with nitrogen gas in chips packets?
Answer: Nitrogen gas is inert and does not react with fats and oils in the food. It displaces oxygen, thus preventing oxidation and rancidity. This extends shelf life and maintains taste and texture in packaged food like potato chips.
Q23. How does the concept of redox reaction explain displacement reactions?
Answer: In displacement reactions, one element replaces another in a compound, involving both oxidation and reduction. For example, in Zn + CuSO₄ → ZnSO₄ + Cu, zinc is oxidized (loses electrons) and copper is reduced (gains electrons). Hence, displacement is a redox process where electrons are transferred.
🔹 6. Long Answer Questions (2 × 5 = 10 Marks)
(Write answers in about 120–150 words each)
Q24. Describe different types of decomposition reactions with examples and mention the energy required for each type.
Answer: Decomposition reactions involve breaking down a compound into simpler substances. Based on the energy source, they are:
Thermal Decomposition – Heat breaks the compound. Example:
CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂
Electrolytic Decomposition – Electricity is used. Example:
2H₂O → 2H₂ + O₂ (electrolysis of water)
Photolytic Decomposition – Light energy breaks the compound. Example:
2AgCl → 2Ag + Cl₂ (in sunlight)
Each type demonstrates how energy input is necessary to overcome the chemical bonds in the compound. These reactions are endothermic and important in processes like metallurgy and photography.
Q25. Explain corrosion and rancidity with examples. What measures can be taken to prevent them?
Answer: Corrosion is the slow degradation of metals due to reactions with oxygen, moisture, or chemicals. For example, iron reacts with water and oxygen forming rust (Fe₂O₃·xH₂O). Corrosion weakens metals and structures.
Rancidity is the spoilage of oils/fats due to oxidation, producing unpleasant odor and taste. Example: spoiled butter.
Prevention of corrosion: Galvanization, painting, greasing.
Prevention of rancidity: Storing in airtight containers, refrigeration, adding antioxidants, nitrogen flushing. Both processes are oxidation-based and impact materials and health.
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
QUESTIONS FROM COMPETITIONS EXAMS
🔵 Question 1:
Which of the following is a chemical change?
(A) Melting of ice
(B) Boiling of water
(C) Rusting of iron
(D) Breaking of glass
✅ Correct Answer: (C) Rusting of iron
📄 Exam: SSC CGL 2018
🟢 Question 2:
Which of the following is not a type of chemical reaction?
(A) Combination reaction
(B) Decomposition reaction
(C) Evaporation reaction
(D) Displacement reaction
✅ Correct Answer: (C) Evaporation reaction
📄 Exam: UPPSC PCS 2019
🔴 Question 3:
The chemical equation is balanced by adjusting:
(A) Temperature
(B) Pressure
(C) Coefficients
(D) Volume
✅ Correct Answer: (C) Coefficients
📄 Exam: RRB NTPC 2020
🟡 Question 4:
Which gas is evolved when dilute HCl reacts with zinc?
(A) Oxygen
(B) Hydrogen
(C) Nitrogen
(D) Carbon dioxide
✅ Correct Answer: (B) Hydrogen
📄 Exam: NDA 2017
🔵 Question 5:
Which of the following is an example of a combination reaction?
(A) 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
(B) AgNO₃ + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO₃
(C) CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂
(D) Zn + HCl → ZnCl₂ + H₂
✅ Correct Answer: (A) 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
📄 Exam: SSC CHSL 2021
🟢 Question 6:
Which of these reactions is an example of decomposition?
(A) CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂
(B) 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
(C) NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H₂O
(D) Zn + CuSO₄ → ZnSO₄ + Cu
✅ Correct Answer: (A) CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂
📄 Exam: SBI PO 2016
🔴 Question 7:
What is formed when copper is exposed to moist air?
(A) CuO
(B) CuCO₃·Cu(OH)₂
(C) CuSO₄
(D) Cu(NO₃)₂
✅ Correct Answer: (B) CuCO₃·Cu(OH)₂
📄 Exam: IBPS Clerk 2018
🟡 Question 8:
Which of the following is a sign of a chemical reaction?
(A) Change in temperature
(B) Formation of a precipitate
(C) Change in color
(D) All of the above
✅ Correct Answer: (D) All of the above
📄 Exam: CDS 2020
🔵 Question 9:
Which of the following metals will displace copper from copper sulphate solution?
(A) Silver
(B) Iron
(C) Gold
(D) Platinum
✅ Correct Answer: (B) Iron
📄 Exam: CAPF 2019
🟢 Question 10:
Which acid reacts with marble to produce carbon dioxide?
(A) Nitric acid
(B) Sulphuric acid
(C) Hydrochloric acid
(D) Acetic acid
✅ Correct Answer: (C) Hydrochloric acid
📄 Exam: SSC CGL 2017
