Class : 9 – Science (English) : Lesson 12. Improvement in Food Resources
EXPLANATION & SUMMARY
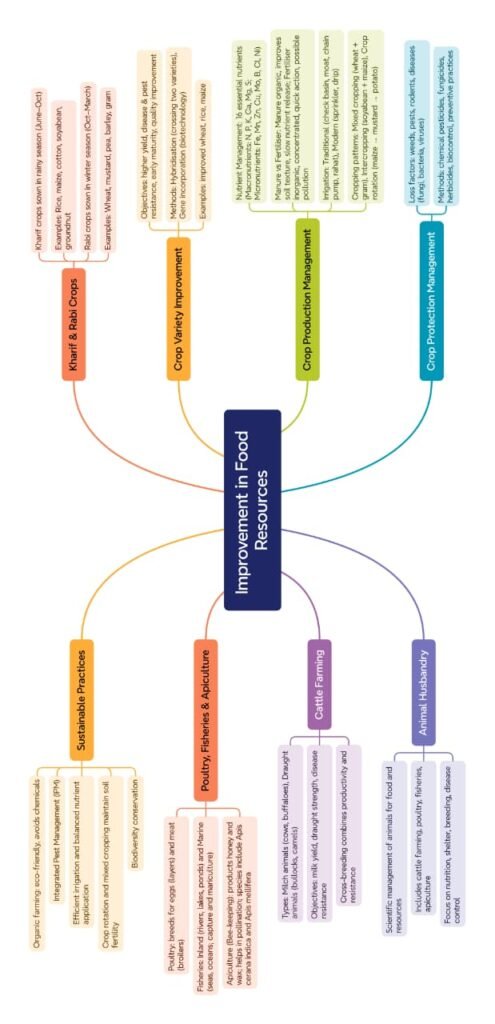
🔵 Introduction
Food is the basic need for survival, growth, and development.
With increasing population, demand for food also rises.
We must adopt improved methods in agriculture, animal husbandry, fisheries, and apiculture to ensure food security.
🟢 Improvement in Crop Yields

Crop Variety Improvement
Objective: Develop crops with better yield, resistance, quality, and adaptability.
Methods:
Hybridisation (cross-breeding of two varieties).
Genetic modification (transferring useful genes).
Desirable Traits:
High yield ✔️
Resistance to pests/diseases 🌿
Tolerance to drought/salinity 🌞
Early maturity ⏳
Better nutritional quality 🍚
Crop Production Management
Nutrient Management:
Plants need nutrients for growth.
Macronutrients (6): N, P, K, Ca, Mg, S.
Micronutrients (7): Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, B, Mo, Cl.
Sources: Manure (organic) and Fertilisers (inorganic).
Manure: Improves soil texture, adds humus, eco-friendly.
Fertilisers: Provide targeted nutrients, faster results.
Integrated Nutrient Management: Combination of both for long-term sustainability.
Irrigation:
Ensures water supply at right time.
Traditional: Moat, chain pump, rahat, dhekli.
Modern: Sprinkler, drip irrigation (saves water).
Cropping Patterns:
Mixed cropping: Two crops grown together (e.g., wheat + gram).
Intercropping: Row-wise alternate crops (e.g., maize + soya).
Crop rotation: Sequential cropping (e.g., rice → wheat → pulses).
Crop Protection Management
Crops face damage from weeds, pests, and diseases.
Weeds: Unwanted plants; compete for nutrients. Controlled by weedicides, tilling, crop rotation.
Pests: Insects, rodents; damage leaves, stems, roots. Controlled by pesticides, natural predators, resistant varieties.
Diseases: Caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses. Controlled by fungicides, antibiotics, improved practices.
🟡 Animal Husbandry
Branch of agriculture that deals with rearing and breeding animals for food and other products.
Cattle Farming
Purpose: Milk production and draught labour.
Breeds:
Milch breeds (high milk yield).
Draught breeds (work animals).
Improvement methods: Cross-breeding, proper shelter, balanced diet, vaccination.
Poultry Farming
Domestic fowl reared for meat and eggs.
Desirable traits: Disease resistance, faster growth, higher egg production.
Care: Balanced feed, clean shelter, vaccination.
Fish Production
Capture fishing: Natural sources (rivers, sea).
Culture fishery: Fish farming in ponds.
Popular species: Rohu, Catla, Hilsa.
Methods: Composite fish culture (different species in same pond).
Bee-Keeping (Apiculture)
Honeybees reared for honey and wax.
Important species: Apis indica.
Conditions: Hives in shady area, flowers nearby, proper care.
Uses: Honey as food/medicine, wax for industry.
Sheep, Goat, and Pig Farming
Sheep → wool, meat.
Goat → milk, meat.
Pig → pork, leather.
Require disease control, shelter, proper diet.
🟣 Fisheries and Marine Resources
Inland fisheries: Ponds, rivers, tanks.
Marine fisheries: Seas, oceans.
Blue Revolution: Rapid increase in fish production through scientific methods.
🔴 Sustainable Practices
Organic farming: Uses natural manures, bio-pesticides, crop rotation.
Integrated pest management (IPM): Combines biological, chemical, cultural control methods.
Water-use efficiency: Drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting.
Biodiversity conservation: Use of indigenous breeds, mixed farming.
🟤 Summary (Revision-Friendly)
Crop improvement → Hybridisation, GM crops, disease resistance.
Nutrient management → Manure + fertilisers for balanced nutrition.
Irrigation & cropping patterns → Drip, sprinkler, rotation, intercropping.
Crop protection → Pesticides, resistant varieties, weedicides.
Animal husbandry → Cattle, poultry, sheep, goats, pigs for milk, eggs, wool, meat.
Fisheries → Inland + marine, composite culture.
Apiculture → Honey + wax production.
Sustainability → Organic farming, IPM, efficient irrigation, biodiversity conservation.
📝 Quick Recap
🌾 Crop variety improvement: hybrids, GM crops.
💧 Nutrient & irrigation management: manure, fertilisers, drip/sprinkler.
🐝 Animal husbandry: cattle, poultry, fish, bees.
🐟 Fisheries: composite culture, blue revolution.
🍯 Apiculture: honey & wax.
🌍 Sustainable farming: organic, biodiversity, IPM.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
QUESTIONS FROM TEXTBOOK
❓ Q1. Explain any one method of crop production which ensures high yield.
✔️ Answer:
🌱 Crop variety improvement is one method.
In this, high-yielding varieties (HYV) are developed by:
Hybridisation 🌿 (cross-breeding two different varieties).
Genetic modification 🧬 (inserting useful traits like pest resistance).
✅ This ensures more production, better quality, and tolerance to stresses.
❓ Q2. Why are manure and fertilizers used in fields?
✔️ Answer:
🌾 Crops need nutrients for proper growth.
Manure: Improves soil fertility, structure, and adds humus.
Fertilizers: Provide specific nutrients (like N, P, K) quickly.
✅ Both are used to increase yield and maintain soil health.
❓ Q3. What are the advantages of inter-cropping and crop rotation?
✔️ Answer:
🌱 Inter-cropping:
Two or more crops grown together in alternate rows.
✅ Prevents pests, reduces spread of diseases, ensures efficient use of nutrients.
🔄 Crop rotation:
Growing different crops one after another in the same field.
✅ Restores soil fertility, prevents soil depletion, and reduces weeds.
❓ Q4. What is genetic manipulation? How is it useful in agricultural practices?
✔️ Answer:
🧬 Genetic manipulation: Altering genetic makeup of organisms to obtain desired traits.
Usefulness in agriculture:
Development of pest-resistant crops 🌿.
Crops with higher yield 🍚.
Improved nutritional value 🥦.
Tolerance to drought/salinity 🌞.
❓ Q5. How do storage grain losses occur?
✔️ Answer:
Losses occur due to:
🐛 Insects and pests.
🐀 Rodents.
🍄 Fungi and bacteria.
💧 Moisture and humidity.
🔥 Improper storage conditions.
✅ Prevented by drying grains, using insecticides, fumigation, and airtight silos.
❓ Q6. How do good animal husbandry practices benefit farmers?
✔️ Answer:
🐄 Higher milk, egg, meat, wool production.