🔴 Question 11:
The brown coating on iron articles is due to:
(A) Electroplating
(B) Rust
(C) Tarnish
(D) Sublimation
✅ Correct Answer: (B) Rust
📄 Exam: RRB ALP 2019
🟡 Question 12:
What type of reaction occurs in respiration?
(A) Endothermic
(B) Exothermic
(C) Reversible
(D) Photochemical
✅ Correct Answer: (B) Exothermic
📄 Exam: NDA 2018
🔵 Question 13:
Which of the following is an oxidation reaction?
(A) Burning of coal
(B) Electrolysis of water
(C) Boiling of water
(D) Sublimation of iodine
✅ Correct Answer: (A) Burning of coal
📄 Exam: SSC CGL 2020
🟢 Question 14:
What is formed when magnesium burns in air?
(A) MgO
(B) MgCO₃
(C) MgCl₂
(D) Mg(NO₃)₂
✅ Correct Answer: (A) MgO
📄 Exam: CDS 2019
🔴 Question 15:
Which of the following is not required for rusting of iron?
(A) Water
(B) Air
(C) Oil
(D) Iron
✅ Correct Answer: (C) Oil
📄 Exam: IBPS PO 2017
🟡 Question 16:
Electrolysis of water produces:
(A) O₂ and CO₂
(B) H₂ and O₂
(C) H₂ and N₂
(D) H₂ and Cl₂
✅ Correct Answer: (B) H₂ and O₂
📄 Exam: SSC CPO 2018
🔵 Question 17:
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a chemical reaction?
(A) Evolution of gas
(B) Change in temperature
(C) Melting of ice
(D) Formation of precipitate
✅ Correct Answer: (C) Melting of ice
📄 Exam: UPPSC PCS 2020
🟢 Question 18:
Redox reactions involve:
(A) Only oxidation
(B) Only reduction
(C) Both oxidation and reduction
(D) Neither oxidation nor reduction
✅ Correct Answer: (C) Both oxidation and reduction
📄 Exam: SBI Clerk 2019
🔴 Question 19:
What is the nature of the chemical reaction involved in photosynthesis?
(A) Exothermic
(B) Endothermic
(C) Displacement
(D) Neutralization
✅ Correct Answer: (B) Endothermic
📄 Exam: RRB JE 2017
🟡 Question 20:
When lime water reacts with CO₂, it forms:
(A) CaO
(B) CaCO₃
(C) Ca(OH)₂
(D) CaSO₄
✅ Correct Answer: (B) CaCO₃
📄 Exam: SSC MTS 2021
🔵 Question 21:
Which process involves a chemical change?
(A) Cooking of food
(B) Melting of ice
(C) Dissolving sugar in water
(D) Breaking glass
✅ Correct Answer: (A) Cooking of food
📄 Exam: SSC GD 2022
🟢 Question 22:
Which reaction shows displacement?
(A) Fe + CuSO₄ → FeSO₄ + Cu
(B) NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H₂O
(C) 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
(D) CaCO₃ → CaO + CO₂
✅ Correct Answer: (A) Fe + CuSO₄ → FeSO₄ + Cu
📄 Exam: AFCAT 2018
🔴 Question 23:
What is the color of copper sulphate solution?
(A) Blue
(B) Green
(C) Red
(D) White
✅ Correct Answer: (A) Blue
📄 Exam: CAPF 2021
🟡 Question 24:
Which of the following is an endothermic reaction?
(A) Decomposition of limestone
(B) Combustion of coal
(C) Rusting of iron
(D) Respiration
✅ Correct Answer: (A) Decomposition of limestone
📄 Exam: NDA 2016
🔵 Question 25:
Which reaction is used in black and white photography?
(A) Decomposition
(B) Combination
(C) Neutralization
(D) Displacement
✅ Correct Answer: (A) Decomposition
📄 Exam: SSC CGL 2015
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
ONE PAGE REVISION SHEET
Chemical Reaction:
A process where one or more substances (reactants) are converted into new substances (products) with new properties.
Example:
2Mg + O₂ → 2MgO
──────────────────────────────
Characteristics of Reactions:
Change in state
Change in color
Evolution of gas
Change in temperature
Formation of precipitate
──────────────────────────────
Chemical Equation:
A shorthand way of showing a chemical reaction using symbols and formulas.
Balanced Example:
3Fe + 4H₂O → Fe₃O₄ + 4H₂
──────────────────────────────
Types of Reactions:
Combination: A + B → AB
(e.g., CaO + H₂O → Ca(OH)₂)
Decomposition: AB → A + B
(e.g., 2Pb(NO₃)₂ → 2PbO + 4NO₂ + O₂)
Displacement: A + BC → AC + B
(e.g., Zn + CuSO₄ → ZnSO₄ + Cu)
Double Displacement: AB + CD → AD + CB
(e.g., Na₂SO₄ + BaCl₂ → BaSO₄↓ + 2NaCl)
Redox: Both oxidation and reduction occur
(e.g., CuO + H₂ → Cu + H₂O)
──────────────────────────────
Oxidation and Reduction:
Oxidation: Gain of oxygen / loss of hydrogen
Reduction: Loss of oxygen / gain of hydrogen
Trick: OIL RIG (Oxidation Is Loss, Reduction Is Gain)
──────────────────────────────
Effects of Oxidation:
Corrosion: Rusting of iron
Rancidity: Spoiling of food with fats/oils
Prevention: Painting, oiling, refrigeration, antioxidants
──────────────────────────────
Tips:
Balance all equations
Use physical states: (s), (l), (g), (aq)
Exothermic = heat released
Endothermic = heat absorbed
Practice balancing equations regularly.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
ACRONYMS

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
MISCONCEPTIONS

————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————

Jee main question