💪 Healthier animals due to vaccination and care.
🌱 Efficient use of fodder and shelter.
💰 Provides additional income to farmers.
✅ Ensures economic stability and better livelihood.
❓ Q7. What are the benefits of cattle farming?
✔️ Answer:
🥛 Provides milk and milk products.
🚜 Draught labour for ploughing and transport.
💩 Cow dung used as manure and fuel.
✅ Improves farmer’s income and food security.
❓ Q8. For increasing production, what is common in poultry, fisheries and bee-keeping?
✔️ Answer:
All involve scientific management for higher yield:
Selective breeding 🐓🐟🐝.
Providing balanced food and nutrition 🍽️.
Proper shelter and disease control 🏡.
✅ Farmers get more profit with less input cost.
❓ Q9. How do you differentiate between capture fishing, mariculture and aquaculture?
✔️ Answer:
🎣 Capture fishing: Obtaining fish from natural water bodies like rivers, lakes, seas.
🌊 Mariculture: Culture of marine fish and other organisms in seawater.
🐟 Aquaculture: Rearing of aquatic animals (fish, prawns) and plants in ponds, tanks, or reservoirs.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMS
🟢 Section A – Multiple Choice Questions (Q1–Q10)
Q1. Which of the following is a Rabi crop?
(a) Paddy
(b) Wheat
(c) Maize
(d) Groundnut
✔️ Answer: (b) Wheat
Q2. The process of growing two or more crops in alternate rows in the same field is called:
(a) Crop rotation
(b) Inter-cropping
(c) Mixed farming
(d) Sustainable farming
✔️ Answer: (b) Inter-cropping
Q3. Which nutrient is supplied by potash fertilizer?
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Potassium
(c) Phosphorus
(d) Sulphur
✔️ Answer: (b) Potassium
Q4. The vaccine given to cattle to prevent Foot and Mouth disease is:
(a) FMD vaccine
(b) BCG
(c) Rabies
(d) Anthrax
✔️ Answer: (a) FMD vaccine
Q5. Poultry farming mainly provides:
(a) Meat and eggs
(b) Wool and milk
(c) Silk and honey
(d) Fish and prawns
✔️ Answer: (a) Meat and eggs
Q6. Which method improves soil fertility without chemicals?
(a) Fertilizers
(b) Manure
(c) Herbicides
(d) Pesticides
✔️ Answer: (b) Manure
Q7. Capture fishing means:
(a) Rearing fish in ponds
(b) Fishing in natural water bodies
(c) Farming marine organisms
(d) Artificial fish breeding
✔️ Answer: (b) Fishing in natural water bodies
Q8. Bee-keeping is scientifically called:
(a) Pisciculture
(b) Sericulture
(c) Apiculture
(d) Horticulture
✔️ Answer: (c) Apiculture
Q9. Hybrid varieties are developed through:
(a) Cross-breeding
(b) Monoculture
(c) Soil enrichment
(d) Irrigation
✔️ Answer: (a) Cross-breeding
Q10. Losses of grains in storage occur due to:
(a) Insects
(b) Rodents
(c) Fungi
(d) All of these
✔️ Answer: (d) All of these
🟡 Section B – Very Short Answer Questions (Q11–Q18)
Q11. Name two Rabi crops.
✔️ Answer: Wheat and Gram.
Q12. Name two Kharif crops.
✔️ Answer: Paddy and Maize.
Q13. What is vermicomposting?
✔️ Answer: The process of preparing manure using earthworms to decompose organic matter.
Q14. Name one exotic breed of cattle used for milk yield.
✔️ Answer: Jersey.
Q15. Name one marine fish cultivated in mariculture.
✔️ Answer: Pomfret / Mackerel.
Q16. What is white revolution related to?
✔️ Answer: Increase in milk production.
Q17. Which nutrient is mainly supplied by urea fertilizer?
✔️ Answer: Nitrogen.
Q18. Write one advantage of bee-keeping.
✔️ Answer: Provides honey and wax as well as helps in cross-pollination of crops.
🔵 Section C – Short Answer Questions (Q19–Q28)
Q19. Differentiate between manure and fertilizer.
✔️ Answer:
Manure: Organic, improves soil fertility, adds humus 🌱.
Fertilizer: Chemical, provides specific nutrients quickly ⚡.
Q20. What are the advantages of crop rotation?
✔️ Answer:
Prevents soil depletion.
Restores soil fertility.
Reduces pests and weeds.
Q21. What is genetic manipulation in crops?
✔️ Answer: Altering genes to develop crops with high yield, pest resistance, and stress tolerance.
Q22. State two benefits of inter-cropping.
✔️ Answer:
Prevents spread of diseases.
Ensures better utilization of nutrients.
Q23. Name two exotic breeds of poultry.
✔️ Answer: White Leghorn and Rhode Island Red.
Q24. Mention two factors responsible for losses of stored grains.
✔️ Answer: Insect pests and moisture.
Q25. What are the benefits of cattle farming?
✔️ Answer: Provides milk, draught labour, dung for fuel and manure.
Q26. What is pisciculture?
✔️ Answer: Rearing and breeding of fish in ponds, tanks, or reservoirs.
Q27. Why is mixed cropping practiced?
✔️ Answer: To minimize risk of crop failure and ensure continuous food supply.
Q28. Define animal husbandry.
✔️ Answer: The branch of agriculture that deals with breeding, feeding, and caring of animals for food and other products.
🔴 Section D – Long Answer Questions (Q29–Q35)
Q29. Explain the differences between capture fishing, mariculture, and aquaculture.
✔️ Answer:
🎣 Capture fishing: Obtaining fish from natural water bodies.
🌊 Mariculture: Farming marine organisms in sea.
🐟 Aquaculture: Rearing fish/prawns in ponds or tanks.
Q30. What are the various energy requirements of dairy animals?
✔️ Answer:
Maintenance (for daily body functions).
Growth (young animals).
Lactation (milk production).
Reproduction (pregnancy).
Q31. What are the benefits of poultry farming?
✔️ Answer:
Provides eggs and meat.
Requires less investment.
Source of income for small farmers.
Q32. Explain biotic and abiotic factors leading to crop losses.
✔️ Answer:
Biotic: Pests, insects, pathogens, weeds 🐛.
Abiotic: Drought, flood, frost, salinity 🌊.
Q33. What are the desirable traits for fodder crops?
✔️ Answer:
High yield of leafy matter.
Quick regrowth after cutting.
High nutrient content.
Q34. What steps are taken to prevent storage losses of grains?
✔️ Answer:
Proper drying of grains ☀️.
Using insecticides and fumigation.
Storing in airtight silos and godowns.
Q35. Explain the advantages of bee-keeping.
✔️ Answer:
Provides honey and wax 🍯.
Helps in cross-pollination 🌸.
Requires small investment but gives good profit.
🟠 Section E – Case-Based / Numericals (Q36–Q39)
Q36. Case Study: A farmer grows wheat continuously in the same field every year. After a few years, the yield decreases. Explain why.
✔️ Answer:
Soil becomes deficient in specific nutrients.
Repeated monoculture leads to pests and weeds.
Solution: Crop rotation, intercropping, and adding manure/fertilizer.
Q37. Case Study: A farmer has 5 cows, but milk yield is low. Suggest steps for improvement.
✔️ Answer:
Provide balanced diet 🍽️.
Maintain clean shelter 🏡.
Vaccinate and protect from diseases 💉.
Use high-yielding breeds 🐄.
Q38. Numerical: A household consumes 2 units of electricity daily for operating a 1 HP water pump. Calculate energy consumed in joules in 30 days.
✔️ Answer (step by step):
1 HP = 746 W.
Power = 746 W.
Time used daily = 2 hr = 2 × 3600 = 7200 s.
Energy per day = Power × Time
➡️ 746 × 7200 = 53,71,200 J.
Energy in 30 days = 53,71,200 × 30 = 1.61 × 10⁸ J.
Q39. Case Study: A farmer practices bee-keeping along with sunflower farming. Why is this advantageous?
✔️ Answer:
Bees get nectar from sunflowers.
Sunflowers get cross-pollinated.
✅ Higher yield of honey + higher seed production.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
MIND MAPS
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
